Abstract
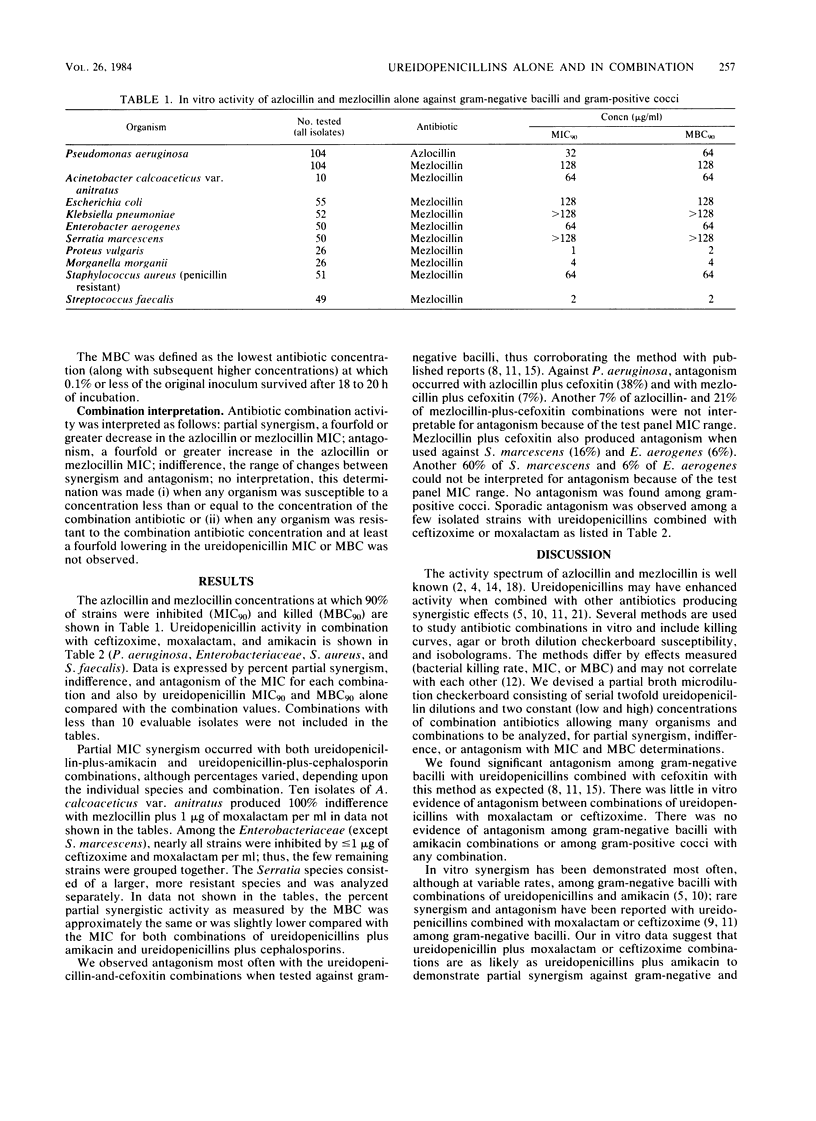
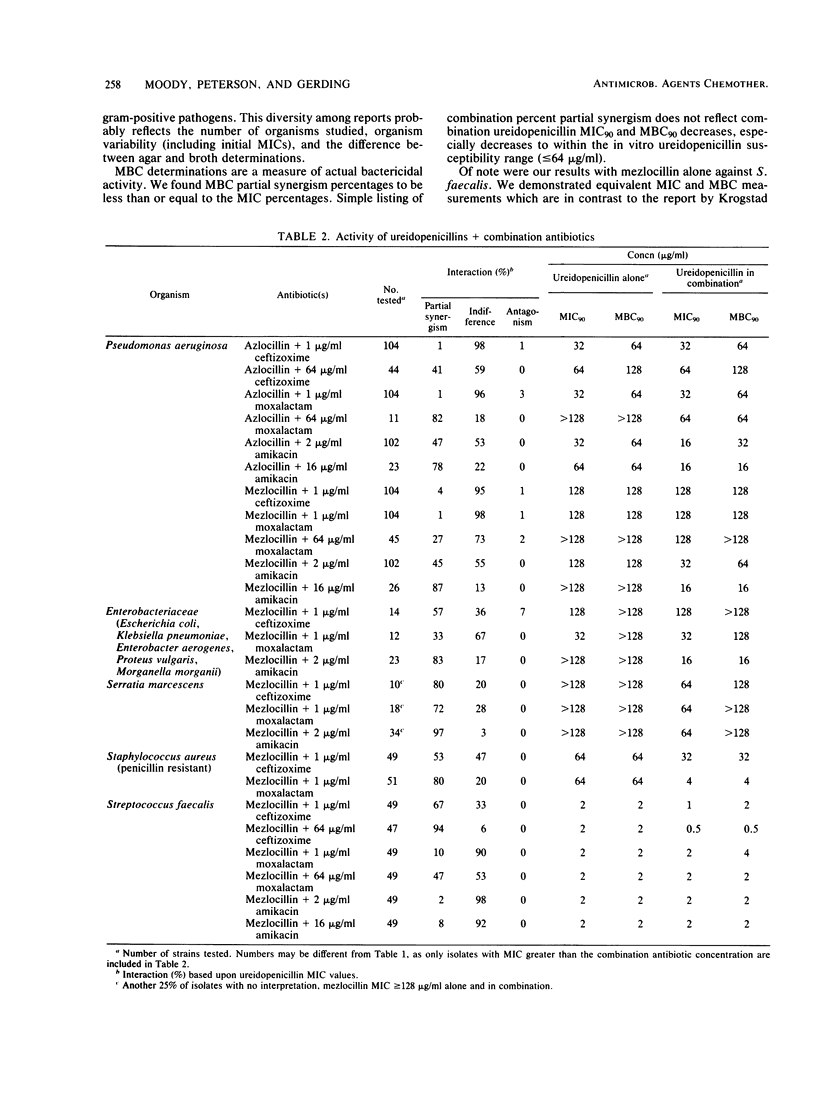
The MIC and MBC activity of mezlocillin alone and in combination with two concentrations of ceftizoxime, moxalactam, and amikacin and a single concentration of cefoxitin was studied in a broth microdilution partial checkerboard against 472 strains of aerobic gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. Azlocillin was tested alone and in the same combinations against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Of the gram-negative bacilli tested, 38% were gentamicin resistant. Antagonism (less than or equal to a fourfold ureidopenicillin MIC increase) was observed frequently with combinations of ureidopenicillins plus cefoxitin and sporadically with ureidopenicillins plus ceftizoxime or moxalactam. Partial synergism (less than or equal to a fourfold ureidopenicillin MIC decrease) was evident with both combinations of ureidopenicillins plus amikacin and ureidopenicillins plus ceftizoxime or moxalactam, the percentage being dependent upon the individual species and combinations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Pan T. Mezlocillin: in vitro studies of a new broad-spectrum penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jan;11(1):74–79. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Wright C. A. Comparative efficacies of mezlocillin and ampicillin alone or in combination with gentamicin in the treatment of Streptococcus faecalis endocarditis in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):408–410. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltham R. K., Power A. K., Pell P. A., Sneath P. A. A simple method for storage of bacteria at--76 degrees C. J Appl Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;44(2):313–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1978.tb00804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. Azlocillin and mezlocillin: new ureido penicillins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jun;13(6):930–938. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.6.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Neu H. C. The comparative synergistic activity of amikacin, gentamicin, netilmicin and azlocillin, mezlocillin, carbenicillin and ticarcillin against Serratia marcescens. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Feb;31(2):135–140. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. L., Freier E. F. The measurement of serum magnesium by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Am J Med Technol. 1967 May-Jun;33(3):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Pargwette A. R. Defective killing of enterococci: a common property of antimicrobial agents acting on the cell wall. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):965–968. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuck N. A., Testa R. T., Forbes M. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial effects of combinations of beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):634–638. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Combination of ceftizoxime with azlocillin, mezlocillin, piperacillin and ticarcillin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Nov;10 (Suppl 100):63–68. doi: 10.1093/jac/10.suppl_c.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Fu K. P. Synergy of azlocillin and mezlocillin combined with aminoglycoside antibiotics and cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):813–819. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Combination of mezlocillin and azlocillin with cephalosporin antibiotics: cefoxitin, cefoperazone, cefotaxime and moxalactam. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jan;9 (Suppl A):101–106. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.suppl_a.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W. Problems in determination of antibiotic synergism in vitro. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):276–281. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahal J. J., Jr Antibiotic combinations: the clinical relevance of synergy and antagonism. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 Mar;57(2):179–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERN J., LEWIS W. H. The colorimetric estimation of calcium in serum with ocresolphthalein complexone. Clin Chim Acta. 1957 Dec;2(6):576–580. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(57)90063-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Mezlocillin: a broad spectrum penicillin highly active against gram-positive organisms and Haemophilus influenzae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1982 Jan;9 (Suppl A):15–21. doi: 10.1093/jac/9.suppl_a.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V. In vitro antagonism of beta-lactam antibiotics by cefoxitin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):968–975. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D., Bodey G. P. Azlocillin: in vitro studies of a new semisynthetic penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):865–870. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton C. W., Weinstein M. P., Reller L. B. Correlation of serum bactericidal activity with antimicrobial agent level and minimal bactericidal concentration. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):160–168. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein A. J. Principles of concomitant antibiotic therapy. Med J Aust. 1977 Oct 8;2(3 Pt 2 Suppl):19–22. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1977.tb113912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. W., Malow J. B., Zimelis V. M., Pahlavanzadeh H., Panwalker A. P., Jackson G. G. Comparative in vitro activity of azlocillin, ampicillin, mezlocillin, piperacillin, and ticarcillin, alone and in combination with an aminoglycoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):540–543. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



