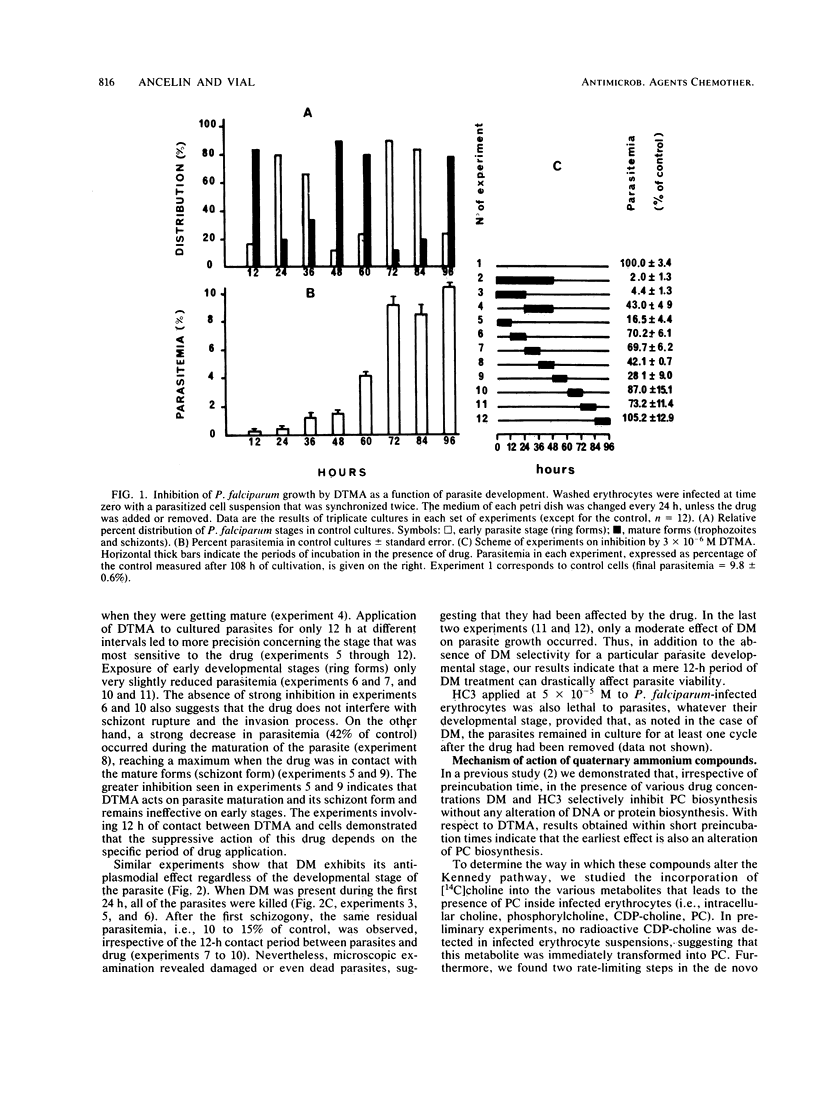
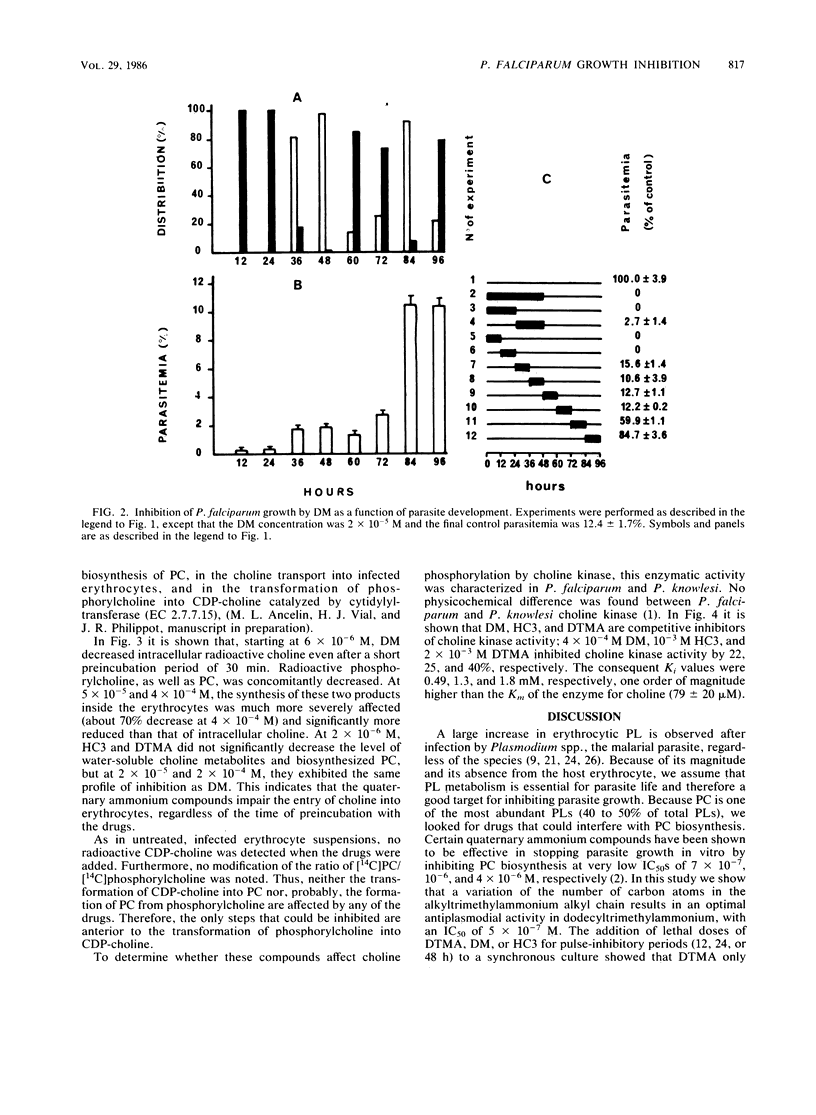
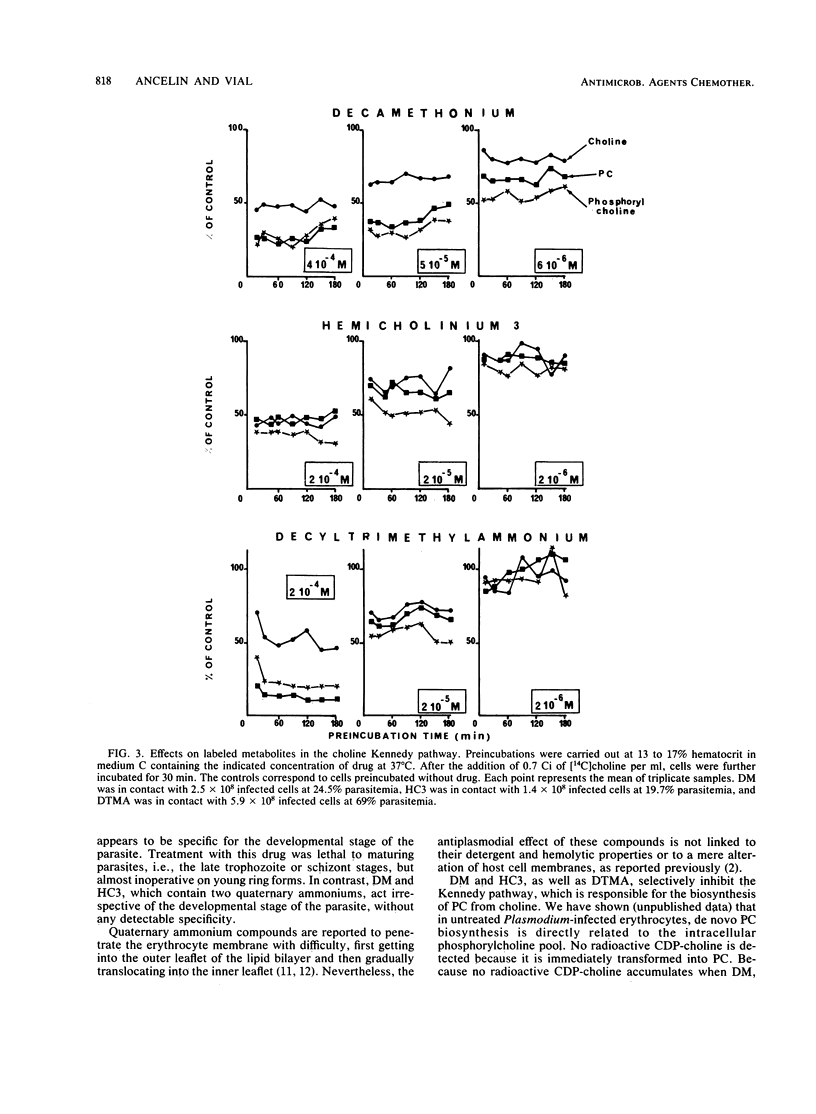
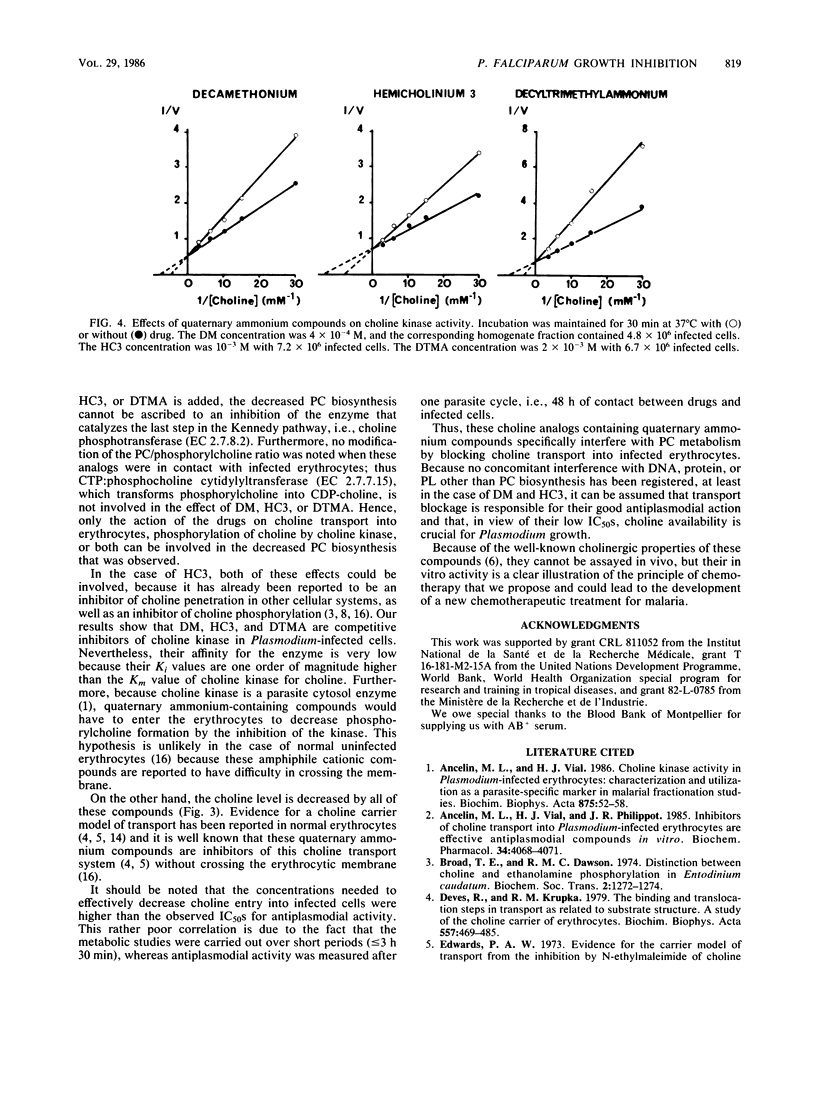
Abstract
Hemicholinium 3, decamethonium, and decyltrimethylammonium previously have been demonstrated to be efficient inhibitors, with 50% inhibitory concentrations of 4 X 10(-6), 10(-6), and 7 X 10(-7) M, respectively. We show that lengthening of the alkyl chain of decyltrimethylammonium by successive additions of two carbon atoms up to hexadecyltrimethylammonium results in a very low 50% inhibitory concentration of 5 X 10(-7) M for dodecyltrimethylammonium. Furthermore, hemicholinium 3 and decamethonium exerted their antiplasmodial activity, regardless of the developmental stage of the parasite, whereas decyltrimethylammonium was particularly lethal for the mature forms. After infected erythrocytes with radioactive choline were supplied, the determination of the water-soluble choline-containing compounds, as well as the assay of choline kinase activity, showed that the specific inhibition of phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis is related to the impairment of choline entry into erythrocytes. Thus, the impairment of the transport of choline, a natural polar head group of phospholipids, appears to be lethal for Plasmodium falciparum in vitro and could be a reasonable approach for a new malaria chemotherapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ancelin M. L., Vial H. J. Choline kinase activity in Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes: characterization and utilization as a parasite-specific marker in malarial fractionation studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 3;875(1):52–58. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ancelin M. L., Vial H. J., Philippot J. R. Inhibitors of choline transport into Plasmodium-infected erythrocytes are effective antiplasmodial compounds in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 15;34(22):4068–4071. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devés R., Krupka R. M. The binding and translocation steps in transport as related to substrate structure. A study of the choline carrier of erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 2;557(2):469–485. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90344-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A., Hanin I. Choline analogs as potential tools in developing selective animal models of central cholinergic hypofunction. Life Sci. 1980 Nov 3;27(18):1615–1634. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90635-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamza M., Lloveras J., Ribbes G., Soula G., Douste-Blazy L. An in vitro study of hemicholinium-3 on phospholipid metabolism of Krebs II ascites cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Jun 15;32(12):1893–1897. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., Jr Lipids and the malarial parasite. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):237–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homewood C. A., Neame K. D. A comparison of methods used for the removal of white cells from malaria-infected blood. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1976 Jun;70(2):249–251. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1976.11687119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomaa B. Interactions of surface-active alkyltrimethylammonium salts with the erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;28(7):975–980. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomaa B., Paatero G. Shape and volume changes in rat erythrocytes induced by surface-active alkyltrimethylammonium salts and sodium dodecyl sulphate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 2;647(2):211–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. B., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum in culture: use of outdated erthrocytes and description of the candle jar method. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):883–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupka R. M., Devés R. The choline transport system of erythrocytes distribution of the free carrier in the membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 16;600(1):228–232. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90427-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. Effects of quaternary ammonium compounds on choline transport in red cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;36(3):458–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb08002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. H., Maples B. K. Studies on Plasmodium falciparum in continuous cultivation. I. The effect of chloroquine and pyrimethamine on parasite growth and viability. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1979 Apr;73(2):99–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieckmann K. H. Falciparum malaria: the urgent need for safe and effective drugs. Annu Rev Med. 1983;34:321–335. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.34.020183.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe A. W., Eyster E., Kellner A. Liquid nitrogen preservation of red blood cells for transfusion; a low glycerol-rapid freeze procedure. Cryobiology. 1968 Sep-Oct;5(2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/s0011-2240(68)80154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W. Biochemistry of Plasmodium (malarial parasites). Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):453–495. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.453-495.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler R., Akesson B. Regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Effect of different substrates. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3359–3367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Philippot J. R., Wallach D. F. A reevaluation of the status of cholesterol in erythrocytes infected by Plasmodium knowlesi and P. falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Sep;13(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Thuet M. J., Ancelin M. L., Philippot J. R., Chavis C. Phospholipid metabolism as a new target for malaria chemotherapy. Mechanism of action of D-2-amino-1-butanol. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 1;33(17):2761–2770. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90693-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial H. J., Thuet M. J., Broussal J. L., Philippot J. R. Phospholipid biosynthesis by Plasmodium knowlesi-infected erythrocytes: the incorporation of phospohlipid precursors and the identification of previously undetected metabolic pathways. J Parasitol. 1982 Jun;68(3):379–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



