Abstract
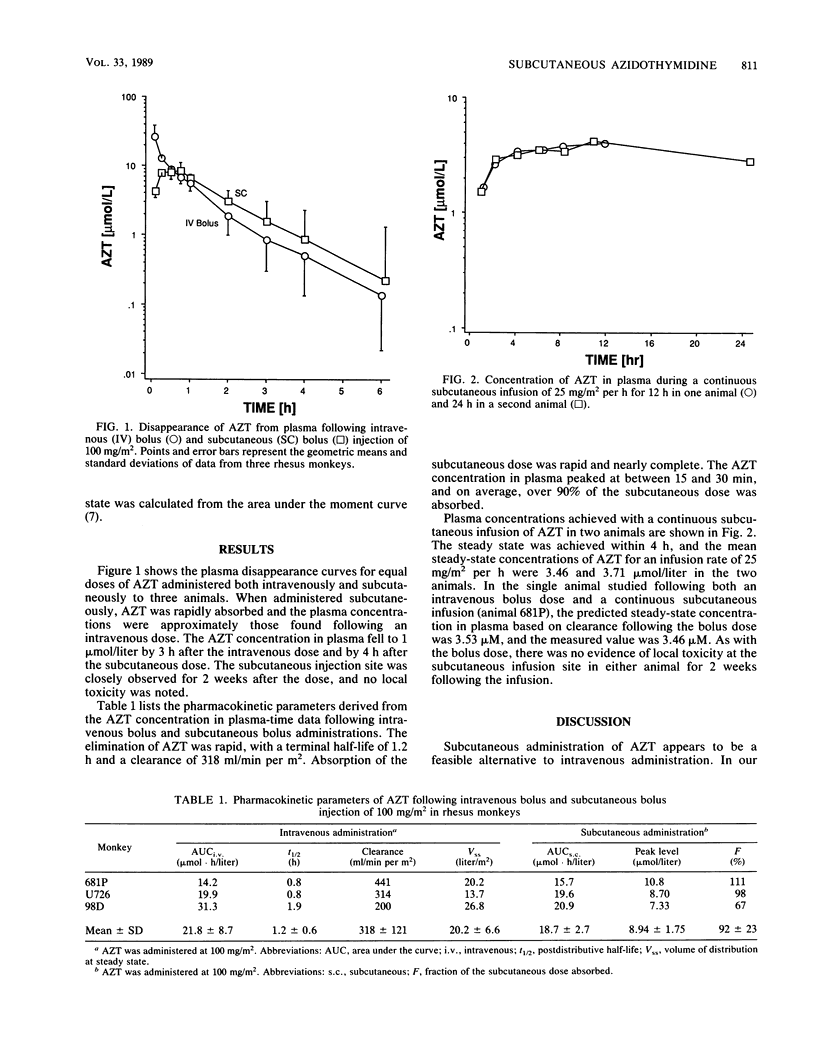
The pharmacokinetics of subcutaneous bolus and continuous infusion azidothymidine (AZT) was studied in rhesus monkeys. Three animals received 100 mg/m2 as a bolus injection both intravenously and subcutaneously, with the order of administration randomly determined. Two animals received a continuous subcutaneous infusion of 25 mg/m2 per h for 12 or 24 h. AZT was measured in plasma by a reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatographic assay. Following intravenous bolus administration, AZT elimination was rapid, with a mean half-life of 1.2 h and a mean clearance of 318 ml/min per m2 (range, 200 to 441 ml/min per m2). The bolus subcutaneous dose was rapidly (time to peak concentration, 15 to 30 min) and nearly completely (fraction absorbed, 92%) absorbed without evidence of local tissue toxicity. With continuous subcutaneous infusion of AZT, the steady state was attained within 4 h and steady-state concentrations in plasma in the two animals exceeded 3.0 mumol/liter. No local tissue toxicity was observed at the infusion site. The subcutaneous route may be a practical alternative to intravenous administration of AZT and deserves further clinical study.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balis F. M., Mirro J., Jr, Reaman G. H., Evans W. E., McCully C., Doherty K. M., Murphy R. F., Jeffries S., Poplack D. G. Pharmacokinetics of subcutaneous methotrexate. J Clin Oncol. 1988 Dec;6(12):1882–1886. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1988.6.12.1882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balis F. M., Pizzo P. A., Murphy R. F., Eddy J., Jarosinski P. F., Falloon J., Broder S., Poplack D. G. The pharmacokinetics of zidovudine administered by continuous infusion in children. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Feb 15;110(4):279–285. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-4-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruera E., Brenneis C., Michaud M., Bacovsky R., Chadwick S., Emeno A., MacDonald N. Use of the subcutaneous route for the administration of narcotics in patients with cancer pain. Cancer. 1988 Jul 15;62(2):407–411. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880715)62:2<407::aid-cncr2820620227>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Richman D. D., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Schooley R. T. The efficacy of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):185–191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M. A., Green N., Flynn D. M., Hussein S., Hoffbrand A. V. Subcutaneous infusion and intramuscular injection of desferrioxamine in patients with transfusional iron overload. Lancet. 1976 Dec 11;2(7998):1278–1280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klecker R. W., Jr, Collins J. M., Yarchoan R., Thomas R., Jenkins J. F., Broder S., Myers C. E. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine: a novel pyrimidine analog with potential application for the treatment of patients with AIDS and related diseases. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1987 Apr;41(4):407–412. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1987.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Weinhold K. J., Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Lehrman S. N., Gallo R. C., Bolognesi D., Barry D. W., Broder S. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine (BW A509U): an antiviral agent that inhibits the infectivity and cytopathic effect of human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7096–7100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrier D., Mayersohn M. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution for any mode of administration. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Mar;71(3):372–373. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo P. A., Eddy J., Falloon J., Balis F. M., Murphy R. F., Moss H., Wolters P., Brouwers P., Jarosinski P., Rubin M. Effect of continuous intravenous infusion of zidovudine (AZT) in children with symptomatic HIV infection. N Engl J Med. 1988 Oct 6;319(14):889–896. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810063191401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



