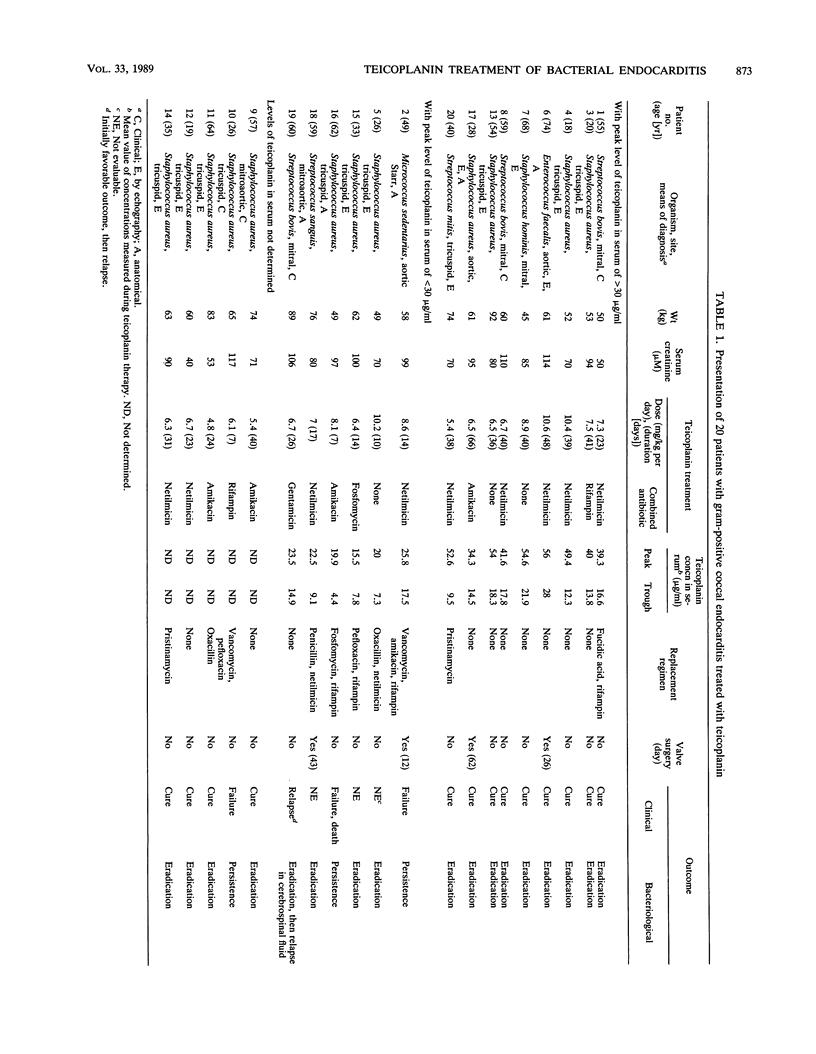
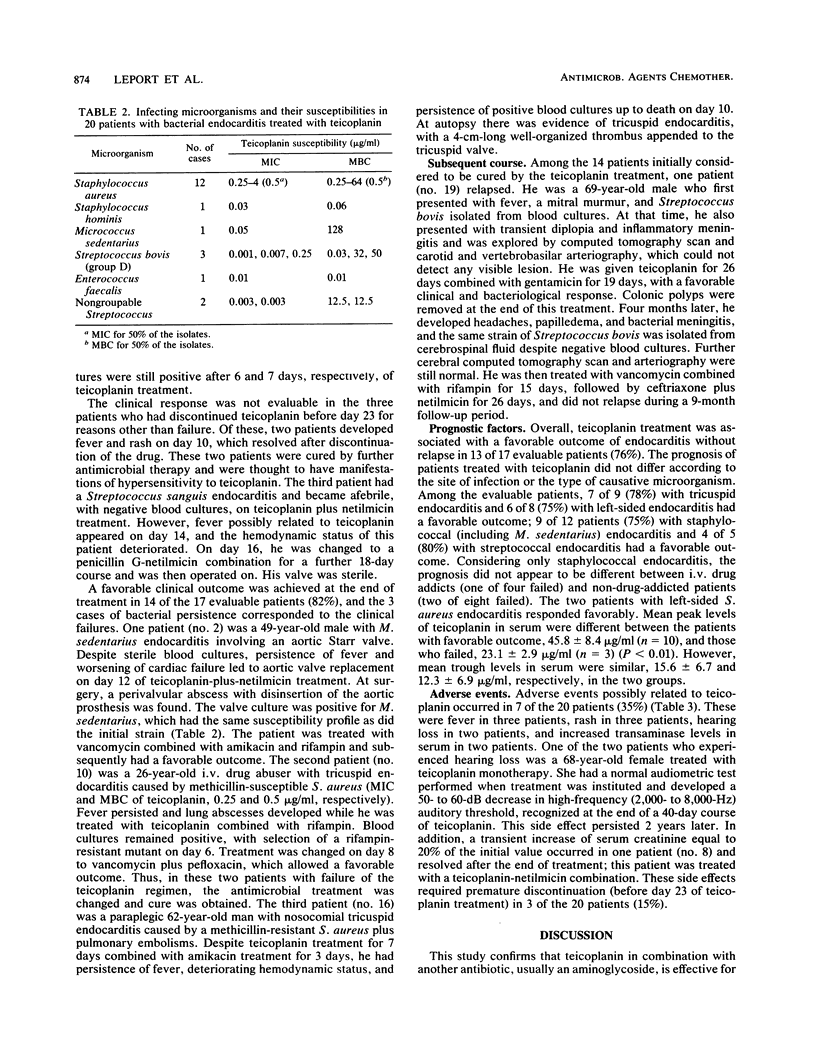
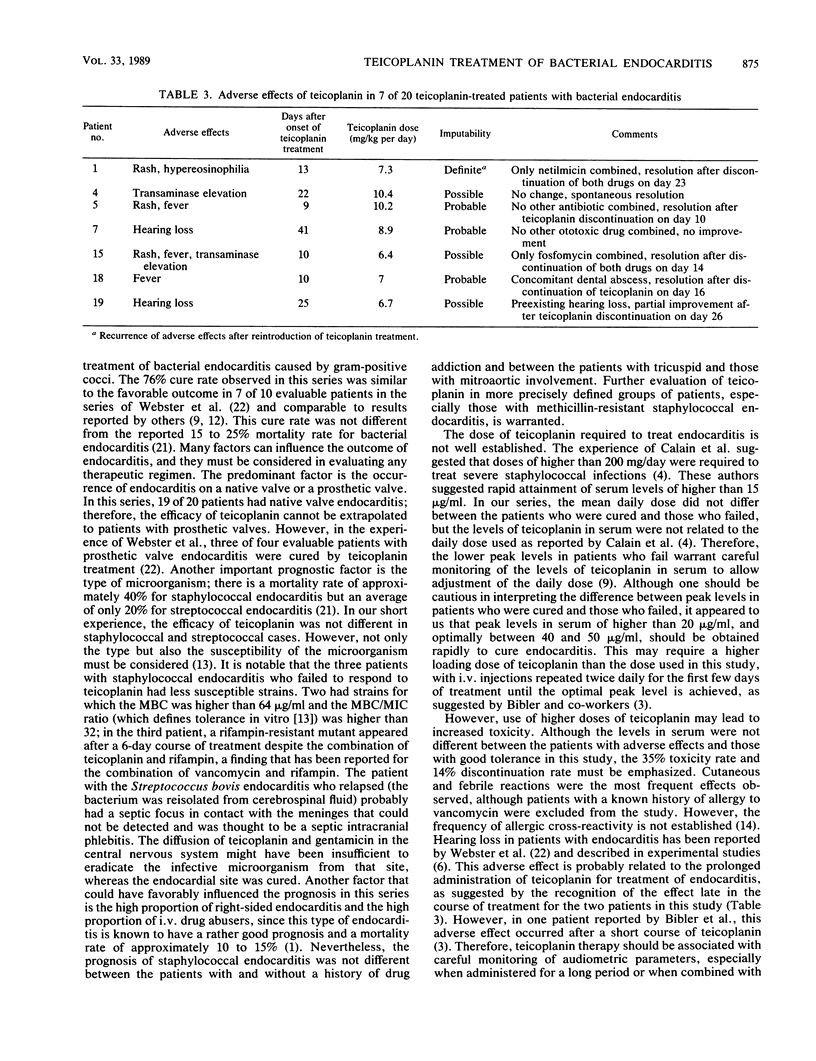
Abstract
Teicoplanin, a new glycopeptide antibiotic similar to vancomycin, was evaluated for the treatment of bacterial endocarditis in an open multicenter study from May 1985 to August 1987. A total of 20 patients with positive blood culture endocarditis received teicoplanin once daily as a mean intravenous injection of 7.3 mg/kg of body weight (range, 4.8 to 10.6 mg/kg); in 17 patients, teicoplanin was combined with another antibiotic, usually an aminoglycoside. The mean duration of therapy was 28 days (range, 7 to 66 days). The diagnosis of endocarditis was confirmed by echocardiography or anatomical findings in 15 patients and established on the basis of clinical manifestations plus positive blood cultures in 5 patients. The tricuspid valve was involved in 11 of the 20 patients. Isolates from blood were 12 Staphylococcus aureus, 1 Staphylococcus hominis, 1 Micrococcus sedentarius, 1 Enterococcus faecalis, 3 Streptococcus bovis, and 2 nongroupable Streptococcus sp. At the end of therapy, bacterial eradication was achieved in 17 of 20 patients (85%), and a favorable clinical outcome had occurred in 14 of 17 evaluable patients (82%). Of these 14 patients, one relapsed 4 months after the end of treatment. Thus, teicoplanin was effective in 13 of 17 patients (76%). Mean peak levels of teicoplanin in serum were lower, 23.1 +/- 2.9 micrograms/ml, in patients who failed than in those who were cured (45.8 +/- 8.4 micrograms/ml). Side effects occurred in 7 of 20 patients (35%), and required premature discontinuation of teicoplanin in 3 patients. These side effects were fever in three patients, rash in three patients, hearing loss in two patients, and increased serum transaminase levels in two patients. This study demonstrates the efficacy of teicoplanin in the treatment of endocarditis and the need for achieving peak levels in serum close to 40 micrograms/ml. Teicoplanin should now be further evaluated in endocarditis caused by gram-positive cocci means of controlled comparative study with standard therapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams B., Sklaver A., Hoffman T., Greenman R. Single or combination therapy of staphylococcal endocarditis in intravenous drug abusers. Ann Intern Med. 1979 May;90(5):789–791. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibler M. R., Frame P. T., Hagler D. N., Bode R. B., Staneck J. L., Thamlikitkul V., Harris J. E., Haregewoin A., Bullock W. E., Jr Clinical evaluation of efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety of teicoplanin for serious gram-positive infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):207–212. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calain P., Krause K. H., Vaudaux P., Auckenthaler R., Lew D., Waldvogel F., Hirschel B. Early termination of a prospective, randomized trial comparing teicoplanin and flucloxacillin for treating severe staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;155(2):187–191. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavenaghi L., Corti A., Cassani G. Comparison of the solid phase enzyme receptor assay (SPERA) and the microbiological assay for teicoplanin. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Mar;7 (Suppl A):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazals Y., Erre J. P., Aurousseau C., Aran J. M. Ototoxicity of teicoplanin in the guinea pig. Br J Audiol. 1987 Feb;21(1):27–30. doi: 10.3109/03005368709077771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Sande M. A. Teicoplanin versus nafcillin and vancomycin in the treatment of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):61–64. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber B. F., Moellering R. C., Jr Retrospective study of the toxicity of preparations of vancomycin from 1974 to 1981. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):138–141. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Lagast H., Van der Auwera P., Thys J. P., Crokaert F., Yourassowsky E., Meunier-Carpentier F., Klastersky J., Kains J. P., Serruys-Schoutens E. Clinical evaluation of teicoplanin for therapy of severe infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jehl F., Monteil H., Tarral A. HPLC quantitation of the six main components of teicoplanin in biological fluids. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21 (Suppl A):53–59. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_a.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. In vitro activity of teichomycin compared with those of other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):425–428. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauluzzi S., Del Favero A., Menichetti F., Baratta E., Moretti V. M., Di Filippo P., Pasticci M. B., Guerciolini R., Patoia L., Frongillo R. F. Treatment of infections by staphylococci and other gram-positive bacteria with teicoplanin: an open study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Sep;20(3):431–438. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.3.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajashekaraiah K. R., Rice T., Rao V. S., Marsh D., Ramakrishna B., Kallick C. A. Clinical significance of tolerant strains of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Dec;93(6):796–801. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-6-796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlemmer B., Falkman H., Boudjadja A., Jacob L., Le Gall J. R. Teicoplanin for patients allergic to vancomycin. N Engl J Med. 1988 Apr 28;318(17):1127–1128. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198804283181711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somma S., Gastaldo L., Corti A. Teicoplanin, a new antibiotic from Actinoplanes teichomyceticus nov. sp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):917–923. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullam P. M., Täuber M. G., Hackbarth C. J., Sande M. A. Therapeutic efficacy of teicoplanin in experimental enterococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):135–136. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Miller H. Comparative in vitro activities of teichomycin and vancomycin alone and in combination with rifampin and aminoglycosides against staphylococci and enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):411–412. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Washburn D. Teicoplanin and rifampicin singly and in combination in the treatment of experimental Staphylococcus epidermidis endocarditis in the rabbit model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Aug;20(2):233–237. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Tjandramaga B., Hendrickx B., Van Hecken A., Van Melle P., Verbesselt R., Verhaegen J., De Schepper P. J. In vitro activity and human pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):881–886. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Reyn C. F., Levy B. S., Arbeit R. D., Friedland G., Crumpacker C. S. Infective endocarditis: an analysis based on strict case definitions. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Apr;94(4 Pt 1):505–518. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-4-505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster A., Wilson A. P., Williams A. H., Treasure T., Grüneberg R. N. The use of a new glycopeptide antibiotic, teicoplanin, in the treatment of bacterial endocarditis. Postgrad Med J. 1987 Aug;63(742):621–624. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.63.742.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. H., Grüneberg R. N. Teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Nov;14(5):441–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



