Abstract
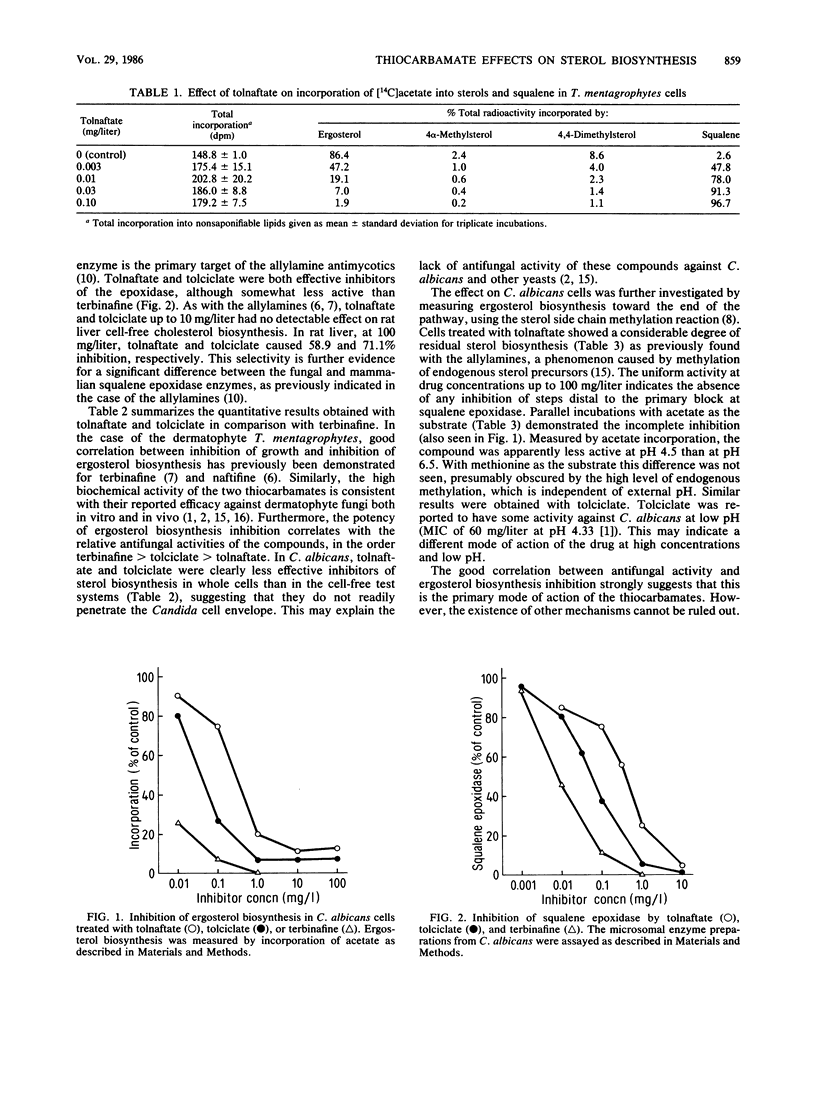
The thiocarbamate antimycotics tolnaftate and tolciclate blocked sterol biosynthesis in fungal cells and cell extracts, with accumulation of squalene. This point of action was confirmed by the direct inhibition of microsomal squalene epoxidase from Candida albicans. There was no inhibition of other steps in ergosterol biosynthesis. In whole Candida cells, ergosterol biosynthesis inhibition was not complete at drug concentrations up to 100 mg/liter, whereas full inhibition occurred in a cell-free test system. Rat liver cell-free cholesterol biosynthesis was much less sensitive to the drugs. The biochemical action of tolnaftate and tolciclate is thus similar to that of the allylamine antimycotics naftifine and terbinafine.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carneri I., Monti G., Bianchi A., Castellino S., Meinardi G., Mandelli V. Tolciclate against dermatophytes. Arzneimittelforschung. 1976;26(5):769–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Nozawa Y. Effects of antifungal agents on ergosterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans and Trichophyton mentagrophytes: differential inhibitory sites of naphthiomate and miconazole. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Nov;85(5):434–437. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12277141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petranyi G., Ryder N. S., Stütz A. Allylamine derivatives: new class of synthetic antifungal agents inhibiting fungal squalene epoxidase. Science. 1984 Jun 15;224(4654):1239–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.6547247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder N. S., Dupont M. C. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase by allylamine antimycotic compounds. A comparative study of the fungal and mammalian enzymes. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):765–770. doi: 10.1042/bj2300765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder N. S., Dupont M. C. Properties of a particulate squalene epoxidase from Candida albicans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 26;794(3):466–471. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder N. S. Effect of allylamine antimycotic agents on fungal sterol biosynthesis measured by sterol side-chain methylation. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jul;131(7):1595–1602. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-7-1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder N. S., Seidl G., Troke P. F. Effect of the antimycotic drug naftifine on growth of and sterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):483–487. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder N. S. Specific inhibition of fungal sterol biosynthesis by SF 86-327, a new allylamine antimycotic agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):252–256. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stütz A., Petranyi G. Synthesis and antifungal activity of (E)-N-(6,6-dimethyl-2-hepten-4-ynyl)-N-methyl-1-naphtha lenemethanamine (SF 86-327) and related allylamine derivatives with enhanced oral activity. J Med Chem. 1984 Dec;27(12):1539–1543. doi: 10.1021/jm00378a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Cools W., Marichal P., Lauwers W. Hypothesis on the molecular basis of the antifungal activity of N-substituted imidazoles and triazoles. Biochem Soc Trans. 1983 Dec;11(6):665–667. doi: 10.1042/bst0110665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildfeuer A., Rozman T. Zur antimykotischen Wirkung von Tolciclat. Mykosen. 1984 Mar;27(3):142–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bossche H., Willemsens G., Cools W., Lauwers W. F., Le Jeune L. Biochemical effects of miconazole on fungi. II. Inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis in Candida albicans. Chem Biol Interact. 1978 Apr;21(1):59–78. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(78)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



