Abstract
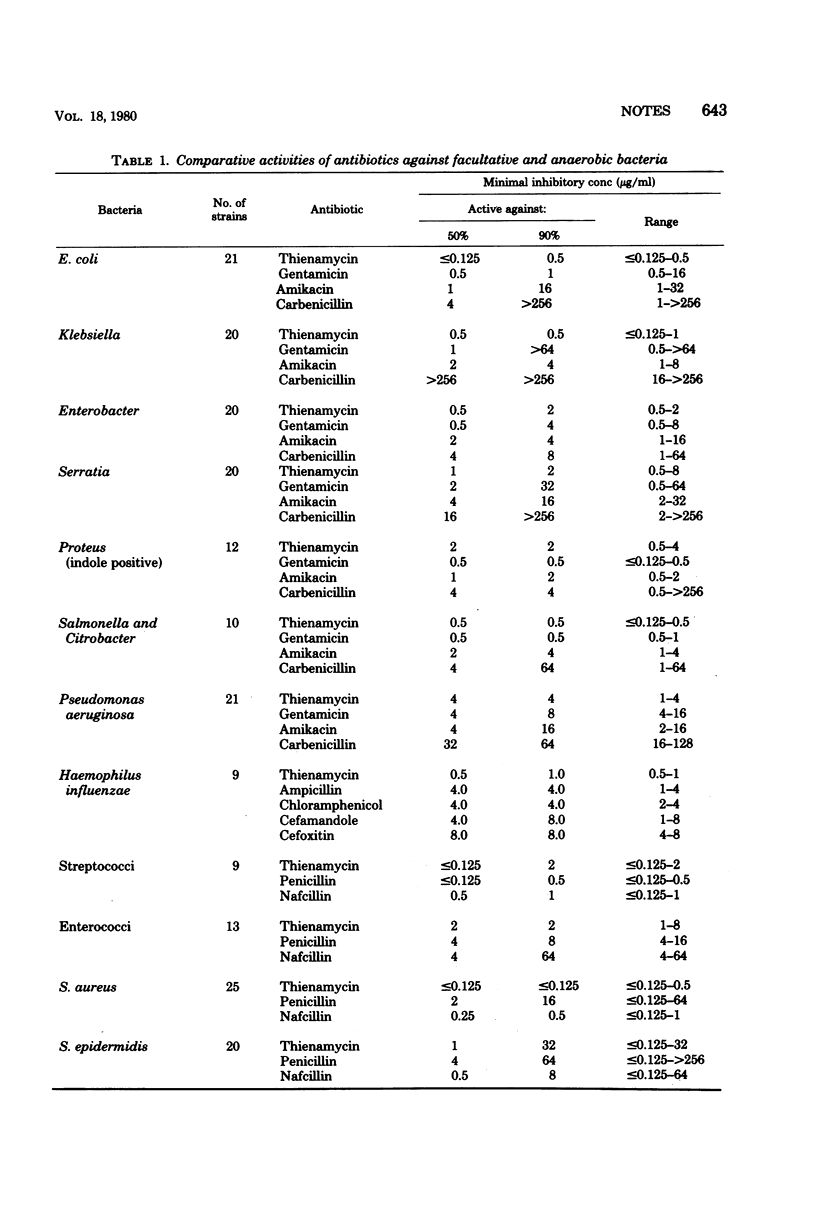
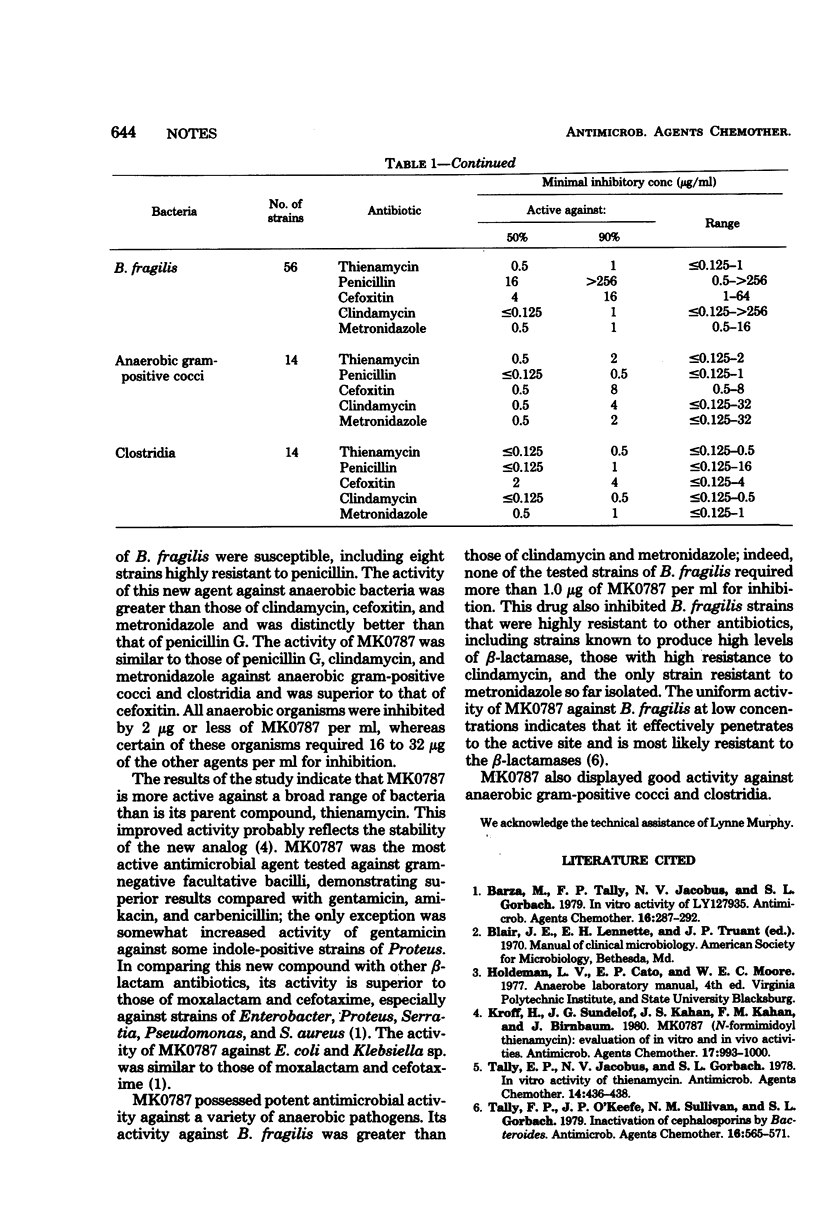
The in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin (MK0787), a stable congener of thienamycin, was determined against 200 species of aerobic and 84 species of anaerobic bacteria. The compound was highly active against resistant gram-negative bacilli, penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, enterococci, and anaerobic bacteria. The new derivative of thienamycin was more active than the parent compound, probably reflecting the stability of the analog.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barza M., Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of LY127935. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):287–292. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropp H., Sundelof J. G., Kahan J. S., Kahan F. M., Birnbaum J. MK0787 (N-formimidoyl thienamycin): evaluation of in vitro and in vivo activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):993–1000. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L. In vitro activity of thienamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):436–438. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., O'Keefe J. P., Sullivan N. M., Gorbach S. L. Inactivation of cephalosporins by Bacteroides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):565–571. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



