Abstract
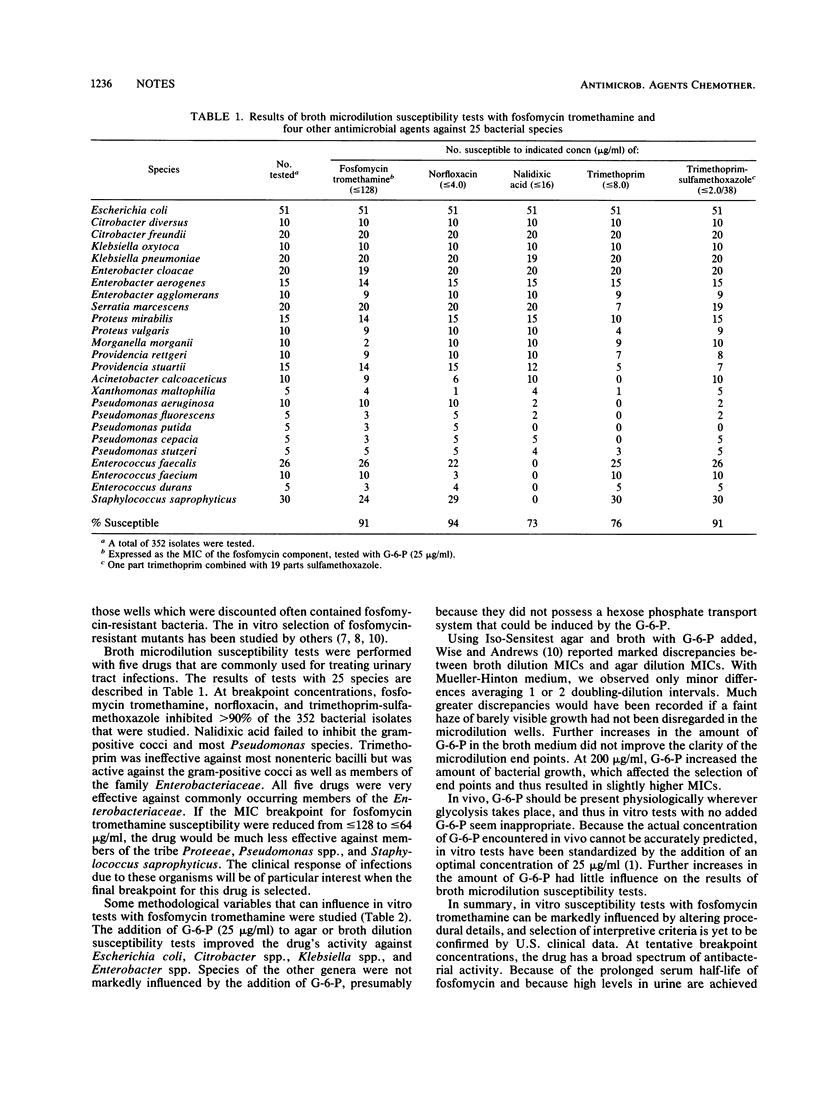
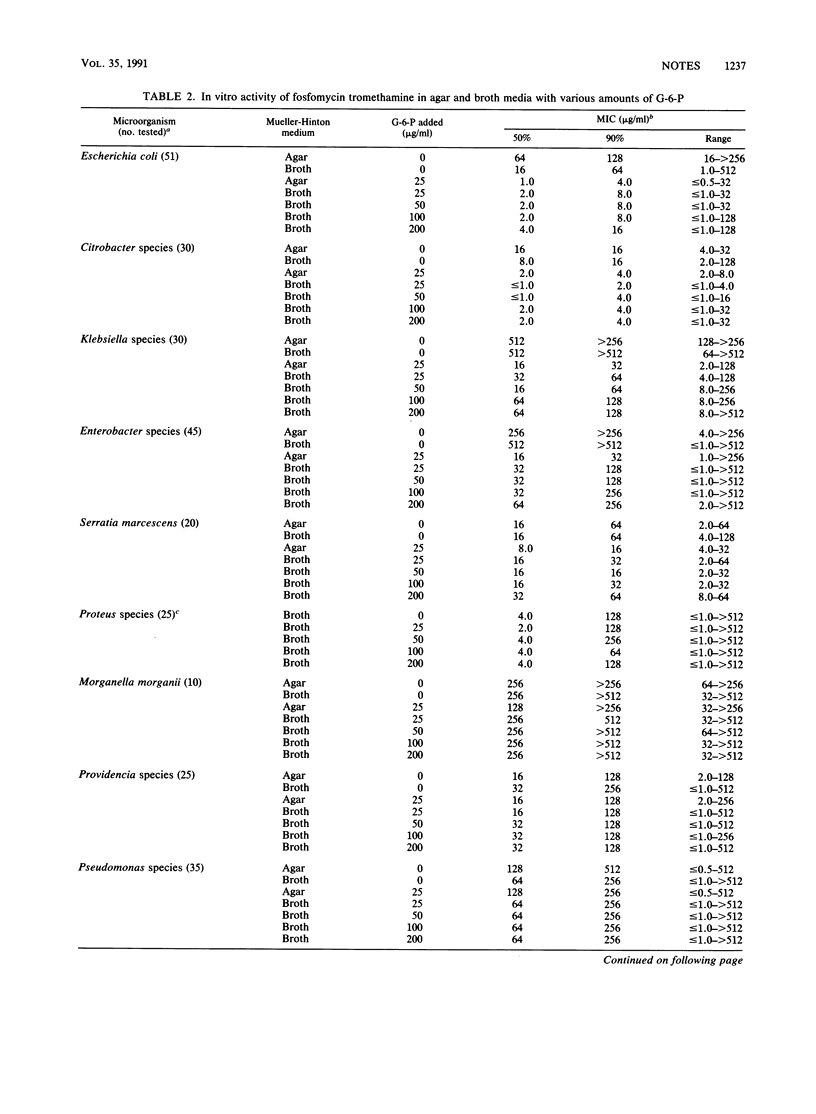
Fosfomycin tromethamine (previously fosfomycin trometamol) is an orally administered fosfomycin which may be used for single-dose therapy of uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Fosfomycin tromethamine, norfloxacin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole inhibited greater than 90% of 352 bacterial isolates representing 25 different species; trimethoprim and nalidixic acid had narrower spectrums of activity. Strains of Escherichia, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, and Klebsiella species were much more susceptible when glucose-6-phosphate was added to the test medium, but isolates belonging to other genera were not affected.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews J. M., Baquero F., Beltran J. M., Canton E., Crokaert F., Gobernado M., Gomez-Ius R., Loza E., Navarro M., Olay T. International collaborative study on standardization of bacterial sensitivity to fosfomycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Oct;12(4):357–361. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.4.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsa F., Leroy A., Fillastre J. P., Godin M., Moulin B. Comparative pharmacokinetics of tromethamine fosfomycin and calcium fosfomycin in young and elderly adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jun;32(6):938–941. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.6.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D., Jones A., Eley A. Factors influencing the activity of the trometamol salt of fosfomycin. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Feb;5(1):29–34. doi: 10.1007/BF02013457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan F. M., Kahan J. S., Cassidy P. J., Kropp H. The mechanism of action of fosfomycin (phosphonomycin). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):364–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Pira G., Pruzzo C., Schito G. C. Monuril and modification of pathogenicity traits in resistant microorganisms. Eur Urol. 1987;13 (Suppl 1):92–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



