Abstract
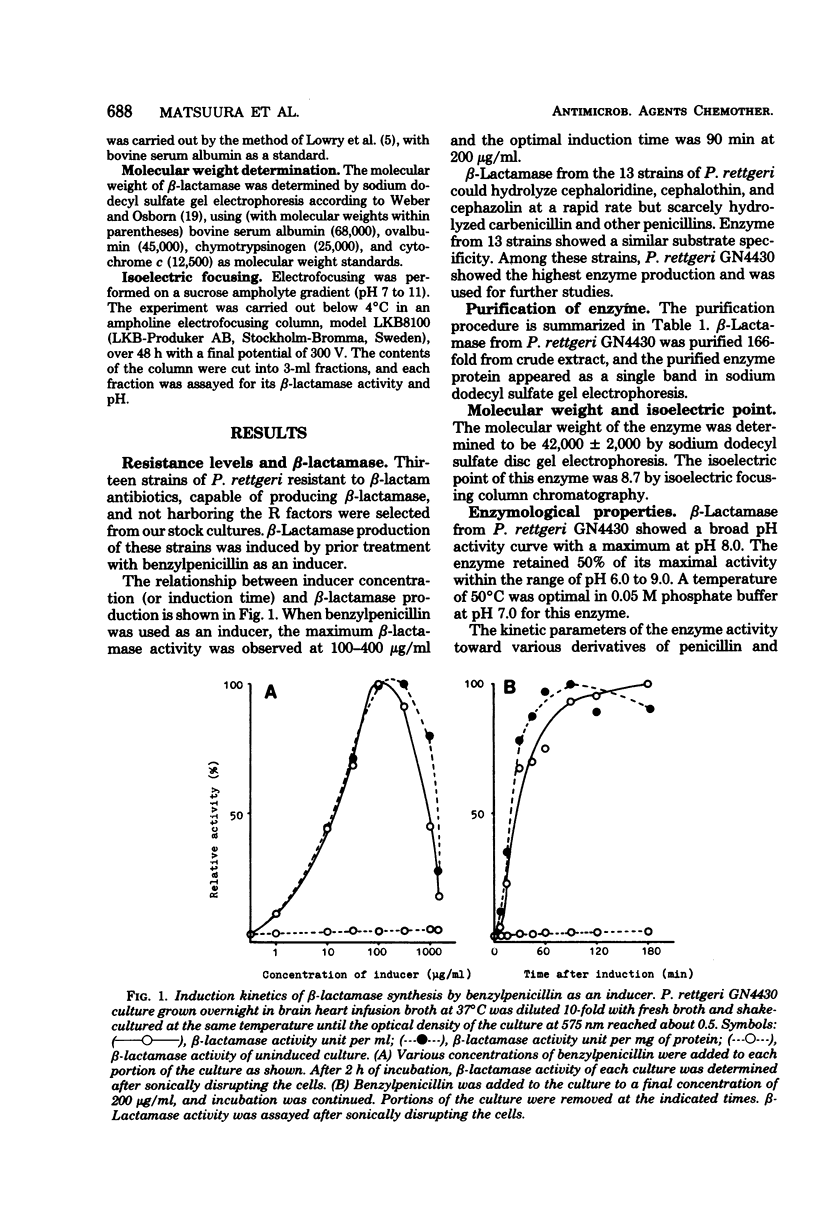
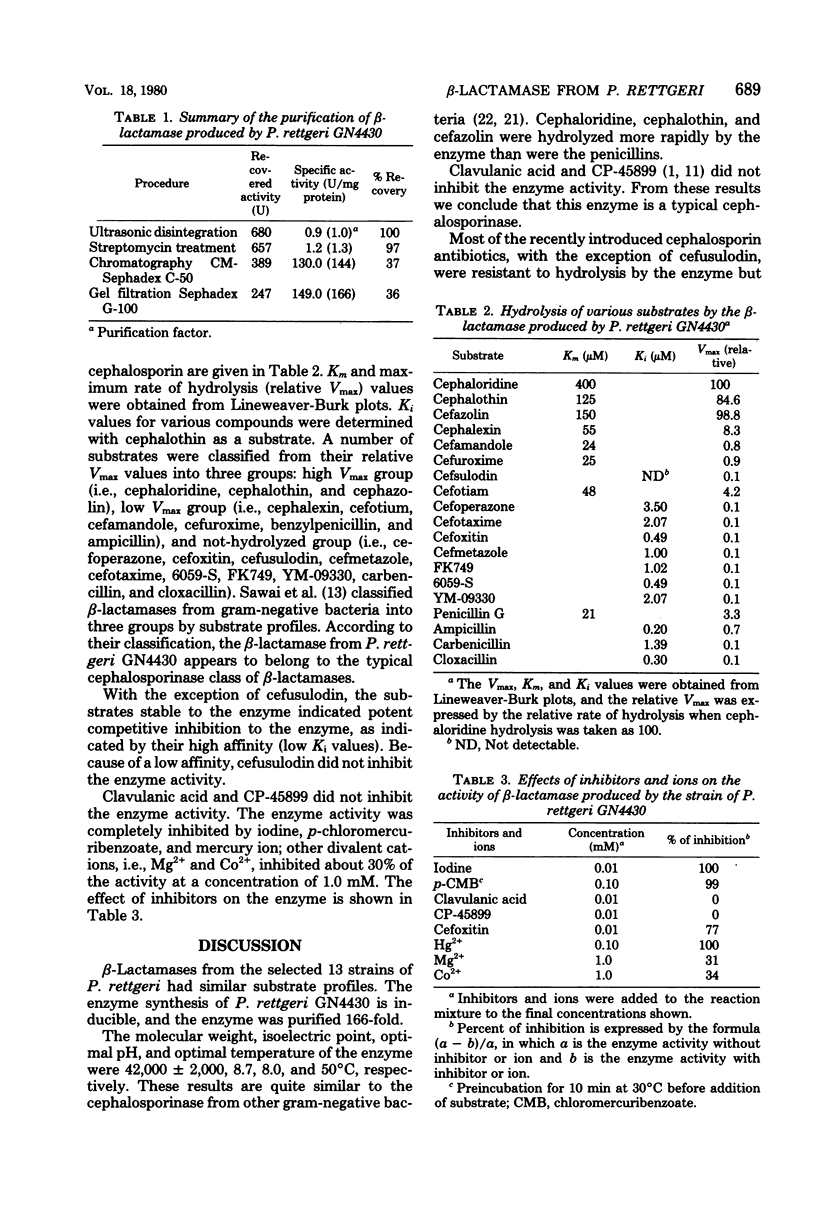
beta-Lactamase produced by Proteus rettgeri was found to be a typical cephalosporin beta-lactamase on the basis of its substrate hydrolysis profile. The enzyme activity was enhanced by prior treatment with an inducer. The enzyme was purified 166-fold by carboxymethyl-Sephadex column chromatography which indicated that its molecular weight was 42,000 +/- 2,000 and its isoelectric point was 8.7. Cefoperazone, cefoxitin, cefusulodin, cefmetazole, cefotaxime, 6059-S, FK749, YM-09330, carbenicillin, and cloxacillin were stable to this enzyme and possessed the function of competitive inhibition, as shown by their affinity for the beta-lactamase. The enzyme activity was inhibited by iodine, p-chloromerburibenzoate, and HG2+ ion. Clavulanic acid and CP-45899 displayed poor inhibitory activity toward this enzyme. The optimal pH was 8.0, and the optimal temperature was 50 degrees C.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- English A. R., Retsema J. A., Girard A. E., Lynch J. E., Barth W. E. CP-45,899, a beta-lactamase inhibitor that extends the antibacterial spectrum of beta-lactams: initial bacteriological characterization. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):414–419. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Yamamoto M., Sugawara S. Purification and properties of beta-lactamase from Proteus morganii. J Bacteriol. 1977 Sep;131(3):726–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.3.726-734.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Iyobe S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of a new beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas cepacia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):355–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara N., Minami S., Muraoka T., Saikawa I., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro antibacterial activity of cefoperazone (T-1551), a new semisynthetic cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):731–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Aswapokee N., Fu K. P., Aswapokee P. Antibacterial activity of a new 1-oxa cephalosporin compared with that of other beta-lactam compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):141–149. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Cefamandole, a cephalosporin antibiotic with an unusually wide spectrum of activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):177–182. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Sykes R. B., Griffiths A., Thornton J. E. Cefuroxime, a new cephalosporin antibiotic: activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):511–519. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C., Cole M. Clavulanic acid: a beta-lactamase-inhiting beta-lactam from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawai T., Mitsuhashi S., Yamagishi S. Drug resistance of enteric bacteria. XIV. Comparison of beta-lactamases in gram-negative rod bacteria resistant to alpha-aminobenzylpenicillin. Jpn J Microbiol. 1968 Dec;12(4):423–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1968.tb00415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kida M., Kondo M., Ono H., Takeuchi M., Nishi T. SCE-963, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):557–568. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya K., Kondo M., Nagatomo H. SCE-129, antipseudomonal cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Feb;13(2):137–145. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.2.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Mitsuhashi S. Antimicrobial evaluation of cefoxitin: a new semisynthetic cephamycin. Comparative studies with cefazolin and cefalotin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1977;27(1):89–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. A spectrophotometric assay of beta-lactamase action on penicillins. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):789–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma S., Sawai T., Yamagishi S., Mitsuhashi S. Beta-lactamase formation and resistance of Proteus morganii to various penicillins and cephalosporins. Jpn J Microbiol. 1974 Mar;18(2):113–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1974.tb00798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



