Abstract
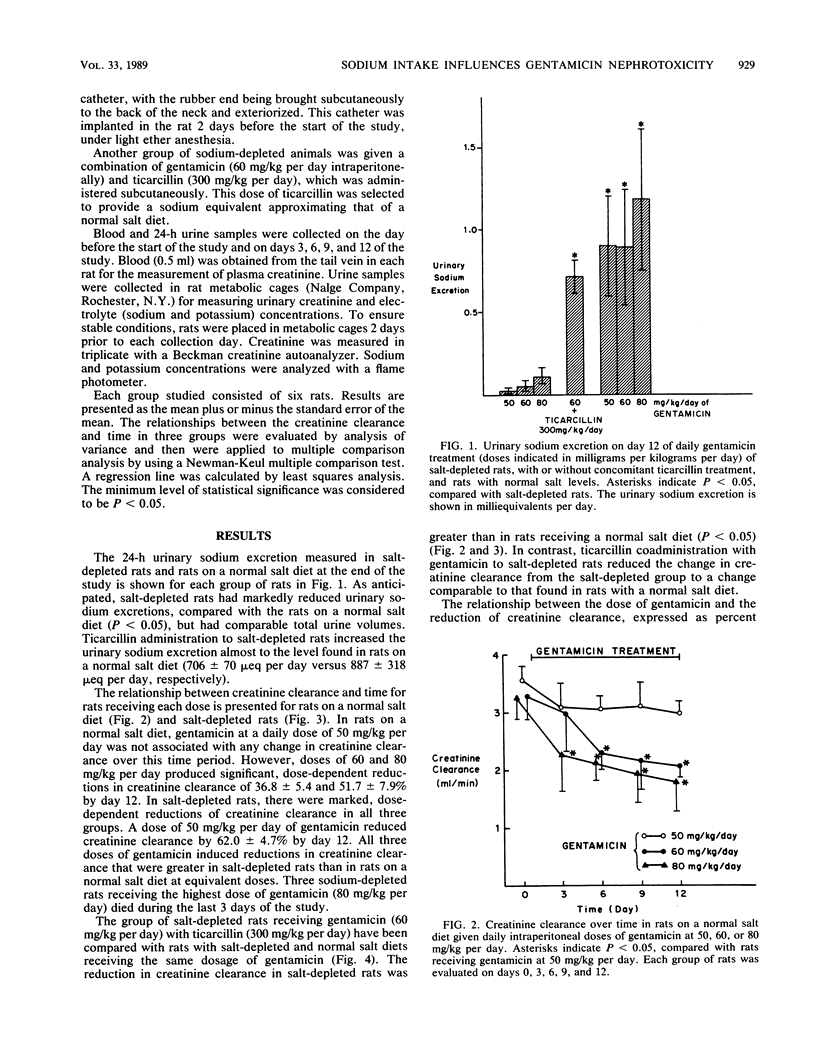
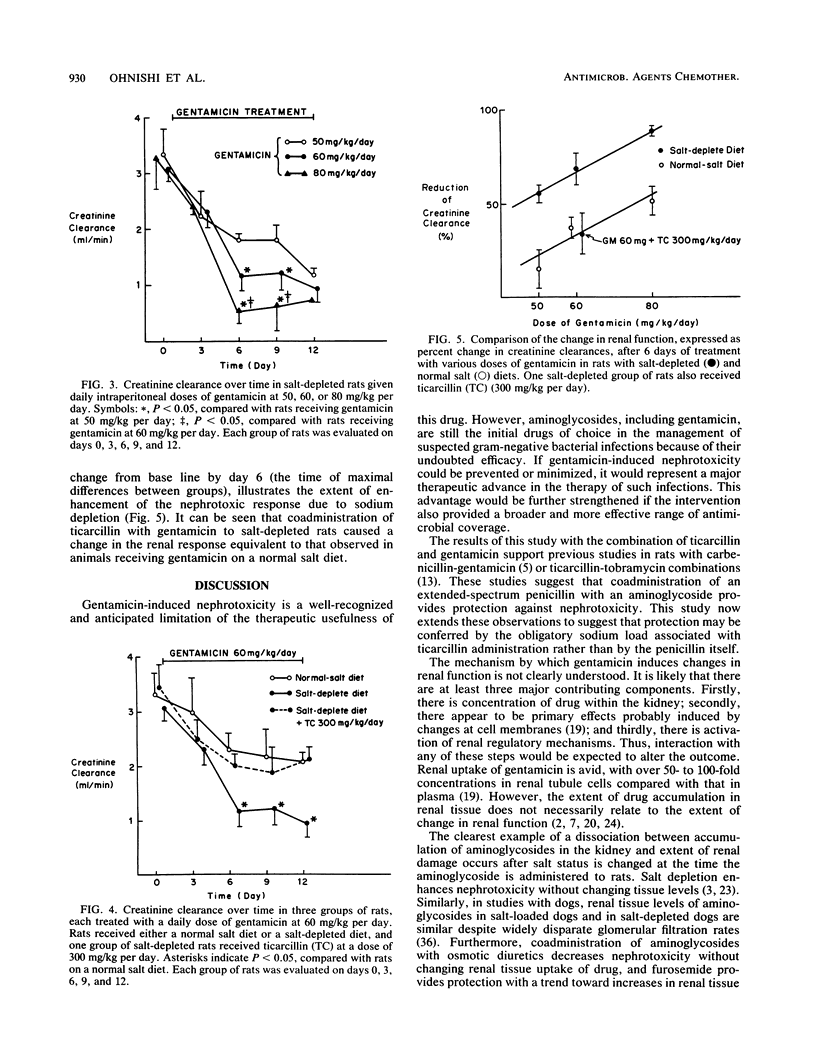
Coadministration of sodium ticarcillin with an aminoglycoside is known to reduce the nephrotoxicity of the aminoglycoside. However, it is not known whether the penicillin or the obligatory sodium load confers protection. To investigate this, gentamicin has been administered intraperitoneally in doses of 50, 60, or 80 mg/kg per day for 12 days in groups of rats receiving either a normal or a low sodium intake. Alterations in creatinine clearance have been measured. Salt depletion resulted in an enhanced nephrotoxic response with a shift in the dose-response curve to the left. Administration of sodium ticarcillin to rats with a salt-depleted intake at a dose sufficient to replace sodium intake conferred an equal degree of protection to rats with a normal salt intake. We report that the obligatory salt supplement with ticarcillin is sufficient to account for the renal sparing effect of the combination treatment without having to infer a direct chemical interaction of penicillin with the aminoglycoside.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel G. B., Neu H. C. The nephrotoxicity of antimicrobial agents (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 31;296(13):722–728. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703312961305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronoff G. R., Pottratz S. T., Brier M. E., Walker N. E., Fineberg N. S., Glant M. D., Luft F. C. Aminoglycoside accumulation kinetics in rat renal parenchyma. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):74–78. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Hartnett M. N., Gilbert D., Houghton D., Porter G. A. Effect of sodium intake on gentamicin nephrotoxicity in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Apr;151(4):736–738. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. C., Duggan D. O., Schroeder E. T. Inactivation of amikacin and gentamicin by carbenicillin in patients with end-stage renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):376–379. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch R., Luft F. C., Rankin L. I., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N., Maxwell D. R. Protection from gentamicin nephrotoxicity by cephalothin and carbenicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jan;15(1):46–49. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brion N., Barge J., Godefroy I., Dromer F., Dubois C., Contrepois A., Carbon C. Gentamicin, netilmicin, dibekacin, and amikacin nephrotoxicity and its relationship to tubular reabsorption in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):168–172. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu P. J., Long J. F. Effects of hydration on gentamicin excretion and renal accumulation in furosemide-treated rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):214–217. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M. S., Quintiliani R., Nightingale C. H. In vivo inactivation of tobramycin by ticarcillin. A case report. JAMA. 1982 Feb 5;247(5):658–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., McDonald F. D., Flamenbaum W., Dammin G. J., Oken D. E. Maintenance of renal function in salt loaded rats despite severe tubular necrosis induced by HgCl 2 . Nephron. 1971;8(3):205–220. doi: 10.1159/000179922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert S. C., Jorgensen J. H., Drutz D. J., Clementi W. A. Comparative assessment of in vitro inactivation of gentamicin in the presence of carbenicillin by three different gentamicin assay methods. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):701–705. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.701-705.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. J., Schentag J. J. In vitro interactions between beta-lactam antibiotics and tobramycin. Clin Chem. 1981 Feb;27(2):341–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English J., Gilbert D. N., Kohlhepp S., Kohnen P. W., Mayor G., Houghton D. C., Bennett W. M. Attenuation of experimental tobramycin nephrotoxicity by ticarcillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jun;27(6):897–902. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervin F. R., Bullock W. E., Jr, Nuttall C. E. Inactivation of gentamicin by penicillins in patients with renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jun;9(6):1004–1011. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.6.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falco F. G., Smith H. M., Arcieri G. M. Nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides and gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1969 Apr-May;119(4):406–409. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.4-5.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerkens J. F., Branch R. A. The influence of sodium status and furosemide on canine acute amphotericin B nephrotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Aug;214(2):306–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T., Watanabe Y., Kumano K., Kitayama R., Yasuda T., Saikawa I., Katahira J., Kumada T., Shimizu K. Protective effect of piperacillin against nephrotoxicity of cephaloridine and gentamicin in animals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):912–918. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky J. J., Lietman P. S. Aminoglycoside inhibition of a renal phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Feb;220(2):287–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky J. J., Lietman P. S. Neomycin inhibition of adenosine triphosphatase: evidence for a neomycin-phospholipid interaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Oct;18(4):532–535. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft F. C., Bloch R., Sloan R. S., Yum M. N., Costello R., Maxwell D. R. Comparative nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics in rats. J Infect Dis. 1978 Oct;138(4):541–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.4.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. A., Weinstock L. B., Gump D. W., Hacker M. P., Yates J. W. Effect of osmotic diuresis on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Arch Toxicol. 1980 Sep;45(3):213–221. doi: 10.1007/BF02419001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., Gearhart P. Effect of time and concentration upon interaction between gentamicin, tobramycin, Netilmicin, or amikacin and carbenicillin or ticarcillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Apr;15(4):592–596. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.4.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., Rutherford I. Effect of concentration and time upon inactivation of tobramycin, gentamicin, netilmicin and amikacin by azlocillin, carbenicillin, mecillinam, mezlocillin and piperacillin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 May;217(2):345–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riff L. J., Thomason J. L. Comparative aminoglycoside inactivation by beta-lactam antibiotics. Effects of a cephalosporin and six penicillins on five aminoglycosides. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Jul;35(7):850–857. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibeci A., Schacht J. Action of neomycin on the metabolism of polyphosphoinositides in the guinea pig kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Oct 1;26(19):1769–1774. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel G., McDonald F. D., Oken D. E. Micropuncture studies of the basis for protection of renin depleted rats from glycerol induced acute renal failure. Nephron. 1970;7(1):67–79. doi: 10.1159/000179809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolins J. P., Raij L. Adverse effect of amphotericin B administration on renal hemodynamics in the rat. Neurohumoral mechanisms and influence of calcium channel blockade. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):594–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. C., Schimpff S. C., Wiernik P. H. Antibiotic combination-associated nephrotoxicity in granulocytopenic patients with cancer. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Dec;141(13):1789–1793. doi: 10.1001/archinte.141.13.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. D., Shah S. V. Evidence suggesting a role for hydroxyl radical in gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):334–341. doi: 10.1172/JCI113325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whelton A., Walker W. G. Editorial: Intrarenal antibiotic distribution in health and disease. Kidney Int. 1974 Sep;6(3):131–137. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



