Abstract
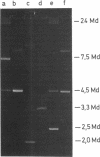
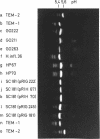
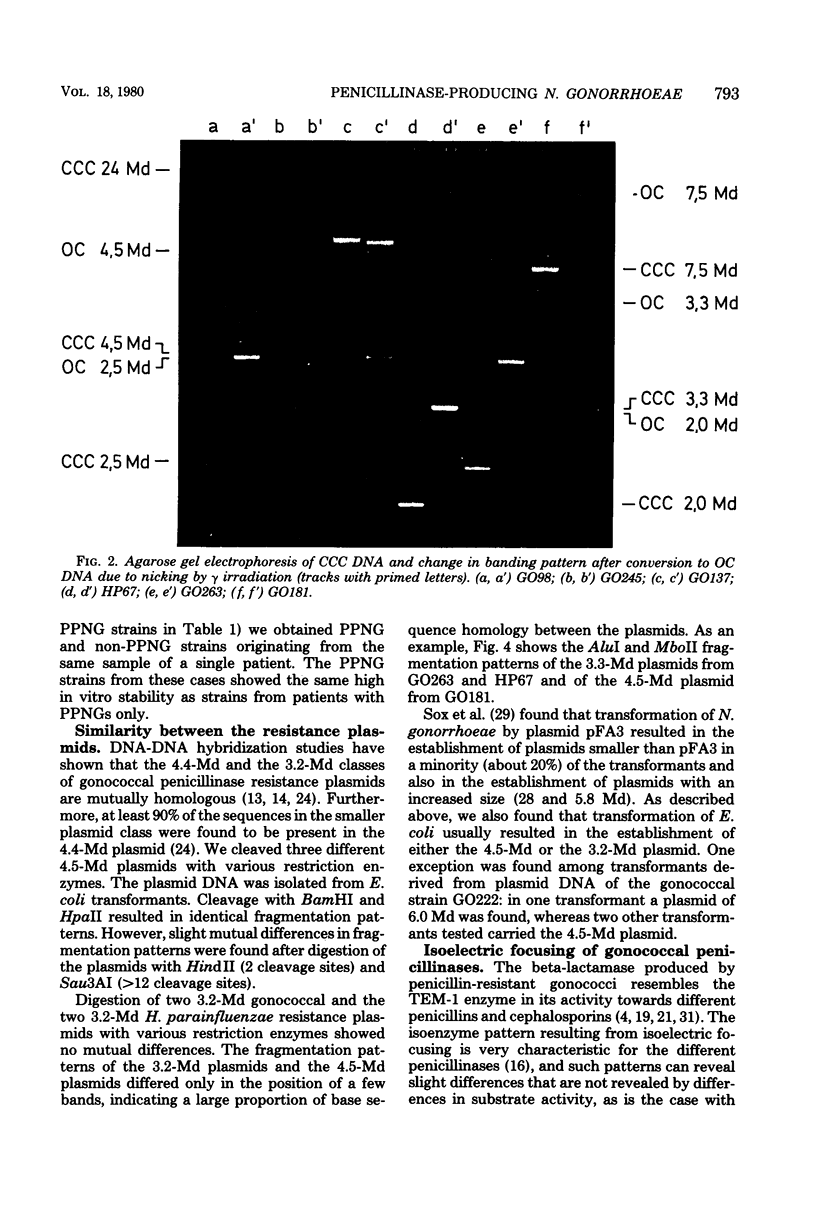
Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains were isolated in the Netherlands with increasing frequency during the period of 1976 to 1979. About 3% of the gonococci isolated in the first half of 1979 produced penicillinase. In contrast to the period of 1976 to 1977, most penicillinase-producing N. gonorrhoeae infections during the period of 1978 to 1979 were contracted in the Netherlands. The results of genetic and molecular studies on 80 penicillinase-producing N. gonorrhoeae strains were similar to earlier observations of others: resistance plasmids of only two sizes, 4.5 and 3.3 megadaltons (Md), occurred in penicillinase-producing N. gonorrhoeae strains, and these encoded for the TEM-1 enzyme. The 4.5-Md plasmid could be transferred to Escherichia coli when it coexisted with a plasmid of 24 Md. The latter plasmid was present in the vast majority of the strains carrying the 4.5-Md plasmid. One strain carried a cryptic 7.5-Md plasmid in addition to the commonly found 2.5-Md plasmid. Two penicillinase-producing strains of Haemophilus parainfluenzae isolated were found to carry a 3.3-Md plasmid species which was indistinguishable from the 3.3-Md gonococcal resistance plasmids. No plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid was found in two strains of penicillinase-producing Branhamella catarrhalis, and these strains produced a penicillinase different from the TEM-1 enzyme.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford W. A., Golash R. G., Hemming V. G. Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):657–658. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92467-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron E. S., Saz A. K., Kopecko D. J., Wohlhieter J. A. Transfer of plasmid-borne beta-lactamase in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):270–280. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Norlander L., Norqvist A., Normark S. Contribution of a TEM-1-like beta-lactamase to penicillin resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):618–623. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blog F. B., Chang A., de Koning G. A., Oranje A. P., Stolze E., Bosscher-Koestsier G., de Jonge-Suy M. P., Michel M. F., O'Niel E., de Weerdt-van Ameyden S. Penicillinase-producing strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated in Rotterdam. Br J Vener Dis. 1977 Apr;53(2):98–100. doi: 10.1136/sti.53.2.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brive C., Barthelemy M., Bouanchaud D. H., Labia R. Microhétérogénéité en électrofocalisation analytique de beta-lactamases d'origine plasmidique. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Oct;128(3):309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Sox T., Biswas G., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Conjugal transfer of the gonococcal penicillinase plasmid. Science. 1977 Mar 11;195(4282):998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.402693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Roberts M., Mayer L. W., Falkow S. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase production in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):528–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. S., Foster G. C. Electrophoretic comparison of endonuclease-digested plasmids from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1297–1304. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1297-1304.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromkova R., Goodgal S. Transformation by plasmid and chromosomal DNAs in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jun 27;88(4):1428–1434. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphreys G. O., Willshaw G. A., Anderson E. S. A simple method for the preparation of large quantities of pure plasmid DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 2;383(4):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufs R., Fock R. Characterization of genes specifying ampicillin resistance in bacterial isolates using a single-strand specific nuclease for analysis of plasmid DNA-DNA duplexes. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Mar;111(1):233–237. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-1-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufs R., Kaulfers P. M., Jahn G., Teschner U. Molecular characterization of a small Haemophilus influenzae plasmid specifying beta-lactamase and its relationship to R factors from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Mar;111(1):223–231. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-1-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmvall B. E., Brorsson J. E., Johnsson J. In vitro sensitivity to penicillin V and beta-lactamase production of Branhamella catarrhalis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1977 Jul;3(4):374–375. doi: 10.1093/jac/3.4.374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival A., Corkill J. E., Rowlands J., Sykes R. B. Pathogenicity of and beta-lactamase production by Branhamella (Neisseria) catarrhalis. Lancet. 1977 Dec 3;2(8049):1175–1175. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91562-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival A., Rowlands J., Corkill J. E., Alergant C. D., Arya O. P., Rees E., Annels E. H. Penicillinase-producing Gonococci in Liverpool. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1379–1382. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91919-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perine P. L., Thornsberry C., Schalla W., Biddle J., Siegel M. S., Wong K. H., Thompson S. E. Evidence for two distinct types of penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Lancet. 1977 Nov 12;2(8046):993–995. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92891-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P., Roberts M., Ninane G. Beta-lactamase production in commensal Neisseriaceae. Lancet. 1979 Mar 17;1(8116):619–619. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piot P. beta-lactamase producing haemophili and Neisseriae. Acta Clin Belg. 1978;33(1):45–75. doi: 10.1080/22953337.1978.11735735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of two beta-lactamase-specifying plasmids isolated from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):557–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.557-563.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Falkow S. Conjugal transfer of R plasmids in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1977 Apr 14;266(5603):630–631. doi: 10.1038/266630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Piot P., Falkow S. The ecology of gonococcal plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):491–494. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel M. S., Thornsberry C., Biddle J. W., O'Mara P. R., Perine P. L., Wiesner P. J. Penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae: results of surveillance in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):170–175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Mohammed W., Blackman E., Biswas G., Sparling P. F. Conjugative plasmids in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.278-286.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sox T. E., Mohammed W., Sparling P. F. Transformation-derived Neisseria gonorrhoeae plasmids with altered structure and function. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.510-518.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussenbach J. S., Monfoort C. H., Schiphof R., Stobberingh E. E. A restriction endonuclease from Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3193–3202. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D. Translocation of an ampicillin resistance determinant within an R-factor aggregate in Salmonella panama. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1978;44(2):203–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00643223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J., Cohen S. N. Molecular and genetic studies of an R factor system consisting of independent transfer and drug resistance plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):699–709. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.699-709.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Klingeren B., van Embden J. D., Dessens-Kroon M. Plasmid-mediated chloramphenicol resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):383–387. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]