Abstract
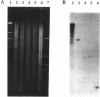
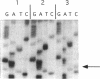
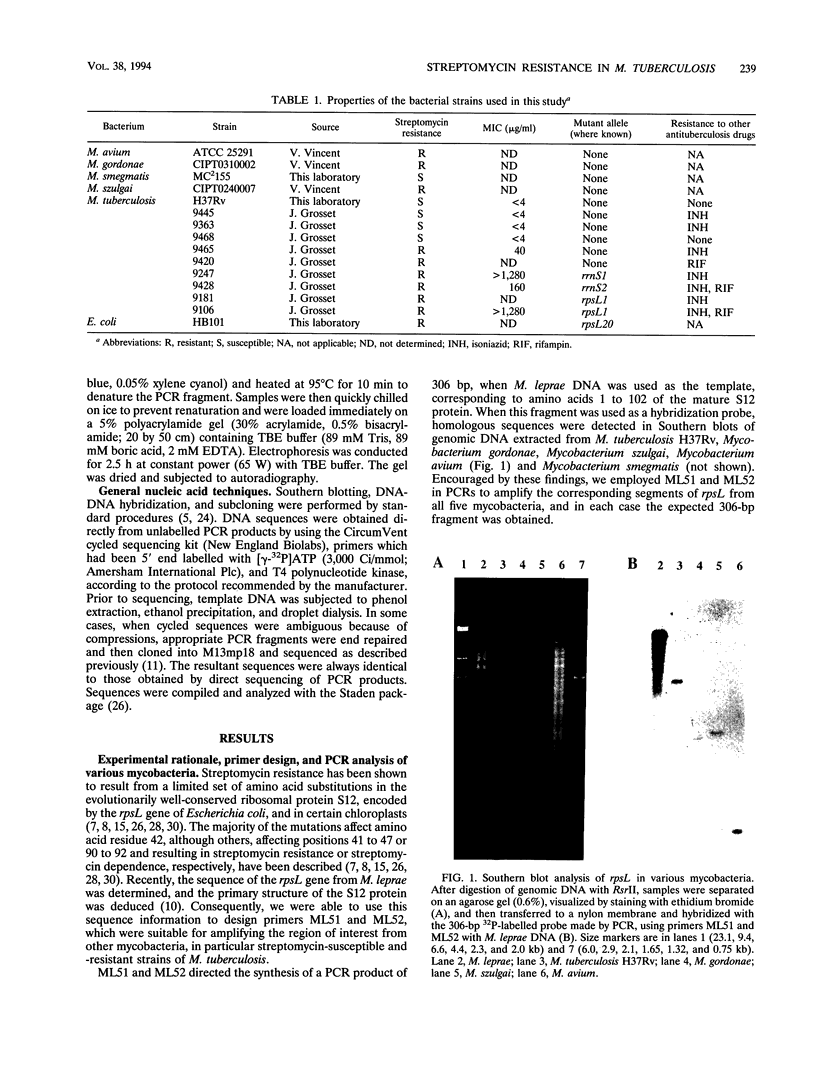
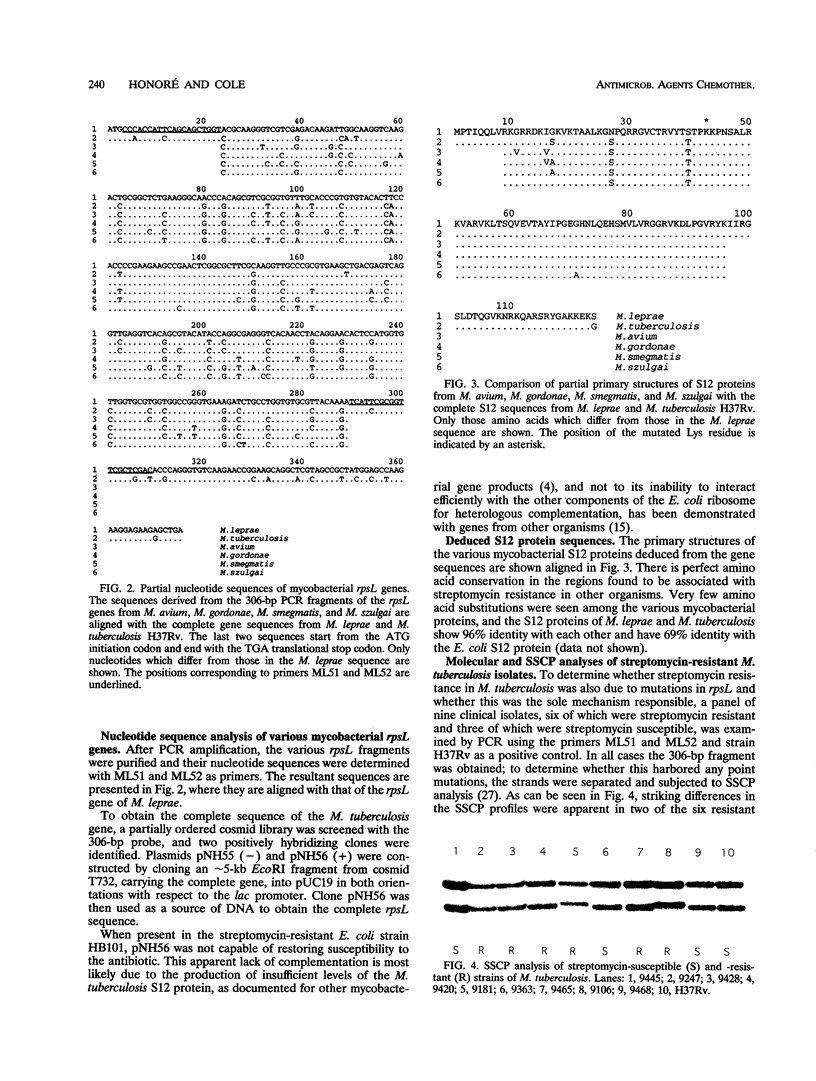
Streptomycin, the first antibiotic used in tuberculosis control programs, perturbs protein synthesis at the ribosome level. It is shown here that streptomycin resistance in some clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is associated either with missense mutations in the rpsL gene, which encodes ribosomal protein S12, or with base substitutions at position 904 in the 16S rRNA. The primary structure of the S12 protein is well conserved among the mycobacteria, even those, such as M. avium, M. gordonae, and M. szulgai, that are naturally resistant to streptomycin. This suggests that permeability barriers may be responsible for the resistance to the antibiotic.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R., Davies J. Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:471–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Murray C. J. Tuberculosis: commentary on a reemergent killer. Science. 1992 Aug 21;257(5073):1055–1064. doi: 10.1126/science.257.5073.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Jacobs W. R., Docherty M. A., Ritchie L. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Molecular analysis of DNA and construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1093-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiglmeier K., Honoré N., Cole S. T. Towards the integration of foreign DNA into the chromosome of Mycobacterium leprae. Res Microbiol. 1991 Jul-Aug;142(6):617–622. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90074-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finken M., Kirschner P., Meier A., Wrede A., Böttger E. C. Molecular basis of streptomycin resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: alterations of the ribosomal protein S12 gene and point mutations within a functional 16S ribosomal RNA pseudoknot. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(6):1239–1246. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. 33. Location of amino-acid replacements in protein S12 isolated from Escherichia coli mutants resistant to streptomycin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili S., Fromm H., Aviv D., Edelman M., Galun E. Ribosomal protein S12 as a site for streptomycin resistance in Nicotiana chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):289–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00331280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier A., Turmel M., Lemieux C. Mapping of chloroplast mutations conferring resistance to antibiotics in Chlamydomonas: evidence for a novel site of streptomycin resistance in the small subunit rRNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):192–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00337710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honore N., Cole S. T. Molecular basis of rifampin resistance in Mycobacterium leprae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):414–418. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré N., Bergh S., Chanteau S., Doucet-Populaire F., Eiglmeier K., Garnier T., Georges C., Launois P., Limpaiboon T., Newton S. Nucleotide sequence of the first cosmid from the Mycobacterium leprae genome project: structure and function of the Rif-Str regions. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(2):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01112.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iseman M. D. Treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 9;329(11):784–791. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309093291108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempsell K. E., Ji Y. E., Estrada I. C., Colston M. J., Cox R. A. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter, 16S rRNA and spacer region of the ribosomal RNA operon of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and comparison with Mycobacterium leprae precursor rRNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Aug;138(Pt 8):1717–1727. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-8-1717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Chloroplast ribosomal protein gene rps12 of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Wild-type sequence, mutation to streptomycin resistance and dependence, and function in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16100–16108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Lemieux C., Brakier-Gingras L. A mutation in the 530 loop of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA causes resistance to streptomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9631–9639. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Nicolas P., Schürmann P., Stutz E. Streptomycin-resistance of Euglena gracilis chloroplasts: identification of a point mutation in the 16S rRNA gene in an invariant position. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4299–4310. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Wagner R., Stutz E. E. coli ribosomes with a C912 to U base change in the 16S rRNA are streptomycin resistant. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3705–3708. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orita M., Iwahana H., Kanazawa H., Hayashi K., Sekiya T. Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. E., Jr, Roper W. L. The new tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 5;326(10):703–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199203053261011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenti A., Imboden P., Marchesi F., Lowrie D., Cole S., Colston M. J., Matter L., Schopfer K., Bodmer T. Detection of rifampicin-resistance mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lancet. 1993 Mar 13;341(8846):647–650. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90417-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods S. A., Cole S. T. A rapid method for the detection of potentially viable Mycobacterium leprae in human biopsies: a novel application of PCR. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Dec;53(3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaguchi M., Wittmann H. G., Cábezon T., De Wilde M., Villarroel R., Herzog A., Bollen A. Cooperative control of translational fidelity by ribosomal proteins in Escherichia coli. II. Localization of amino acid replacements in proteins S5 and S12 altered in double mutants resistant to neamine. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 23;142(1):35–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00268753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Acken U. Proteinchemical studies on ribosomal proteins S4 and S12 from ram (ribosomal ambiguity) mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Sep 15;140(1):61–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00268989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]