Abstract
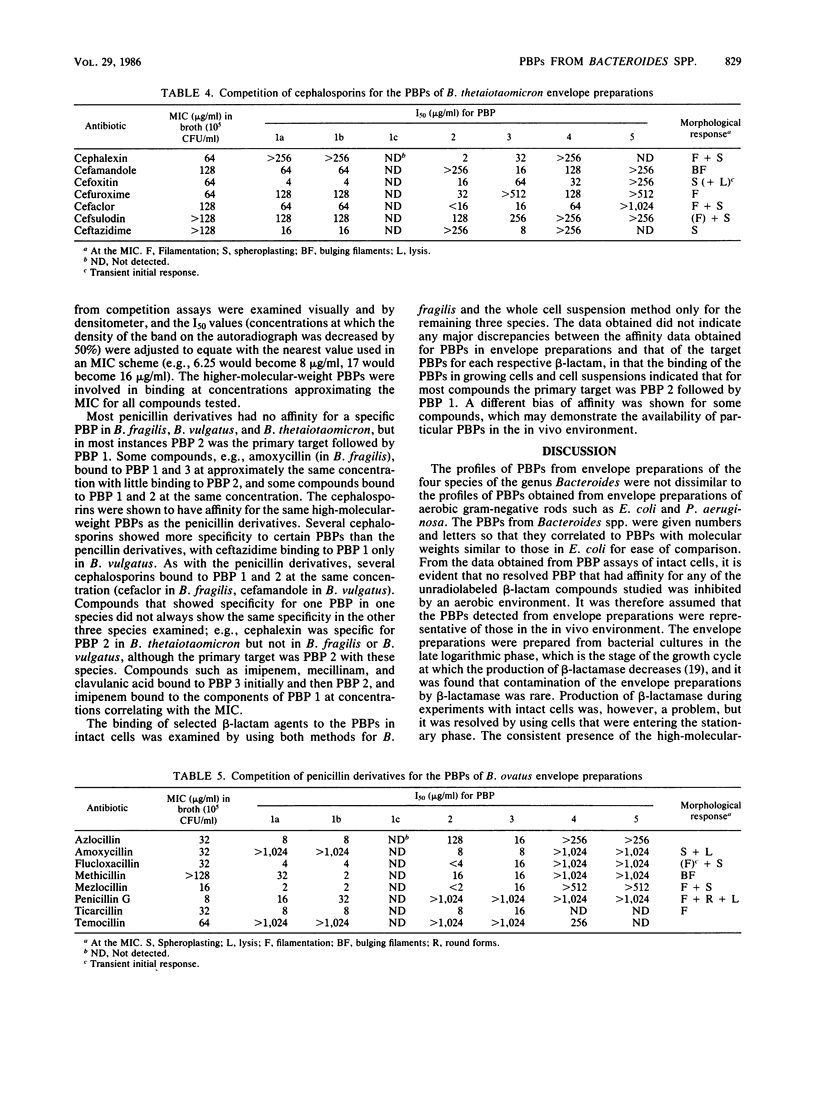
The penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) of four species of the genus Bacteroides were examined in cell envelope preparations from exponentially growing cultures and intact cells. Upon examination by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide electrophoresis, three major high-molecular-weight PBPs (molecular weight, 58,000 to 82,000) were resolved, and low-molecular-weight PBPs were seen in all strains except Bacteroides fragilis. The sporadic appearance of PBP 4 in B. fragilis (molecular weight, approximately 45,000) was shown not to be influenced by the concentration of free iron available in the medium or by the stage of growth at which the batch culture was harvested. No PBP that was inhibited by an aerobic environment was demonstrated. The affinity of 35 beta-lactam antibiotics for the PBPs from envelope preparations was examined and correlated with the morphological response. Most compounds bound initially to PBP 2 and then PBP 1, correlating with a primary response of filamentation and then spheroplasting and lysis. Compounds such as clavulanic acid bound to PBP 3 at concentrations causing round cells. Based on the data from this study, it is proposed that the three high-molecular-weight PBPs of Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides vulgatus, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, and Bacteroides ovatus correlate to the three high-molecular-weight PBPs of Escherichia coli and that the PBPs of Bacteroides species perform the same enzymic role in cell wall biosynthesis as their counterparts in E. coli. Therefore, the components of PBP 1 are involved in cell elongation, PBP 2 is involved in septum formation, and PBP 3 is involved in maintenance of cell shape (i.e., PBP 2 in Bacteroides spp. = PBP 3 in E. coli, and PBP 3 in Bacteroides spp. = BPB 2 in E. coli).
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botta G. A., Privitera G., Menozzi M. G. Penicillin-binding proteins in Bacteroides fragilis and their affinities for several new cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Apr;11(4):325–331. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.4.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuchural G. J., Jr, Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Marsh P. K., Mayhew J. W. Cefoxitin inactivation by Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Dec;24(6):936–940. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.6.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Orr D., Ross G. W., Boulton M. G. Affinities of penicillins and cephalosporins for the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K-12 and their antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):533–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Orr D., Ross G. W., Boulton M. G. Competition of beta-lactam antibiotics for the penicillin-binding proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter cloacae, Klebsiella aerogenes, Proteus rettgeri, and Escherichia coli: comparison with antibacterial activity and effects upon bacterial morphology. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):325–328. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornbusch K., Olsson-Lijequist B., Nord C. E. Antibacterial activity of new beta-lactam antibiotics on cefoxitin-resistant strains of Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Mar;6(2):207–216. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. S., Greenwood D. The morphological response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to azthreonam, cefoperazone, ceftazidime and N-formimidoyl thienamycin. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Apr;17(2):159–169. doi: 10.1099/00222615-17-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M. Pathogenic anaerobes. Arch Intern Med. 1982 Oct 25;142(11):1988–1992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Cerini R., Longoni P., Grossato A., Canepari P. Identification of a streptococcal penicillin-binding protein that reacts very slowly with penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1343–1350. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1343-1350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Smith S. A., Cimarusti C. M., Sykes R. B. Binding of monobactams to penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):98–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Smith S. A., Sykes R. B. Penicillin-binding proteins in Bacteroides fragilis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Jul;36(7):907–910. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes M. V., Orr D. C. Mode of action of ceftazidime: affinity for the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Aug;12(2):119–126. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Matsuhashi M., Mitsuhashi S. Comparative studies of penicillin-binding proteins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan R. D., Jude D. A. The interactions of [14C]cefotetan with penicillin binding proteins of a wide variety of Gram-positive and gram-negative species. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jan;11 (Suppl):169–177. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.suppl_a.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya S., Yamazaki M., Sugawara S., Matsuhashi M. Penicillin-binding proteins in Proteus species. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):474–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.474-479.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Dornbusch K., Nord C. E. Factors contributing to resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Feb;15(2):263–268. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Dornbusch K., Nord C. E. Susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics and production of beta-lactamase in Bacteroides fragilis. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1977 Oct 7;163(3):183–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02126677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson B., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Formation of beta-lactamase in Bacteroides fragilis: cell-bound and extracellular activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):727–735. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onoe T., Umemoto T., Sagawa H., Suginaka H. Filament formation of Fusobacterium nucleatum cells induced by mecillinam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Mar;19(3):487–489. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.3.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd S. T., Chase H. A., Reynolds P. E. The separation and properties of two penicillin-binding proteins from Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):521–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sowell M. O., Buchanan C. E. Changes in penicillin-binding proteins during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1331–1337. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1331-1337.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Jobanputra V. Mutants of Escherichia coli which lack a component of penicillin-binding protein 1 are viable. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80824-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Ward J. B. Benzylpenicillin-induced filament formation of Clostridium perfringens. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Dec;128(12):3025–3035. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-12-3025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann W., Rosselet A. Function of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli as a permeability barrier to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):368–372. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]