Abstract
Mutants resistant to the 2-deoxystreptamine aminoglycosides hygromycin B and gentamicin were analyzed biochemically and genetically. In hygromycin B-resistant strains, ribosomal alterations were not detectable by electrophoretic or genetic experiments. Rather, as was demonstrated for one strain in detail, resistance to this drug seems to be the consequence of several mutations, each impairing drug accumulation, namely of a deletion of a gene close to the proC marker which potentiates the effect of a second mutation in the unc gene cluster. Three mutants resistant to gentamicin which were previously demonstrated to harbor an altered ribosomal protein, L6, were shown in addition to contain unc. Both the unc and the ribosomal mutation greatly impair the drug accumulation ability of the mutants. Further evidence for the direct effect of ribosomal mutations on the uptake of aminoglycosides was obtained with strains that possess ribosomes with increased affinity for dihydrostreptomycin. Dihydrostreptomycin transport by these cells is greatly stimulated; thus, the hypersensitivity of these mutants is caused by increased binding affinity for dihydrostreptomycin and its secondary effect on the uptake process. Experiments were also performed on the biochemical basis of the third phase of aminoglycoside transport (acceleration phase). The condition for its onset is that ribosomes are active in protein synthesis irrespective of whether the proteins synthesized are functional. This, and the failure to observe the synthesis of new proteins upon the addition of aminoglycosides, do not support the view of autoinduction of a cognate or related transport system.
Full text
PDF



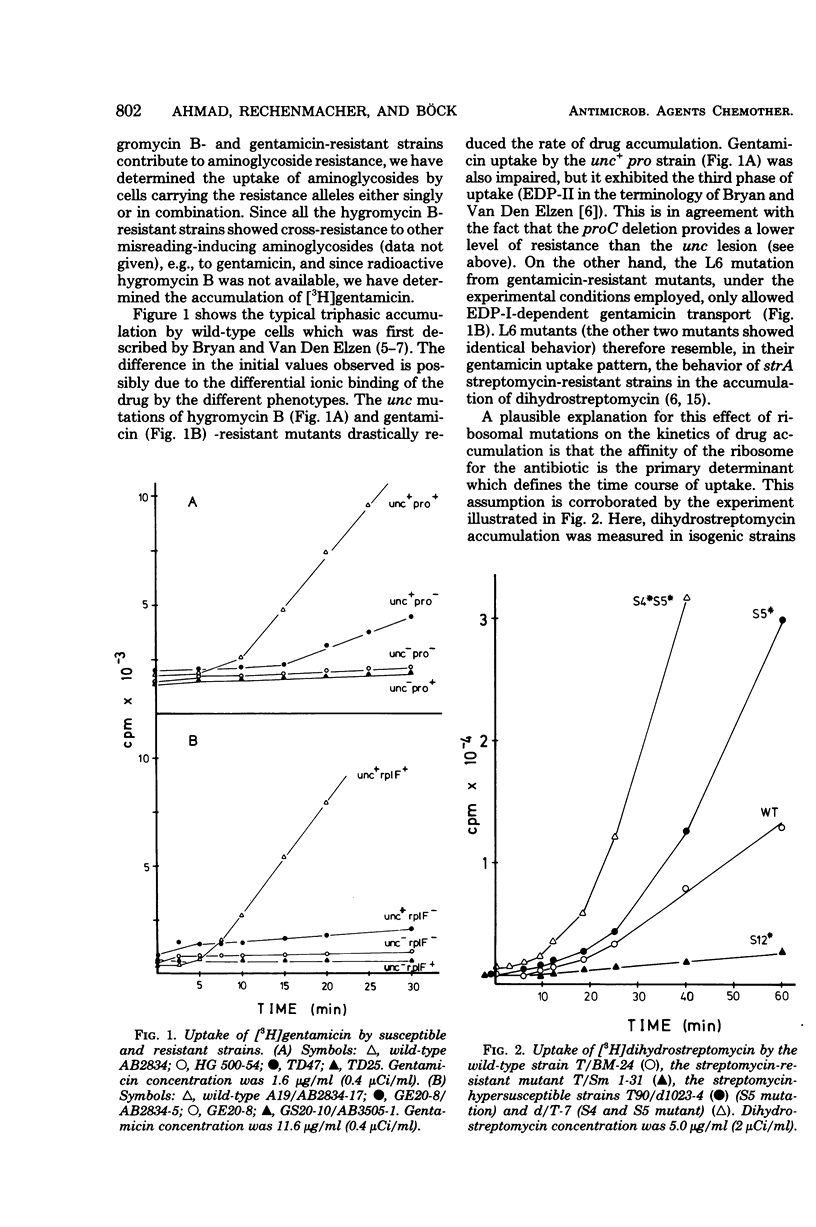

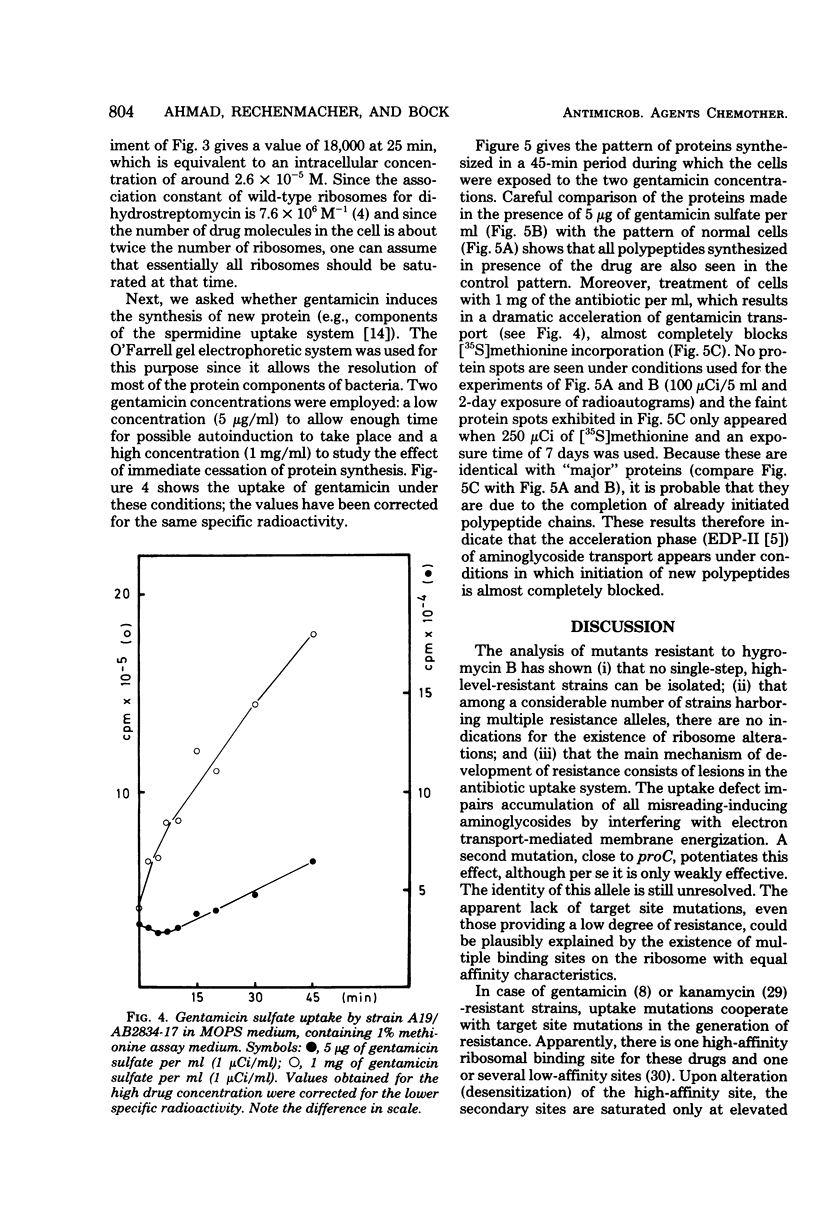
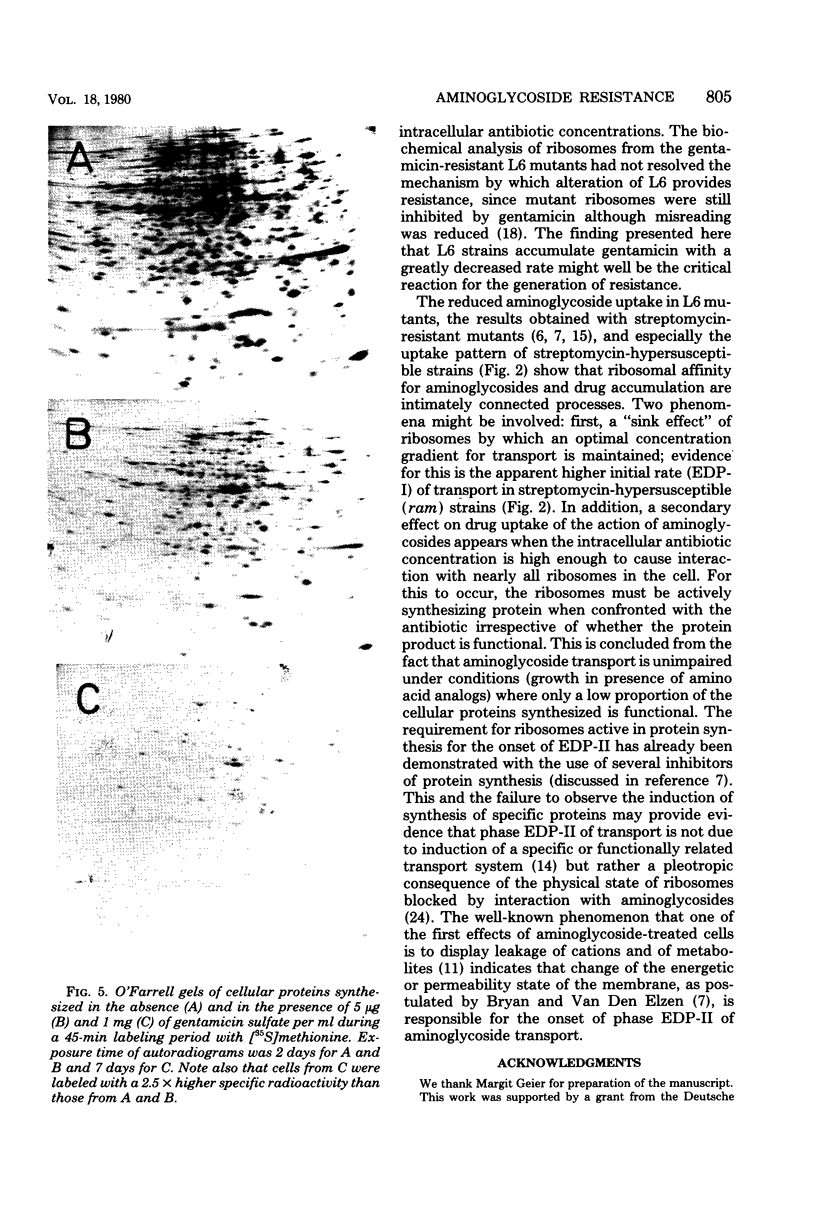

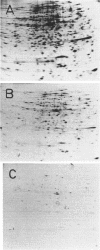
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler L. W., Rosen B. P. Properties of Escherichia coli mutants with alterations in Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):248–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.248-256.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELJANSKI M. Sur la formation d'enzymes respiratoires chez un mutant d'Escherichia coli streptomycino-résistant et auxotrophe pour l'hémine. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1957 Mar;92(3):396–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Effects of membrane-energy mutations and cations on streptomycin and gentamicin accumulation by bacteria: a model for entry of streptomycin and gentamicin in susceptible and resistant bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):163–177. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van Den Elzen H. M. Gentamicin accumulation by sensitive strains of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1975 Sep;28(9):696–703. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.28.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., Van den Elzen H. M. Streptomycin accumulation in susceptible and resistant strains of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):928–938. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckel P., Buchberger A., Böck A., Wittmann H. G. Alteration of ribosomal protein L6 in mutants of Escherichia coli resistant to gentamicin. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 14;158(1):47–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00455118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A., Petzet A., Piepersberg W. Ribosomal ambiguity (ram) mutations facilitate diyhydrostreptomycin binding to ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 15;104(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80842-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabañas M. J., Vázquez D., Modolell J. Dual interference of hygromycin B with ribosomal translocation and with aminoacyl-tRNA recognition. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):21–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBIN D. T., HANCOCK R., DAVIS B. D. THE SEQUENCE OF SOME EFFECTS OF STREPTOMYCIN IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 13;74:476–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Davis B. D. Misreading of ribonucleic acid code words induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. The effect of drug concentration. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3312–3316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL D. G., NEIDHARDT F. C. Use of chloramphenicol to study control of RNA synthesis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Oct 14;53:96–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90797-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F. Isolation and characterization of ribonuclease I mutants of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V. Induction of streptomycin uptake in resistant strains of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):177–181. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V. Streptomycin uptake via an inducible polyamine transport system in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May 16;86(2):345–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Gutnick D. L. Use of neomycin in the isolation of mutants blocked in energy conservation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):287–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.287-289.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühberger R., Piepersberg W., Petzet A., Buckel P., Böck A. Alteration of ribosomal protein L6 in gentamicin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli. Effects on fidelity of protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):187–193. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goffic F., Capmau M. L., Tangy F., Baillarge M. Mechanism of action of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Binding studies of tobramycin and its 6'-N-acetyl derivative to the bacterial ribosome and its subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Dec;102(1):73–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb06264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConville M. L., Charles H. P. Isolation of haemin-requiring mutants of Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Jul;113(1):155–164. doi: 10.1099/00221287-113-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misumi M., Nishimura T., Komai T., Tanaka N. Interaction of kanamycin and related antibiotics with the large subunit of ribosomes and the inhibition of translocation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Sep 29;84(2):358–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piepersberg W., Böck A., Yaguchi M., Wittmann H. G. Genetic position and amino acid replacements of several mutations in ribosomal protein S5 from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 30;143(1):43–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00269419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piepersberg W., Noseda V., Böck A. Bacterial ribosomes with two ambiguity mutations: effects of translational fidelity, on the response to aminoglycosides and on the rate of protein synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 9;171(1):23–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00274011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. P. Restoration of active transport in an Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase-deficient mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1124–1129. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1124-1129.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Săsărman A., Surdeanu M., Szégli G., Horodniceanu T., Greceanu V., Dumitrescu A. Hemin-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):570–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.570-572.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorbjarnardóttir S. H., Magnúsdóttir R. A., Eggertsson G. Mutations determining generalized resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 25;161(1):89–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00266619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierhut G., Piepersberg W., Böck A. Comparative analysis of the effect of aminoglycosides on bacterial protein synthesis in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):577–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]