Abstract
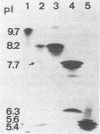
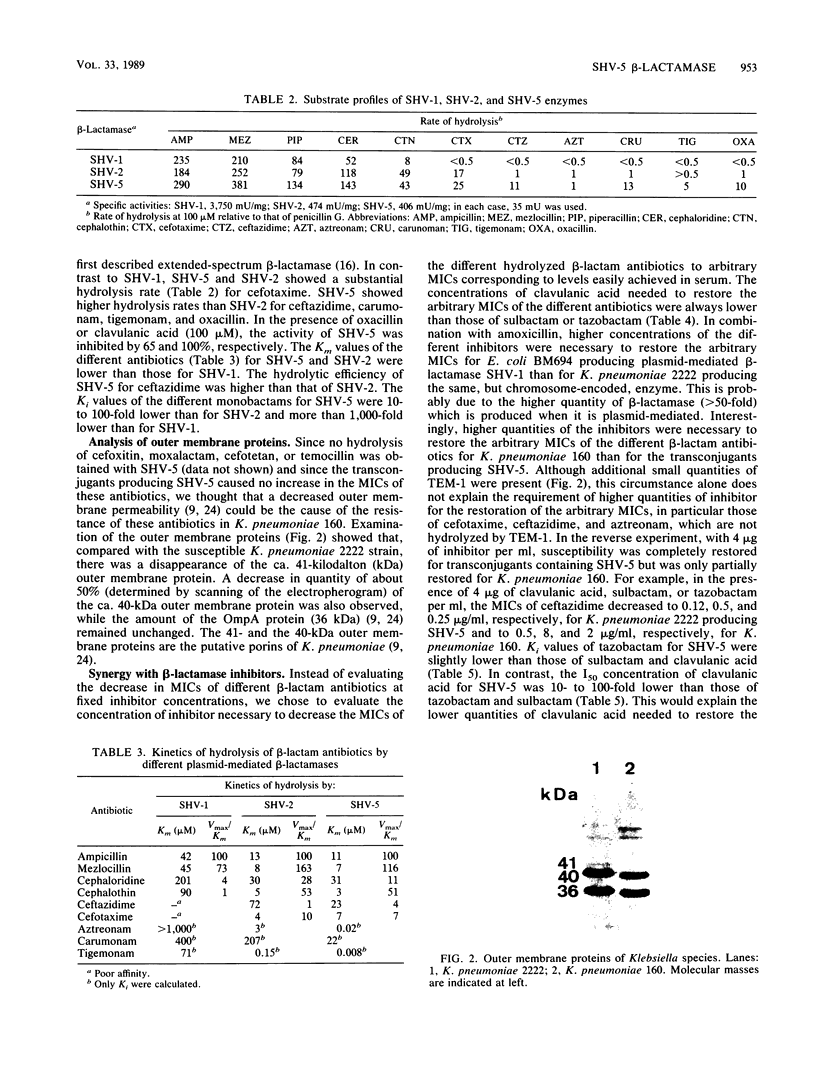
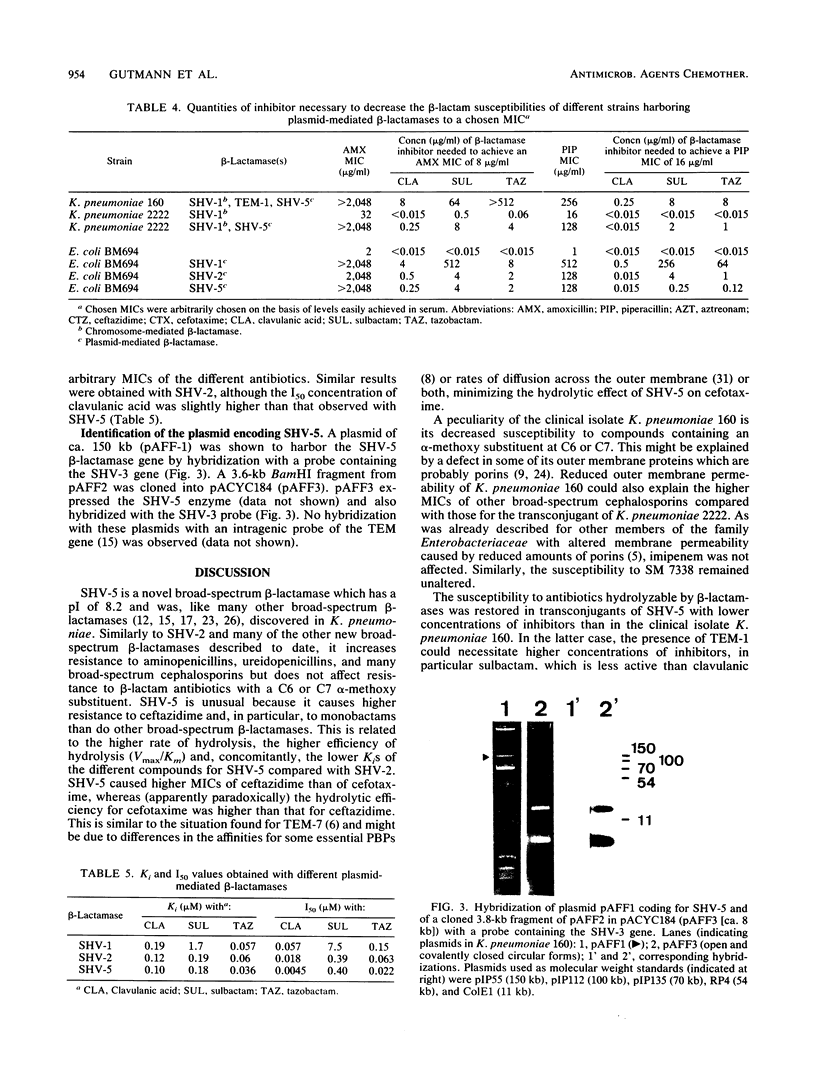
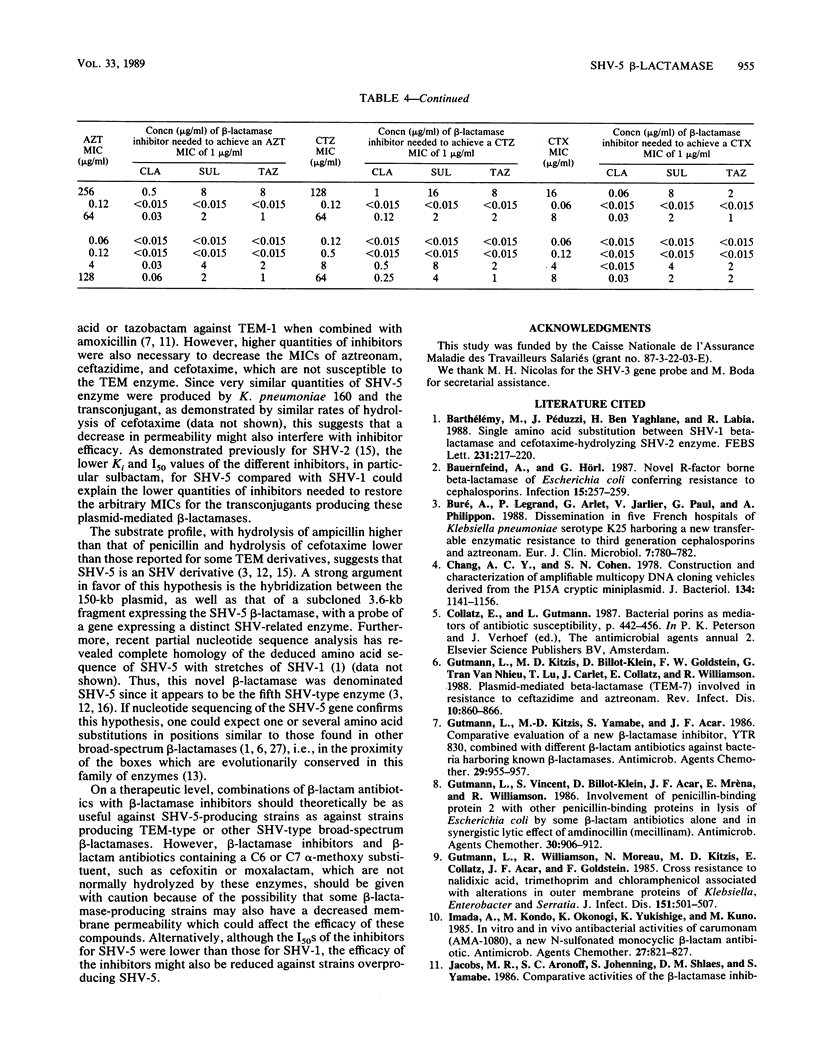
SHV-5 (pI 8.2), a novel broad-spectrum beta-lactamase encoded by a ca. 150-kilobase plasmid, was found in Klebsiella pneumoniae 160. SHV-5 beta-lactamase caused decreased susceptibility to most penicillins, cephalosporins, and monobactams, except imipenem and compounds which have a C6 or C7 alpha-methoxy substituent. beta-Lactamase inhibitors (clavulanic acid, sulbactam, and tazobactam) inhibited its activity and showed a synergistic effect when associated with different hydrolyzable beta-lactam compounds. Hybridization studies suggested that this enzyme may be related to, or derived from, the SHV enzyme. Increased MICs of cephamycins and temocillin associated with a decreased synergistic effect of the inhibitors on K. pneumoniae 160 might be linked to a decrease in two outer membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barthélémy M., Péduzzi J., Ben Yaghlane H., Labia R. Single amino acid substitution between SHV-1 beta-lactamase and cefotaxime-hydrolyzing SHV-2 enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 11;231(1):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Hörl G. Novel R-factor borne beta-lactamase of Escherichia coli confering resistance to cephalosporins. Infection. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):257–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01644127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buré A., Legrand P., Arlet G., Jarlier V., Paul G., Philippon A. Dissemination in five French hospitals of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K25 harbouring a new transferable enzymatic resistance to third generation cephalosporins and aztreonam. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;7(6):780–782. doi: 10.1007/BF01975048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F., Tran Van Nhieu G., Lu T., Carlet J., Collatz E., Williamson R. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (TEM-7) involved in resistance to ceftazidime and aztreonam. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):860–866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Kitzis M. D., Yamabe S., Acar J. F. Comparative evaluation of a new beta-lactamase inhibitor, YTR 830, combined with different beta-lactam antibiotics against bacteria harboring known beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):955–957. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Vincent S., Billot-Klein D., Acar J. F., Mrèna E., Williamson R. Involvement of penicillin-binding protein 2 with other penicillin-binding proteins in lysis of Escherichia coli by some beta-lactam antibiotics alone and in synergistic lytic effect of amdinocillin (mecillinam). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):906–912. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Williamson R., Moreau N., Kitzis M. D., Collatz E., Acar J. F., Goldstein F. W. Cross-resistance to nalidixic acid, trimethoprim, and chloramphenicol associated with alterations in outer membrane proteins of Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Serratia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):501–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada A., Kondo M., Okonogi K., Yukishige K., Kuno M. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of carumonam (AMA-1080), a new N-sulfonated monocyclic beta-lactam antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):821–827. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarlier V., Nicolas M. H., Fournier G., Philippon A. Extended broad-spectrum beta-lactamases conferring transferable resistance to newer beta-lactam agents in Enterobacteriaceae: hospital prevalence and susceptibility patterns. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):867–878. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joris B., Ghuysen J. M., Dive G., Renard A., Dideberg O., Charlier P., Frère J. M., Kelly J. A., Boyington J. C., Moews P. C. The active-site-serine penicillin-recognizing enzymes as members of the Streptomyces R61 DD-peptidase family. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 1;250(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2500313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F. W., Williamson R., Tran Van Nhieu G., Carlet J., Acar J. F., Gutmann L. Dissemination of the novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase CTX-1, which confers resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins, and its inhibition by beta-lactamase inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):9–14. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliebe C., Nies B. A., Meyer J. F., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Evolution of plasmid-coded resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Shah P., Krcmery V., Antal M., Mitsuhashi S. Transferable resistance to cefotaxime, cefoxitin, cefamandole and cefuroxime in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):315–317. doi: 10.1007/BF01641355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labigne-Roussel A., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Translocation of sequences encoding antibiotic resistance from the chromosome to a receptor plasmid in Salmonella ordonez. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):390–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00293927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque R. C., Medeiros A. A., Jacoby G. A. Molecular cloning and DNA homology of plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):252–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00333581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Moosdeen F., Lindridge M. A., Kho P., Williams J. D. Behaviour of TEM-1 beta-lactamase as a resistance mechanism to ampicillin, mezlocillin and azlocillin in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Feb;17(2):139–146. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.2.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A., Sirot D. L., Chanal C. M., Sirot J. L., Labia R., Gerbaud G., Cluzel R. A. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae more resistant to ceftazidime than to other broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):626–630. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V., Werner V. Selection of multiple antibiotic resistance by quinolones, beta-lactams, and aminoglycosides with special reference to cross-resistance between unrelated drug classes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):797–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot D., Sirot J., Labia R., Morand A., Courvalin P., Darfeuille-Michaud A., Perroux R., Cluzel R. Transferable resistance to third-generation cephalosporins in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae: identification of CTX-1, a novel beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Sep;20(3):323–334. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Goussard S., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to third-generation cephalosporins caused by point mutations in TEM-type penicillinase genes. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):879–884. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S. K., Summerill R. A., Minassian B. F., Bush K., Visnic D. A., Bonner D. P., Sykes R. B. In vitro evaluation of tigemonam, a novel oral monobactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):219–225. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witchitz J. L. Plasmid-mediated gentamicin resistance not associated with kanamycin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Oct;25(10):622–624. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]