Abstract
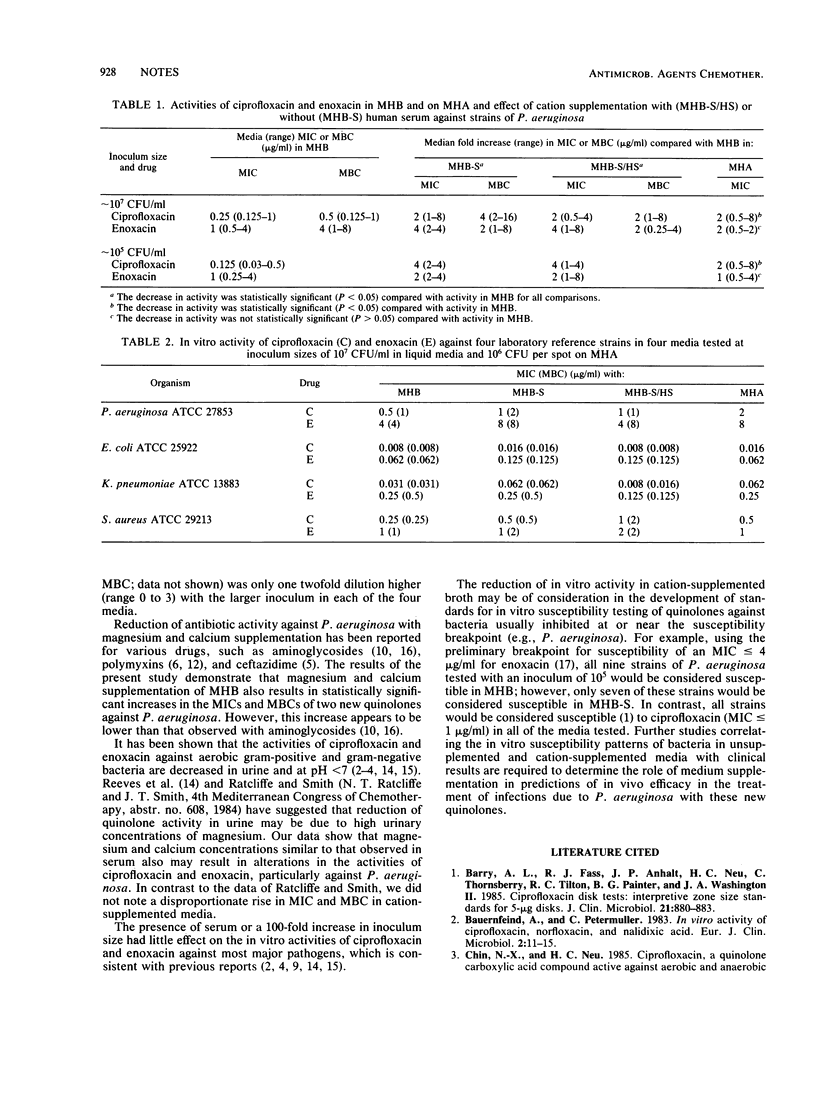
Ciprofloxacin and enoxacin were two- to fourfold less active against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in calcium- and magnesium-supplemented broth compared with unsupplemented broth regardless of inoculum size, presence of serum, or use of inhibitory or bactericidal endpoints (P less than 0.01). The effect of cation supplementation was less pronounced and less consistent for Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Staphylococcus aureus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Fass R. J., Anhalt J. P., Neu H. C., Thornsberry C., Tilton R. C., Painter B. G., Washington J. A., 2nd Ciprofloxacin disk susceptibility tests: interpretive zone size standards for 5-microgram disks. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):880–883. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.880-883.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of enoxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid, compared with those of norfloxacin, new beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, and trimethoprim. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):754–763. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. D., Iannetta A., Wedgwood R. J. Activity of colistin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: inhibition by calcium. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):610–612. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J. The quinolones. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Mar;102(3):400–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-3-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuenberger P., Vrantchev S. Cefaclor versus amoxicillin in the treatment of bacterial pneumonia: a comparative double-blind study. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Feb;2(1):11–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02019916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., O'Brien T. F., Wacker W. E., Yulug N. F. Effect of salt concentration on the apparent in-vitro susceptibility of Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacilli to gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S59–S64. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON B. A. Reversal of the antibacterial activity of polymyxin by divalent cations. Nature. 1953 Jul 25;172(4369):160–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. D., Steigbigel R. T., Davis H. T., Chapman S. W. Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):699–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Bywater M. J., Holt H. A. The activity of enoxacin against clinical bacterial isolates in comparison with that of five other agents, and factors affecting that activity. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Sep;14 (Suppl 100):7–17. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.suppl_c.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Bywater M. J., Holt H. A., White L. O. In-vitro studies with ciprofloxacin, a new 4-quinolone compound. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Apr;13(4):333–346. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer L. G., Stratton C. W., Reller L. B. Minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations of 44 antimicrobial agents against three standard control strains in broth with and without human serum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1050–1055. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudrik J. T., Cavalieri S. J., Britt E. M. Proposed quality control and interpretive criteria for disk diffusion susceptibility testing with enoxacin. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):332–334. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.332-334.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahn S. A., Good J. T., Jr, Reller L. B. Cephradine concentrations in serum, pleural fluid, pleura, and lung of normal rabbits. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):345–346. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton C. W., Reller L. B. Serum dilution test for bactericidal activity. I. Selection of a physiologic diluent. J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136(2):187–195. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



