Abstract
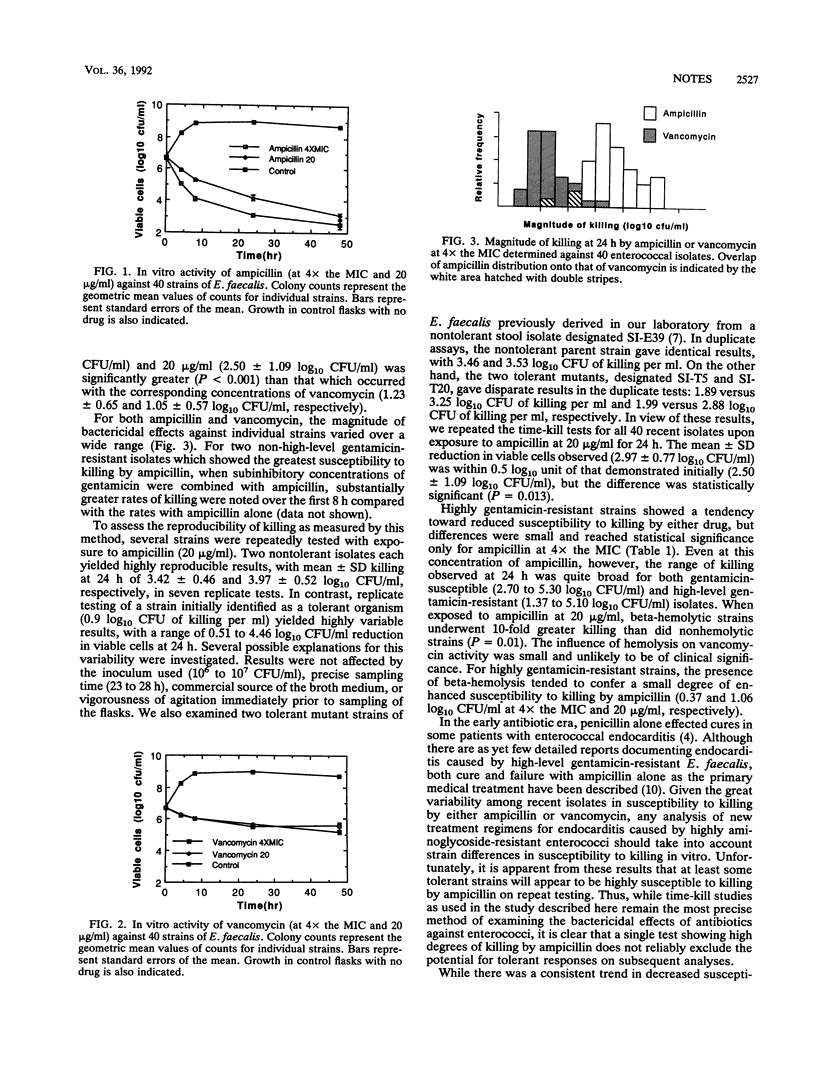
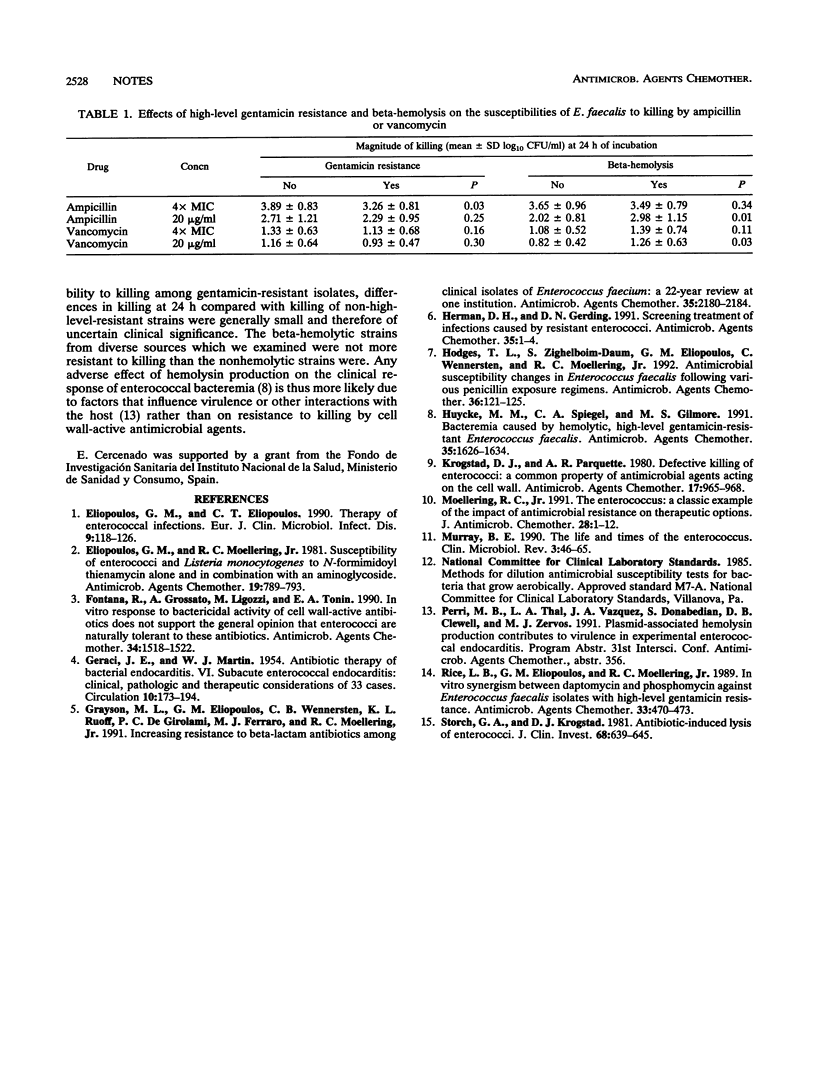
The bactericidal activities of ampicillin and vancomycin against 40 recent isolates of Enterococcus faecalis were examined by kill-kinetic studies at concentrations of 4 x the MIC and 20 micrograms/ml. Greater killing was seen with ampicillin (3.57 +/- 0.87 and 2.50 +/- 1.09 log10 CFU/ml, respectively; mean +/- standard deviation) than with vancomycin (1.23 +/- 0.65 and 1.05 +/- 0.57 log10 CFU/ml, respectively). Highly gentamicin-resistant strains showed a tendency toward reduced susceptibility to killing; beta-hemolytic strains were more susceptible than nonhemolytic strains when exposed to ampicillin at 20 micrograms/ml. Within each group, individual isolates demonstrated great variability in susceptibility to killing by the drugs.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eliopoulos G. M., Eliopoulos C. T. Therapy of enterococcal infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;9(2):118–126. doi: 10.1007/BF01963636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Moellering R. C., Jr Susceptibility of enterococci and Listeria monocytogenes to N-Formimidoyl thienamycin alone and in combination with an aminoglycoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):789–793. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Grossato A., Ligozzi M., Tonin E. A. In vitro response to bactericidal activity of cell wall-active antibiotics does not support the general opinion that enterococci are naturally tolerant to these antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1518–1522. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERACI J. E., MARTIN W. J. Antibiotic therapy of bacterial endocarditis. VI. Subacute enterococcal endocarditis; clinical, pathologic and therapeutic consideration of 33 cases. Circulation. 1954 Aug;10(2):173–194. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.10.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson M. L., Eliopoulos G. M., Wennersten C. B., Ruoff K. L., De Girolami P. C., Ferraro M. J., Moellering R. C., Jr Increasing resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics among clinical isolates of Enterococcus faecium: a 22-year review at one institution. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2180–2184. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman D. J., Gerding D. N. Antimicrobial resistance among enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. L., Zighelboim-Daum S., Eliopoulos G. M., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr Antimicrobial susceptibility changes in Enterococcus faecalis following various penicillin exposure regimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):121–125. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huycke M. M., Spiegel C. A., Gilmore M. S. Bacteremia caused by hemolytic, high-level gentamicin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Aug;35(8):1626–1634. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.8.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogstad D. J., Pargwette A. R. Defective killing of enterococci: a common property of antimicrobial agents acting on the cell wall. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jun;17(6):965–968. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr The Garrod Lecture. The enterococcus: a classic example of the impact of antimicrobial resistance on therapeutic options. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Jul;28(1):1–12. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E. The life and times of the Enterococcus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jan;3(1):46–65. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice L. B., Eliopoulos G. M., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro synergism between daptomycin and fosfomycin against Enterococcus faecalis isolates with high-level gentamicin resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):470–473. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch G. A., Krogstad D. J. Antibiotic-induced lysis of enterococci. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):639–645. doi: 10.1172/JCI110298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



