Abstract
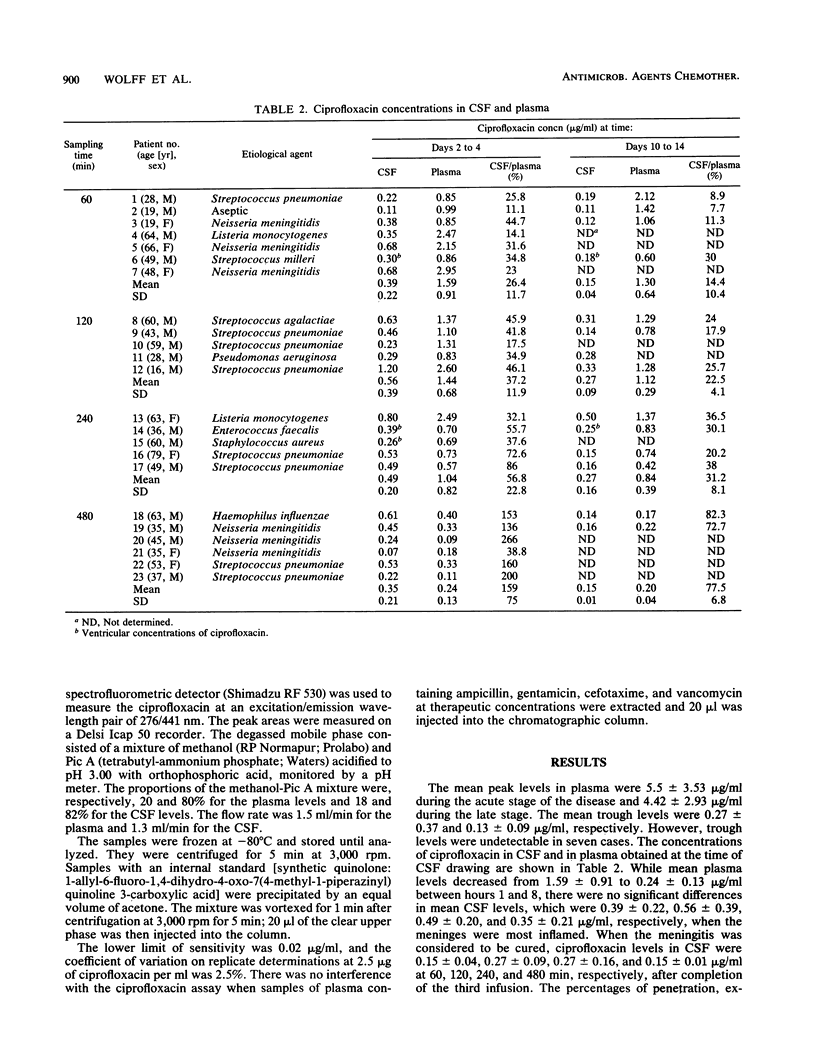
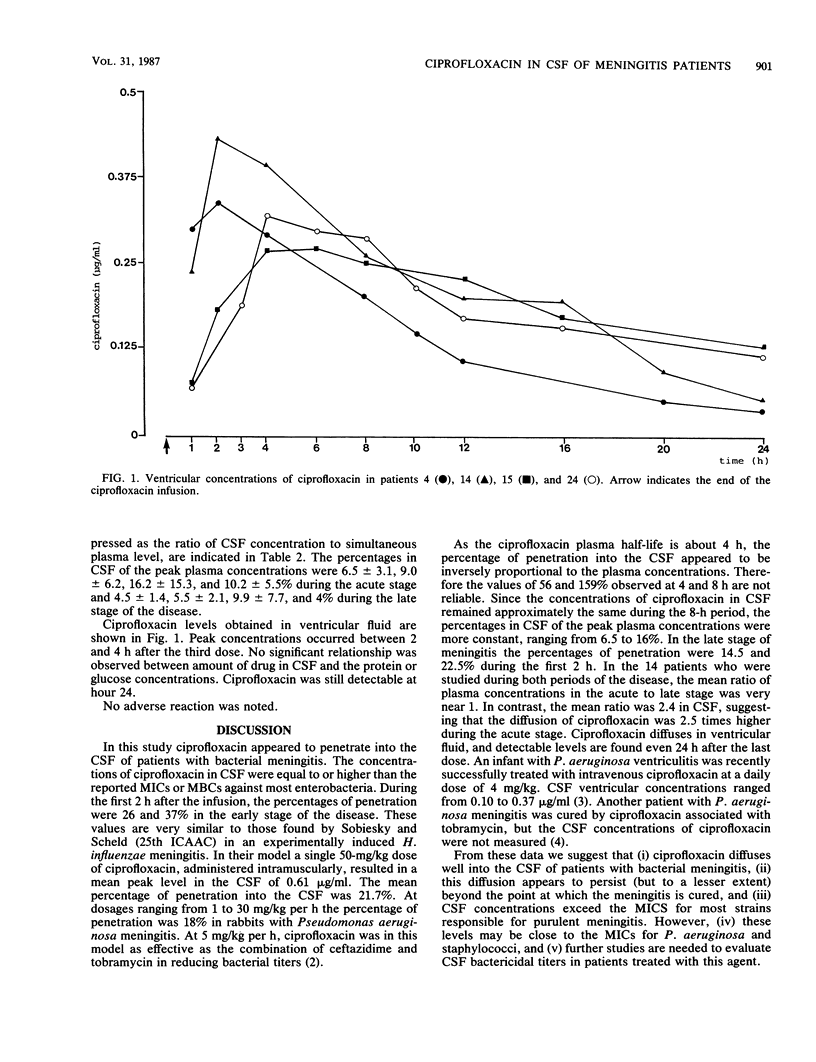
We evaluated the diffusion of ciprofloxacin into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in 23 patients with bacterial meningitis or ventriculitis undergoing treatment with other antibiotics. Three successive ciprofloxacin doses of 200 mg were administered intravenously at 12-h intervals, first between days 2 and 4 and again between days 10 and 20 after the admission. Concentrations of ciprofloxacin in plasma and CSF obtained at 60, 120, 240, and 480 min after the third infusion were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. In addition, serial samples were obtained from ventricular fluid in four patients. The concentrations of ciprofloxacin in CSF ranged from 0.35 to 0.56 micrograms/ml. These concentrations were equal to or higher than the MICs for most of the enterobacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F., Stella F., Shibl A. M., Sande M. A. Ciprofloxacin in experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa meningitis in rabbits. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):65–69. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs D., Slack M. P., Wilkinson A. R., Westwood A. W. Successful treatment of Pseudomonas ventriculitis with ciprofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Apr;17(4):535–538. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar M. R., Bransby-Zachary M. A., Tompkins D. S., Hawkey P. M., Myles Gibson R. Ciprofloxacin for Pseudomonas aeruginosa meningitis. Lancet. 1986 Jun 7;1(8493):1325–1325. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



