Abstract
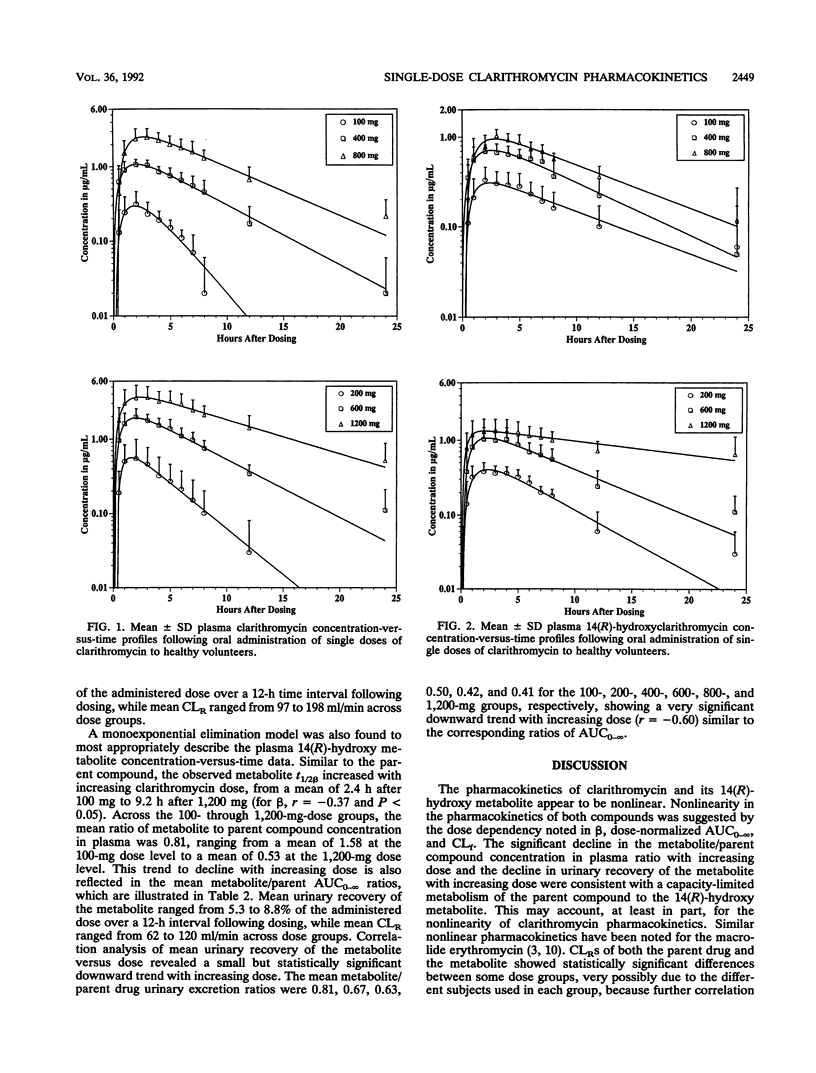
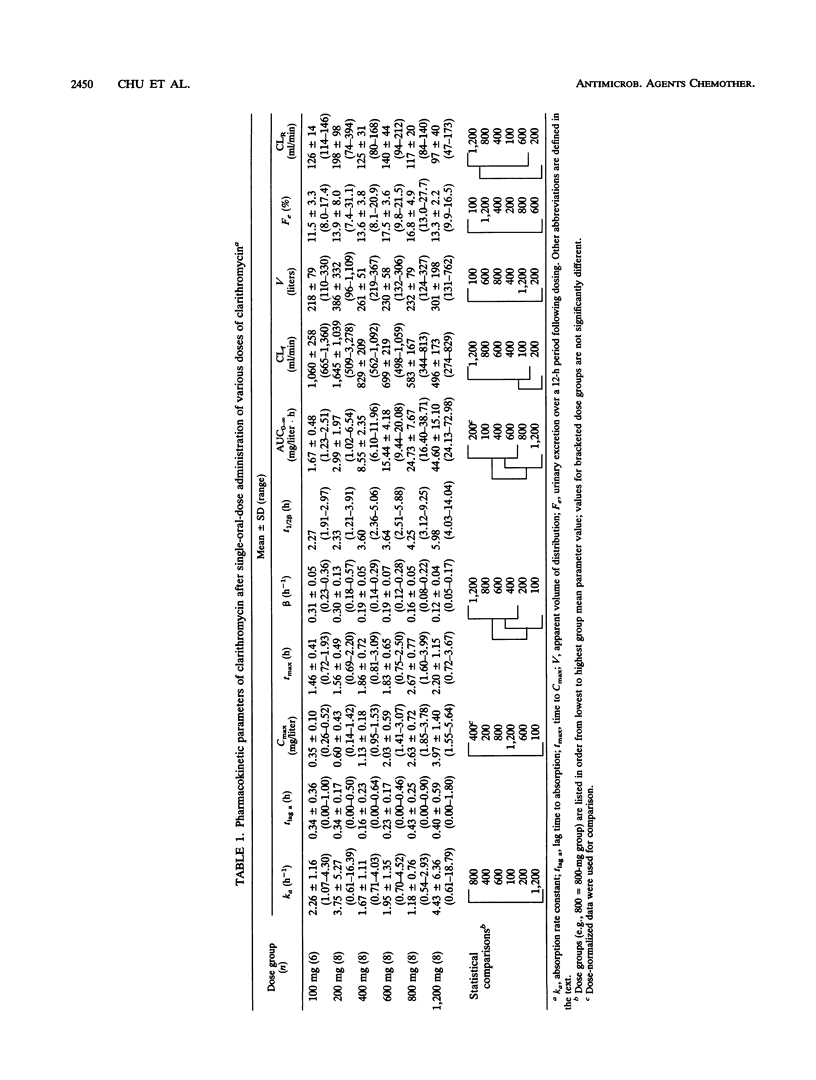
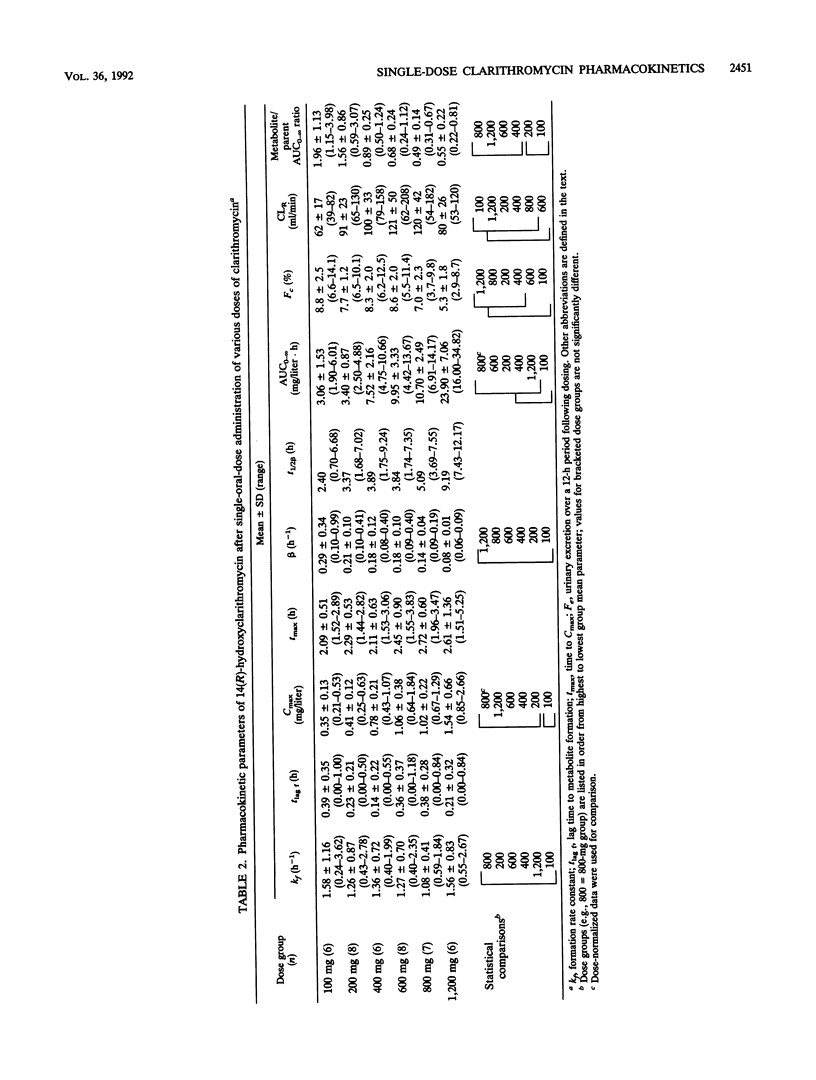
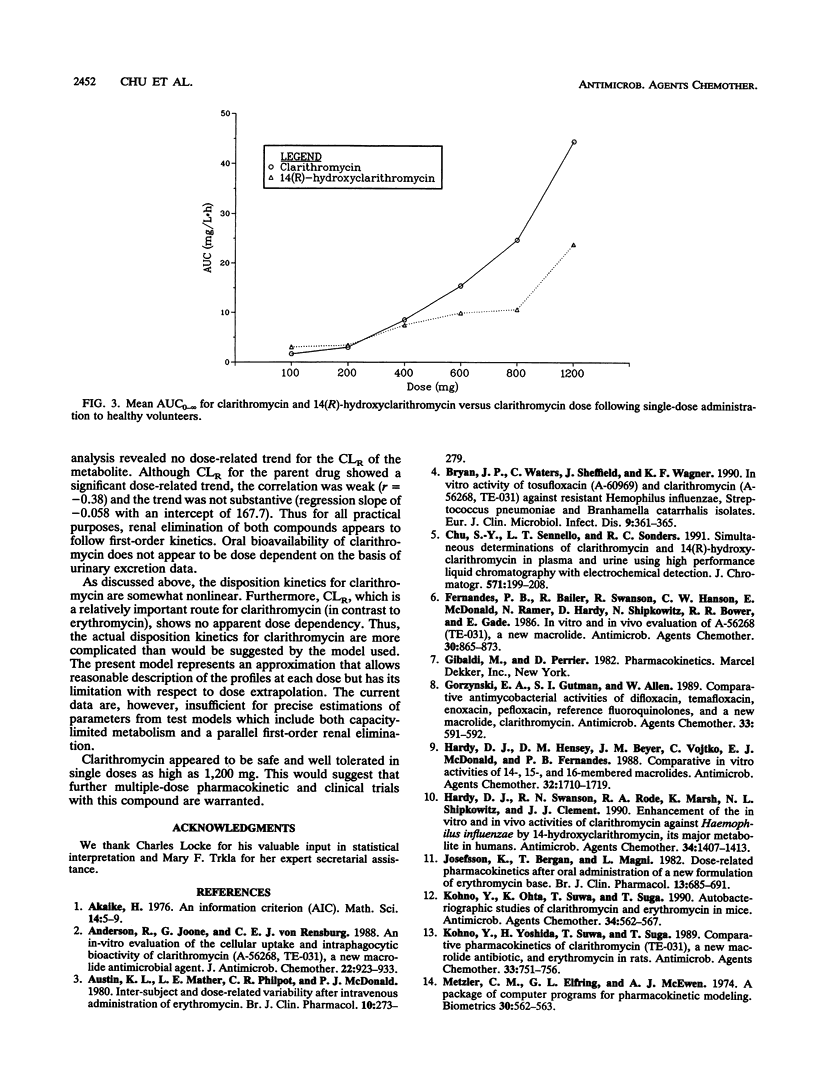
The pharmacokinetics and safety of single ascending doses of clarithromycin (6-0-methylerythromycin A) were assessed in a placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial with 39 healthy male volunteers. Subjects were randomized to receive single doses of either placebo or 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, or 1,200 mg of clarithromycin. Blood and urine collections were performed over the 24 h following administration of the test preparation. Biological specimens were analyzed for clarithromycin and 14(R)-hydroxyclarithromycin content by a high-performance liquid chromatographic technique. The pharmacokinetics of clarithromycin appeared to be dose dependent, with terminal disposition half-life ranging from 2.3 to 6.0 h and mean +/- standard deviation area under the concentration-versus-time curve from time 0 to infinity for plasma ranging from 1.67 +/- 0.48 to 3.72 +/- 1.26 mg/liter.h per 100-mg dose over the 100- to 1,200-mg dose range. Similar dose dependency was noted in the pharmacokinetics of the 14(R)-hydroxy metabolite. Mean urinary excretion of clarithromycin and its 14(R)-hydroxy metabolite ranged from 11.5 to 17.5% and 5.3 to 8.8% of the administered dose, respectively. Urinary excretion data and plasma metabolite/parent compound concentration ratio data suggested that capacity-limited formation of the active metabolite may account, at least in part, for the nonlinear pharmacokinetics of clarithromycin. No substantive dose-related trend was observed for the renal clearance of either compound. There were no clinically significant drug-related alterations in laboratory and nonlaboratory safety parameters. In addition, there was no significant difference between placebo and clarithromycin recipients in the incidence or severity of adverse events. Clarithromycin appears to be safe and well tolerated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryan J. P., Waters C., Sheffield J., Wagner K. F. In vitro activity of tosufloxacin (A-60969) and clarithromycin (A-56268, TE-031) against resistant Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Branhamella catarrhalis isolates. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 May;9(5):361–365. doi: 10.1007/BF01973747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S. Y., Sennello L. T., Sonders R. C. Simultaneous determination of clarithromycin and 14(R)-hydroxyclarithromycin in plasma and urine using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr. 1991 Nov 15;571(1-2):199–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(91)80446-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Bailer R., Swanson R., Hanson C. W., McDonald E., Ramer N., Hardy D., Shipkowitz N., Bower R. R., Gade E. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of A-56268 (TE-031), a new macrolide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Dec;30(6):865–873. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.6.865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorzynski E. A., Gutman S. I., Allen W. Comparative antimycobacterial activities of difloxacin, temafloxacin, enoxacin, pefloxacin, reference fluoroquinolones, and a new macrolide, clarithromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):591–592. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. J., Hensey D. M., Beyer J. M., Vojtko C., McDonald E. J., Fernandes P. B. Comparative in vitro activities of new 14-, 15-, and 16-membered macrolides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1710–1719. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy D. J., Swanson R. N., Rode R. A., Marsh K., Shipkowitz N. L., Clement J. J. Enhancement of the in vitro and in vivo activities of clarithromycin against Haemophilus influenzae by 14-hydroxy-clarithromycin, its major metabolite in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jul;34(7):1407–1413. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.7.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josefsson K., Bergan T., Magni L. Dose-related pharmacokinetics after oral administration of a new formulation of erythromycin base. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 May;13(5):685–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno Y., Ohta K., Suwa T., Suga T. Autobacteriographic studies of clarithromycin and erythromycin in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Apr;34(4):562–567. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.4.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno Y., Yoshida H., Suwa T., Suga T. Comparative pharmacokinetics of clarithromycin (TE-031), a new macrolide antibiotic, and erythromycin in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):751–756. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto S., Takahashi Y., Watanabe Y., Omura S. Chemical modification of erythromycins. I. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 6-O-methylerythromycins A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Feb;37(2):187–189. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perronne C., Gikas A., Truffot-Pernot C., Grosset J., Pocidalo J. J., Vilde J. L. Activities of clarithromycin, sulfisoxazole, and rifabutin against Mycobacterium avium complex multiplication within human macrophages. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1508–1511. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman A. J., Wagner J. G. CSTRIP, a fortran IV computer program for obtaining initial polyexponential parameter estimates. J Pharm Sci. 1976 Jul;65(7):1006–1010. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600650713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton A. M., Maskell J. P., Yong F. J., Chi S. J., Williams J. D. Comparative in vitro activity of A-56268. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;7(6):798–802. doi: 10.1007/BF01975054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K., Nakagawa T., Uno T. Application of Akaike's information criterion (AIC) in the evaluation of linear pharmacokinetic equations. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Apr;6(2):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01117450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



