Abstract
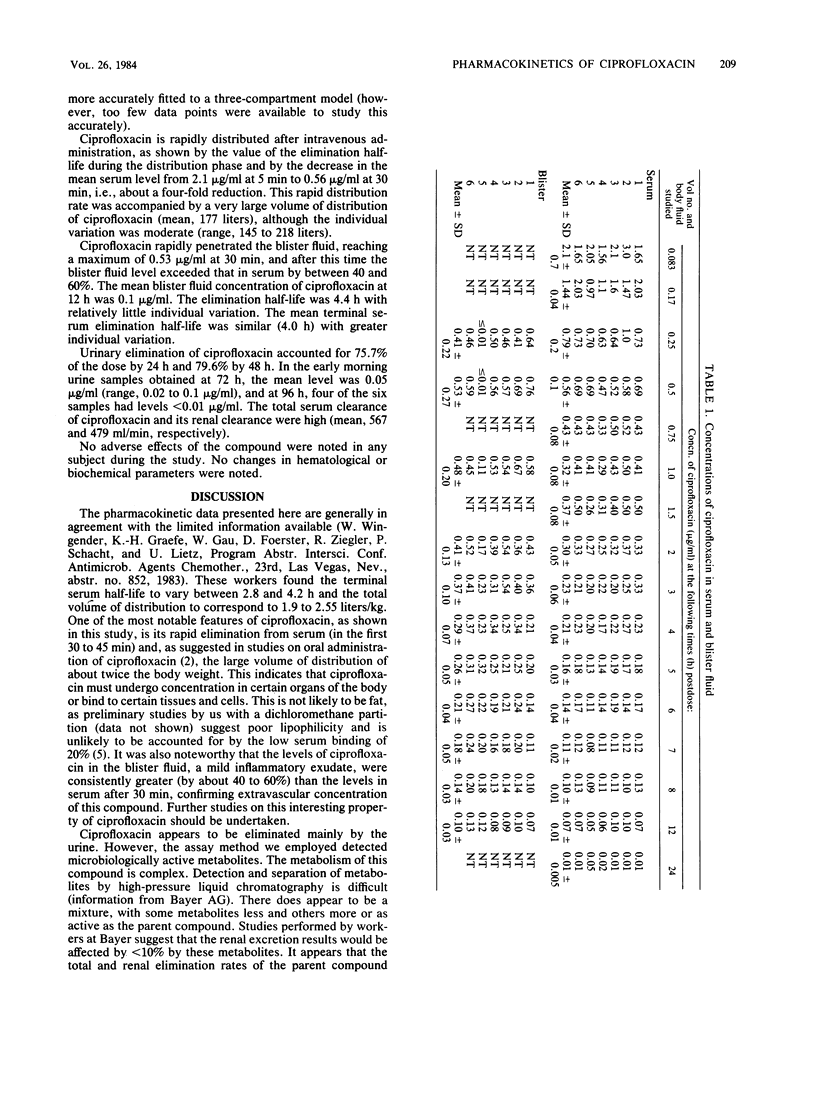
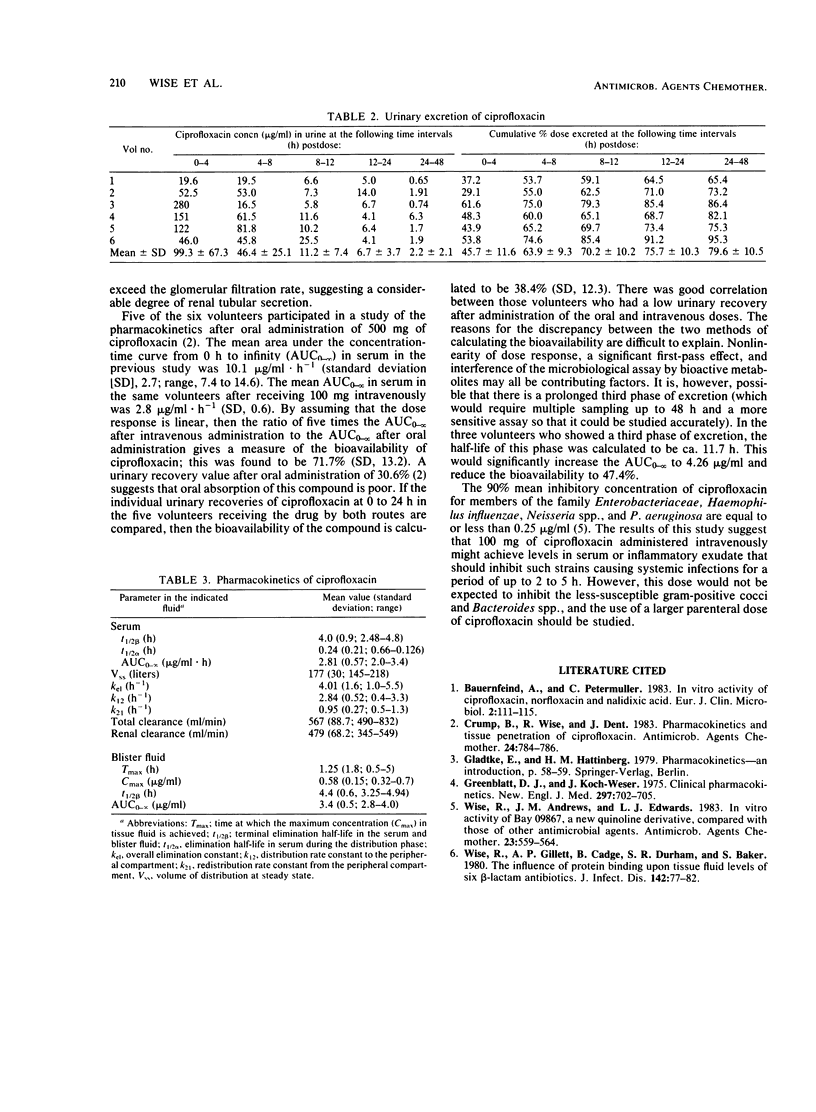
A 100-mg dose of ciprofloxacin was given as an intravenous bolus injection to each of six healthy volunteers, after which the levels of this agent were measured in serum, blister fluid, and urine. After administration, distribution of ciprofloxacin was very rapid, and the mean distribution volume was very large (177 liters). The mean terminal serum half-life was 4.0 h. The agent penetrated blister fluid rapidly, with the mean maximum level being 0.53 micrograms/ml at 30 min, after which time the blister levels exceeded those in serum. The 48-h urinary recovery of ciprofloxacin was about 80%.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump B., Wise R., Dent J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):784–786. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Kock-Weser J. Drug therapy. Clinical Pharmacokinetics (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 2;293(14):702–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510022931406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Edwards L. J. In vitro activity of Bay 09867, a new quinoline derivative, compared with those of other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):559–564. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Gillett A. P., Cadge B., Durham S. R., Baker S. The influence of protein binding upon tissue fluid levels of six beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



