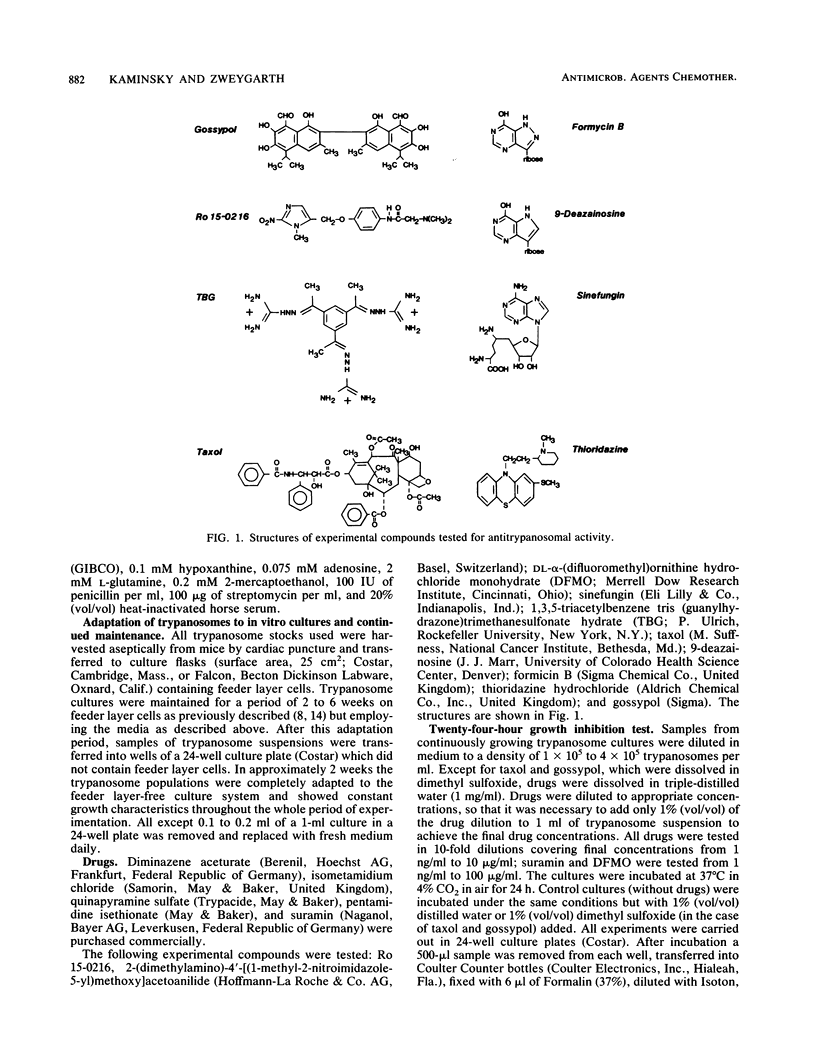
Abstract
A drug-susceptible Trypanosoma brucei brucei stock, a multidrug-resistant T. b. brucei stock, and a T. b. evansi stock resistant to two commercial trypanocides were adapted to a feeder layer-free culture system. Bloodstream forms were grown continuously in a liquid medium at 37 degrees C in 4% CO2 in air. Samples of trypanosome populations in the logarithmic growth phase were incubated with various concentrations of commercial and experimental compounds. Growth inhibition was monitored after a 24-h incubation and quantified by comparing the number of generations between control and drug-treated cultures. Some of the experimental compounds [taxol, formicin B, thioridazine, Ro 15-0216, and DL-alpha-(difluoromethyl)ornithine hydrochloride monohydrate] showed activity against both drug-susceptible and drug-resistant trypanosomes. Other compounds [sinefungin, 1,3,5-triacetylbenzene tris(guanylhydrazone)trimethanesulfonate hydrate, and 9-deazainosine] which inhibited the growth of drug-susceptible trypanosomes showed little or no effect upon drug-resistant parasites. Gossypol, however, had no antitrypanosomal effect on either trypanosome stock. The results obtained in this study correlate with observations obtained from drug screening in mice. The main advantages of the described in vitro screening assay are as follows: (i) lower amounts of drugs are required, (ii) results are obtained more rapidly, (iii) animals are not necessary, and (iv) the method is less labor intensive. These advantages result in an economical and rapid assay for primary drug screening.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacchi C. J., Nathan H. C., Hutner S. H., McCann P. P., Sjoerdsma A. Polyamine metabolism: a potential therapeutic target in trypanosomes. Science. 1980 Oct 17;210(4467):332–334. doi: 10.1126/science.6775372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz T., Baltz D., Giroud C., Crockett J. Cultivation in a semi-defined medium of animal infective forms of Trypanosoma brucei, T. equiperdum, T. evansi, T. rhodesiense and T. gambiense. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1273–1277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03772.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum S. G., Wittner M., Nadler J. P., Horwitz S. B., Dennis J. E., Schiff P. B., Tanowitz H. B. Taxol, a microtubule stabilizing agent, blocks the replication of Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4571–4575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitonti A. J., Dumont J. A., McCann P. P. Characterization of Trypanosoma brucei brucei S-adenosyl-L-methionine decarboxylase and its inhibition by Berenil, pentamidine and methylglyoxal bis(guanylhydrazone). Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):685–689. doi: 10.1042/bj2370685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt R. T., Eiden L. E., Wu B., Rutledge C. O. Sinefungin, a potent inhibitor or S-adenosylmethionine: protein O-methyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):919–924. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91866-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowy N. K., Hirumi H., Waithaka H. K., Mkoji G. An assay for screening drugs against animal-infective bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei brucei in vitro. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1985;11(3):155–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun R., Jenni L., Schönenberger M., Schell K. F. In vitro cultivation of bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma brucei, T. rhodesiense, and T. gambiense. J Protozool. 1981 Nov;28(4):470–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1981.tb05322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Sten M., Nordenskjöld M., Lambert B., Matlin S. A., Zhou R. H. The effect of gossypol on the frequency of DNA-strand breaks in human leukocytes in vitro. Mutat Res. 1986 Feb;164(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0165-1161(86)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft S. L., Walker J. J., Gutteridge W. E. Screening of drugs for rapid activity against Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes in vitro. Trop Med Parasitol. 1988 Jun;39(2):145–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dube D. K., Mpimbaza G., Allison A. C., Lederer E., Rovis L. Antitrypanosomal activity of sinefungin. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jan;32(1):31–33. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eid J. E., Ueno H., Wang C. C., Donelson J. E. Gossypol-induced death of African trypanosomes. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Jun;66(1):140–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish W. R., Marr J. J., Berens R. L., Looker D. L., Nelson D. J., LaFon S. W., Balber A. E. Inosine analogs as chemotherapeutic agents for African trypanosomes: metabolism in trypanosomes and efficacy in tissue culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):33–36. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirumi H., Doyle J. J., Hirumi K. African trypanosomes: cultivation of animal-infective Trypanosoma brucei in vitro. Science. 1977 May 27;196(4293):992–994. doi: 10.1126/science.558652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminsky R., Zweygarth E. Effect of in vitro cultivation on the stability of resistance of Trypanosoma brucei brucei to diminazene, isometamidium, quinapyramine, and Mel B. J Parasitol. 1989 Feb;75(1):42–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinabo L. D., Bogan J. A. Solid-phase extraction and ion-pair reversed-phase HPLC of isometamidium in bovine serum and tissues. Acta Trop. 1988 Jun;45(2):165–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach T. M., Roberts C. J. Present status of chemotherapy and chemoprophylaxis of animal trypanosomiasis in the Eastern hemisphere. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;13(1):91–147. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. N., Turner M. J. Analysis of antigenic types appearing in first relapse populations of clones of Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitology. 1981 Feb;82(1):63–80. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000041871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Othman M. A., Abou-Donia M. B. Pharmacokinetic profile of (+/-)-gossypol in male Sprague-Dawley rats following single intravenous and oral and subchronic oral administration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1988 May;188(1):17–22. doi: 10.3181/00379727-188-42700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice H., Ruben L., Gould S., Njogu A. R., Patton C. L. Phenothiazines in murine African trypanosomiasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1987;81(6):932–932. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(87)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röttcher D., Schillinger D. Multiple drug resistance in Trypanosoma vivax in the Tana River District of Kenya. Vet Rec. 1985 Nov 23;117(21):557–558. doi: 10.1136/vr.117.21.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seebeck T., Gehr P. Trypanocidal action of neuroleptic phenothiazines in Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Nov;9(3):197–208. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrenato L., Shrestha S., Dixit K. A., Luzzatto L., Modiano G., Morpurgo G., Arese P. Decreased malaria morbidity in the Tharu people compared to sympatric populations in Nepal. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1988 Feb;82(1):1–11. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1988.11812202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turrens J. F. The potential of antispermatogenic drugs against trypanosomatids. Parasitol Today. 1986 Dec;2(12):351–352. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(86)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweygarth E., Röttcher D. Efficacy of experimental trypanocidal compounds against a multiple drug-resistant Trypanosoma brucei brucei stock in mice. Parasitol Res. 1989;75(3):178–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00931271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweygarth E., Röttcher D. Trypanocidal activity of a 5-substituted 2-nitroimidazole compound (Ro 15-0216) in mice. Trop Med Parasitol. 1987 Sep;38(3):171–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweygarth E., Schillinger D., Kaufmann W., Röttcher D. Evaluation of sinefungin for the treatment of Trypanosoma (Nannomonas) congolense infections in goats. Trop Med Parasitol. 1986 Sep;37(3):255–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


