Abstract
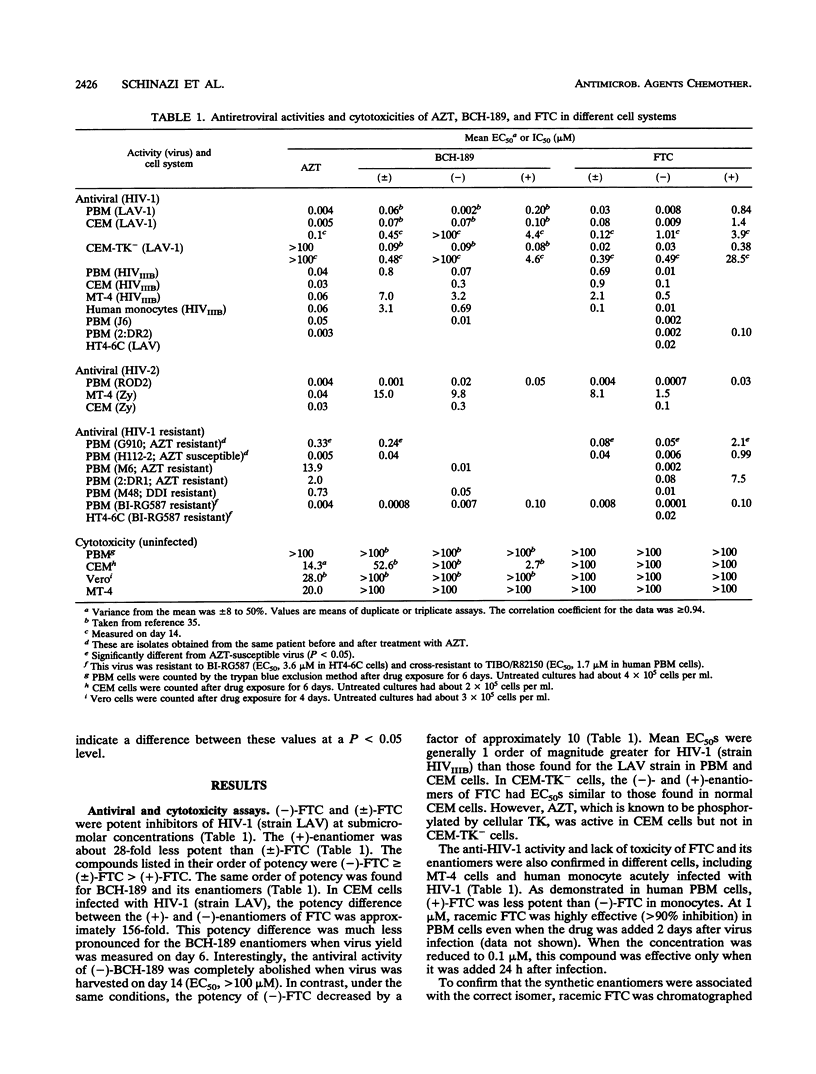
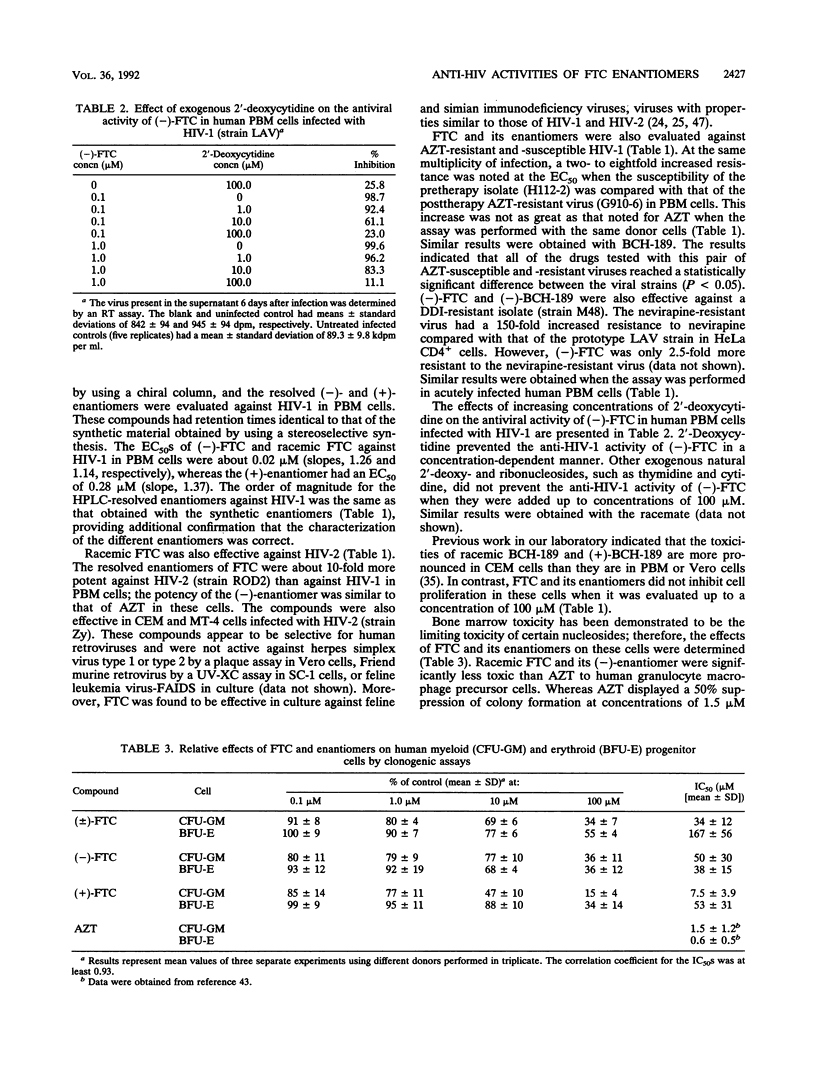
2',3'-Dideoxy-5-fluoro-3'-thiacytidine (FTC) has been shown to be a potent and selective compound against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in acutely infected primary human lymphocytes. FTC is also active against human immunodeficiency virus type 2, simian immunodeficiency virus, and feline immunodeficiency virus in various cell culture systems, including human monocytes. The antiviral activity can be prevented by 2'-deoxycytidine, but not by other natural nucleosides, suggesting that FTC must be phosphorylated to be active and 2'-deoxycytidine kinase is responsible for the phosphorylation. By using chiral columns or enzymatic techniques, the two enantiomers of FTC were separated. The (-)-beta-enantiomer of FTC was about 20-fold more potent than the (+)-beta-enantiomer against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and was also effective in thymidine kinase-deficient CEM cells. Racemic FTC and its enantiomers were nontoxic to human lymphocytes and other cell lines at concentrations of up to 100 microM. Studies with human bone marrow cells indicated that racemic FTC and its (-)-enantiomer had a median inhibitory concentration of > 30 microM. The (+)-enantiomer was significantly more toxic than the (-)-enantiomer to myeloid progenitor cells. The susceptibilities to FTC of pretherapy isolates in comparison with those of posttherapy 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine-resistant viruses in human lymphocytes were not substantially different. Similar results were obtained with well-defined 2',3'-dideoxyinosine- and nevirapine-resistant viruses. (-)-FTC-5'-triphosphate competitively inhibited human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase, with an inhibition constant of 2.9 microM, when a poly(I)n.oligo(dC)19-24 template primer was used. These results suggest that further development of the (-)-Beta-enantiomer of FTC is warranted as an antiviral agent for infections caused by human immunodeficiency viruses.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averett D. R. Anti-HIV compound assessment by two novel high capacity assays. J Virol Methods. 1989 Mar;23(3):263–276. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates J. A., Cammack N., Jenkinson H. J., Jowett A. J., Jowett M. I., Pearson B. A., Penn C. R., Rouse P. L., Viner K. C., Cameron J. M. (-)-2'-deoxy-3'-thiacytidine is a potent, highly selective inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and type 2 replication in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):733–739. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates J. A., Cammack N., Jenkinson H. J., Mutton I. M., Pearson B. A., Storer R., Cameron J. M., Penn C. R. The separated enantiomers of 2'-deoxy-3'-thiacytidine (BCH 189) both inhibit human immunodeficiency virus replication in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):202–205. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doong S. L., Tsai C. H., Schinazi R. F., Liotta D. C., Cheng Y. C. Inhibition of the replication of hepatitis B virus in vitro by 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine and related analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8495–8499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornsife R. E., St Clair M. H., Huang A. T., Panella T. J., Koszalka G. W., Burns C. L., Averett D. R. Anti-human immunodeficiency virus synergism by zidovudine (3'-azidothymidine) and didanosine (dideoxyinosine) contrasts with their additive inhibition of normal human marrow progenitor cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):322–328. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Ferone R., Freeman G. A., Fyfe J. A., Hill J. A., Ray P. H., Richards C. A., Singer S. C., Knick V. B., Rideout J. L. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (BW A509U). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):274–280. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B. F., Chu C. K., Schinazi R. F. Phosphorylation of 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxyuridine and preferential inhibition of human and simian immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptases by its 5'-triphosphate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Oct;33(10):1729–1734. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.10.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Collalti E., Ratner L., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. A molecular clone of HTLV-III with biological activity. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):262–265. doi: 10.1038/316262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover E. A., Zeidner N. S., Perigo N. A., Quackenbush S. L., Strobel J. D., Hill D. L., Mullins J. I. Feline leukemia virus-induced immunodeficiency syndrome in cats as a model for evaluation of antiretroviral therapy. Intervirology. 1989;30 (Suppl 1):12–25. doi: 10.1159/000150120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurovcik M., Holý A. Metabolism of pyrimidine L-nucleosides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Aug;3(8):2143–2154. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.8.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin T. S., Guo J. Y., Schinazi R. F., Chu C. K., Xiang J. N., Prusoff W. H. Synthesis and antiviral activity of various 3'-azido analogues of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1, HTLV-III/LAV). J Med Chem. 1988 Feb;31(2):336–340. doi: 10.1021/jm00397a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North T. W., Cronn R. C., Remington K. M., Tandberg R. T. Direct comparisons of inhibitor sensitivities of reverse transcriptases from feline and human immunodeficiency viruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1505–1507. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner M. R., Elboim H. S., Cannon T., Cavacini L., Hideshima T. Functional activity of an HIV-1 neutralizing IgG human monoclonal antibody: ADCC and complement-mediated lysis. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 May;8(5):553–558. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington K. M., Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Pedersen N. C., North T. W. Mutants of feline immunodeficiency virus resistant to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):308–312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.308-312.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Fischl M. A., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Hirsch M. S. The toxicity of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):192–197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Shih C. K., Lowy I., Rose J., Prodanovich P., Goff S., Griffin J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants resistant to nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase arise in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11241–11245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Cannon D. L., Arnold B. H., Martino-Saltzman D. Combinations of isoprinosine and 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine in lymphocytes infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1784–1787. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Chou T. C., Scott R. T., Yao X. J., Nahmias A. J. Delayed treatment with combinations of antiviral drugs in mice infected with herpes simplex virus and application of the median effect method of analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Sep;30(3):491–498. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.3.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Chu C. K., Eriksson B. F., Sommadossi J. P., Doshi K. J., Boudinot F. D., Oswald B., McClure H. M. Antiretroviral activity, biochemistry, and pharmacokinetics of 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxy-5-methylcytidine. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;616:385–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Chu C. K., Peck A., McMillan A., Mathis R., Cannon D., Jeong L. S., Beach J. W., Choi W. B., Yeola S. Activities of the four optical isomers of 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine (BCH-189) against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in human lymphocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Mar;36(3):672–676. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.3.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinazi R. F., Sommadossi J. P., Saalmann V., Cannon D. L., Xie M. Y., Hart G. C., Smith G. A., Hahn E. F. Activities of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine nucleotide dimers in primary lymphocytes infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1061–1067. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P., Carlisle R., Schinazi R. F., Zhou Z. Uridine reverses the toxicity of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine in normal human granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells in vitro without impairment of antiretroviral activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):997–1001. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P., Carlisle R., Zhou Z. Cellular pharmacology of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine with evidence of incorporation into DNA of human bone marrow cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):9–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P., Zhu Z., Carlisle R., Xie M. Y., Weidner D. A. Pharmacologic studies of nucleosides active against the human immunodeficiency virus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;616:356–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soudeyns H., Yao X. I., Gao Q., Belleau B., Kraus J. L., Nguyen-Ba N., Spira B., Wainberg M. A. Anti-human immunodeficiency virus type 1 activity and in vitro toxicity of 2'-deoxy-3'-thiacytidine (BCH-189), a novel heterocyclic nucleoside analog. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jul;35(7):1386–1390. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.7.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Martin J. L., Tudor-Williams G., Bach M. C., Vavro C. L., King D. M., Kellam P., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1716788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Follis K. E., Yarnall M., Deaver L. E., Benveniste R. E., Sager P. R. In vitro screening for antiretroviral agents against simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). Antiviral Res. 1990 Aug;14(2):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(90)90046-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E. L., Parker W. B., Macy L. J., Shaddix S. C., McCaleb G., Secrist J. A., 3rd, Vince R., Shannon W. M. Comparison of the effect of Carbovir, AZT, and dideoxynucleoside triphosphates on the activity of human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase and selected human polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92611-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]