Abstract
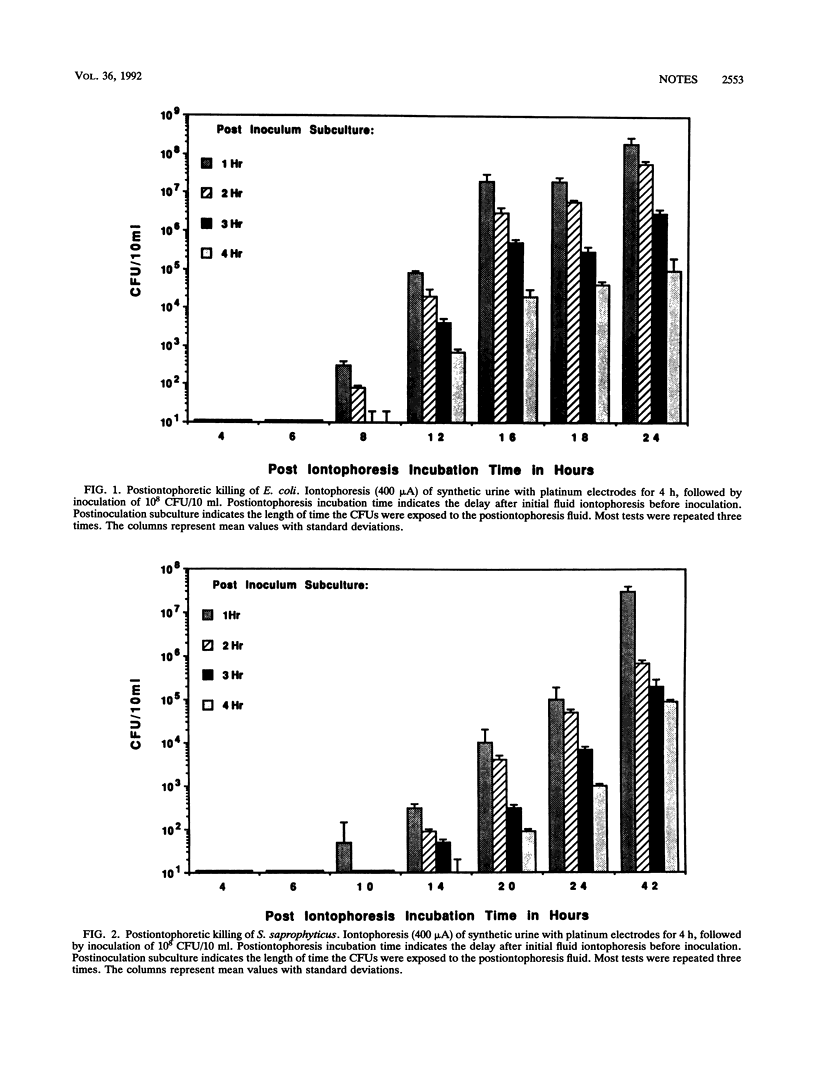
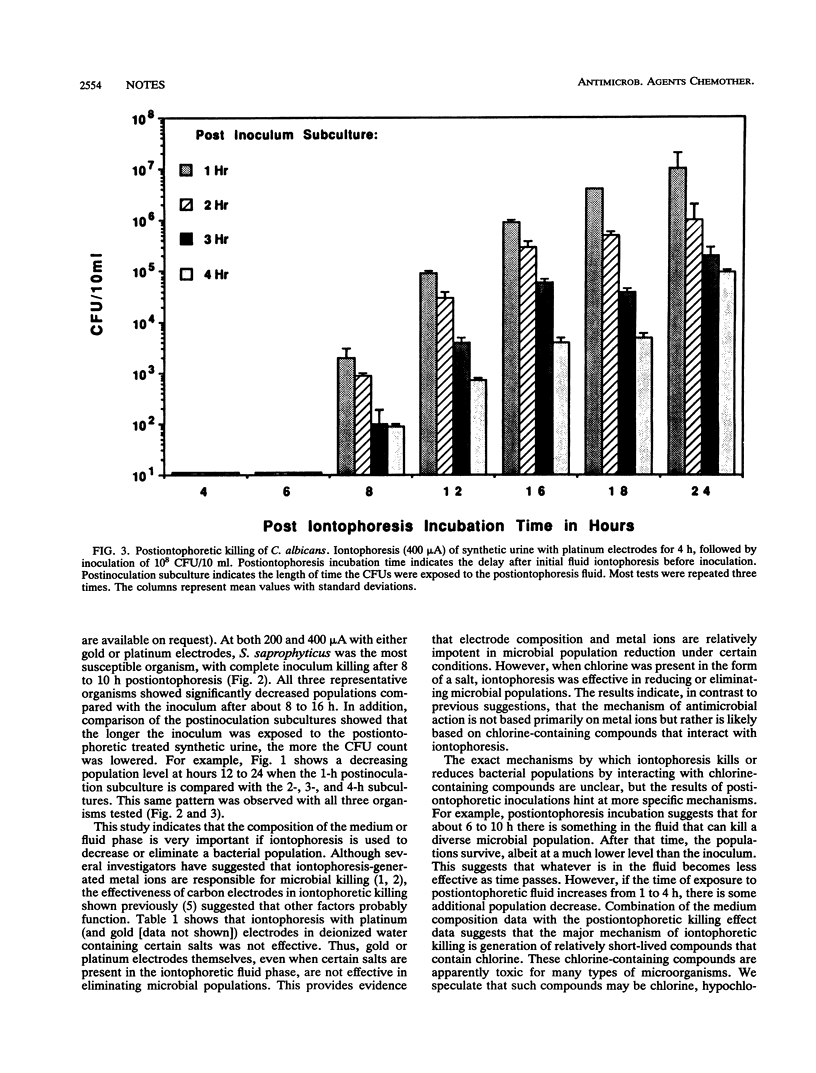
Iontophoresis required chlorine-containing compounds in the medium for effective microbial population reduction and killing. After iontophoresis ceased, the antimicrobial effect generated by iontophoresis remained but slowly decreased. Antimicrobial effects of iontophoresis may be related to the generation of short-lived chlorine-containing compounds.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger T. J., Spadaro J. A., Bierman R., Chapin S. E., Becker R. O. Antifungal properties of electrically generated metallic ions. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Nov;10(5):856–860. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.5.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger T. J., Spadaro J. A., Chapin S. E., Becker R. O. Electrically generated silver ions: quantitative effects on bacterial and mammalian cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Feb;9(2):357–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Anderson M. D., Hoskins S., Warren M. M. Electrode and bacterial survival with iontophoresis in synthetic urine. J Urol. 1992 May;147(5):1310–1313. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)37551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Arnett D., Warren M. M. Iontophoretic killing of Escherichia coli in static fluid and in a model catheter system. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 May;15(5):891–894. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.5.891-894.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Wagle N., Anderson M. D., Warren M. M. Bacterial and fungal killing by iontophoresis with long-lived electrodes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2131–2134. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Weinberg S., Anderson M. D., Rao G. M., Warren M. M. Effects of microamperage, medium, and bacterial concentration on iontophoretic killing of bacteria in fluid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):442–447. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith D. P., Musher D. M., Itin C. Urease. The primary cause of infection-induced urinary stones. Invest Urol. 1976 Mar;13(5):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



