Abstract
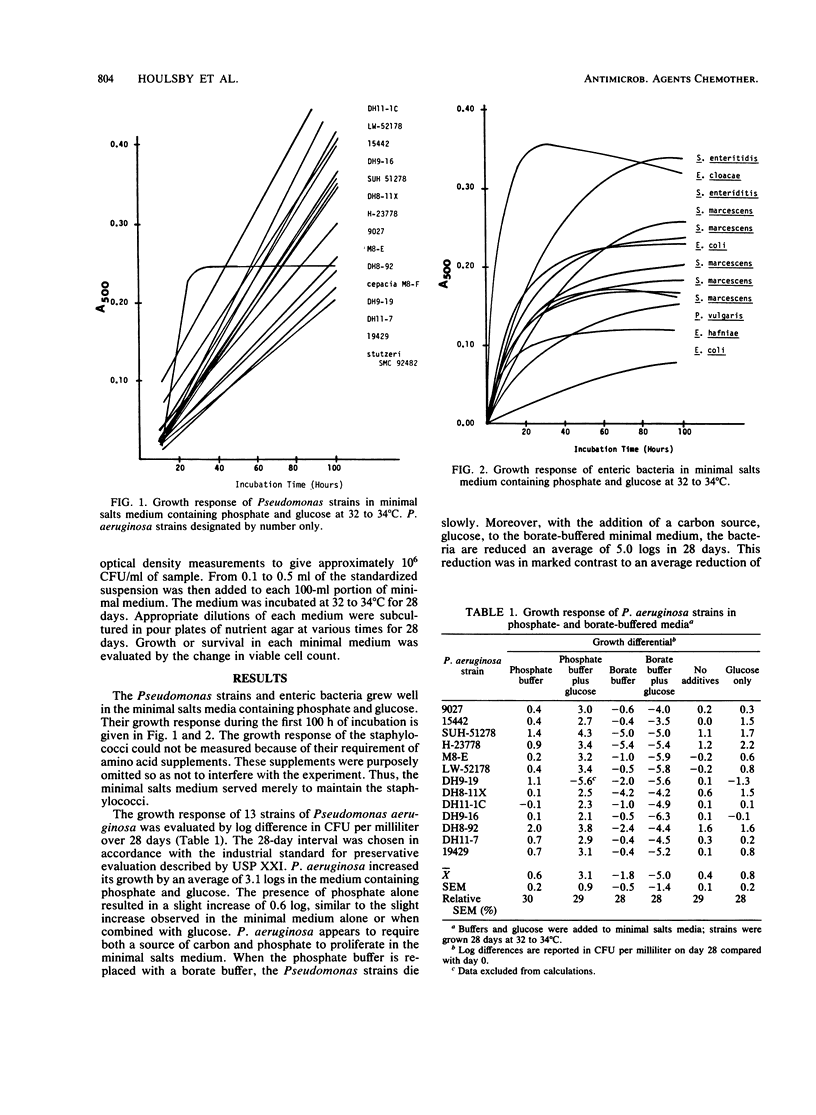
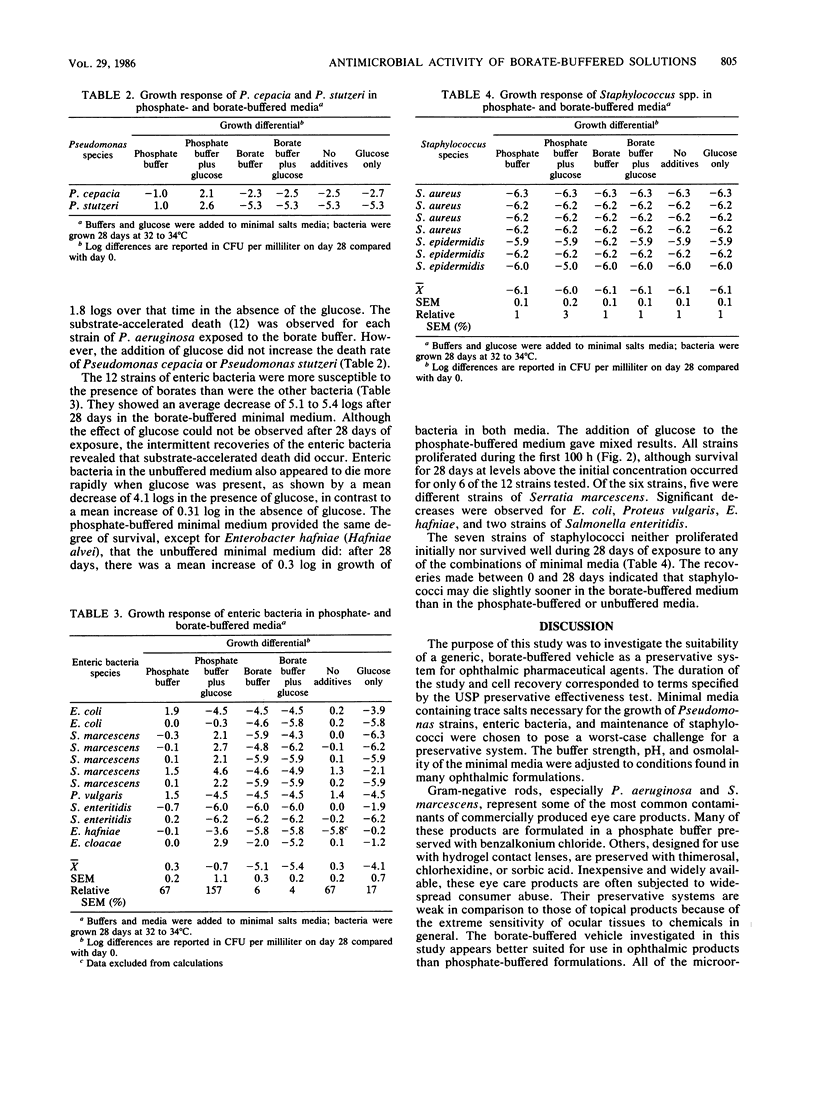
A minimal salts medium adjusted to physiological pH and osmolality was buffered with either 0.3% phosphate or 1.2% borate and evaluated for antimicrobial activity. The borate-buffered medium, either with or without a carbon source, exhibited significant antimicrobial activity against 15 Pseudomonas strains, 12 strains of enteric bacteria, and 7 strains of staphylococci. The borate-buffered system appears suitable for use as a generic vehicle for ophthalmic pharmaceutical agents.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelhardt M., Fogh A. Boraks--er det farligt? 12 års forespørgsler til giftinformationscentralen. Ugeskr Laeger. 1983 Dec 5;145(49):3808–3810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosio M., Bertoncini L. Intossicazione acuta neonatale da acido borico. Descrizione di un caso ad evoluzione favorevole con trattamento dialitico peritoneale e revisione della letteratura. Minerva Pediatr. 1983 Oct 31;35(20):1021–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER R. S. The use of boric acid in dermatologic practice. AMA Arch Derm. 1956 Apr;73(4):336–341. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1956.01550040030005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayinka O. A. Boric acid--a useful preservative for urine samples. Afr J Med Sci. 1971 Oct;2(4):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis-Hansen B., Aggerbeck B., Jansen J. A. Unaffected blood boron levels in newborn infants treated with a boric acid ointment. Food Chem Toxicol. 1982 Aug;20(4):451–454. doi: 10.1016/s0278-6915(82)80111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. R., Prasanna H. R., Viswanathan L., Venkitasubramanian T. A. Synthesis of aflatoxins by the non-growing mycelia of Aspergillus parasiticus and the effect of inhibitors. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Dec;91(2):417–420. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-2-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna C., Fraunfelder F. T., Cable M., Hardberger R. E. The effect of ophthalmic ointments on corneal wound healing. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973 Aug;76(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(73)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen J. A., Andersen J., Schou J. S. Boric acid single dose pharmacokinetics after intravenous administration to man. Arch Toxicol. 1984 Mar;55(1):64–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00316588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINGMA H. The pharmacology and toxicology of boron compounds. Can Med Assoc J. 1958 Apr 15;78(8):620–622. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan K., Taylor M. Chronic boric acid poisoning in infants. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Sep;58(9):737–739. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.9.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter I. A., Brodie J. Boric acid preservation of urine samples. Br Med J. 1969 May 10;2(5653):353–355. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5653.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schou J. S., Jansen J. A., Aggerbeck B. Human pharmacokinetics and safety of boric acid. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1984;7:232–235. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69132-4_32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swate T. E., Weed J. C. Boric acid treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Jun;43(6):893–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson P. G., Duerden B. I. Laboratory assessment of physical and chemical methods of preserving urine specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jun;30(6):532–536. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.6.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



