Abstract
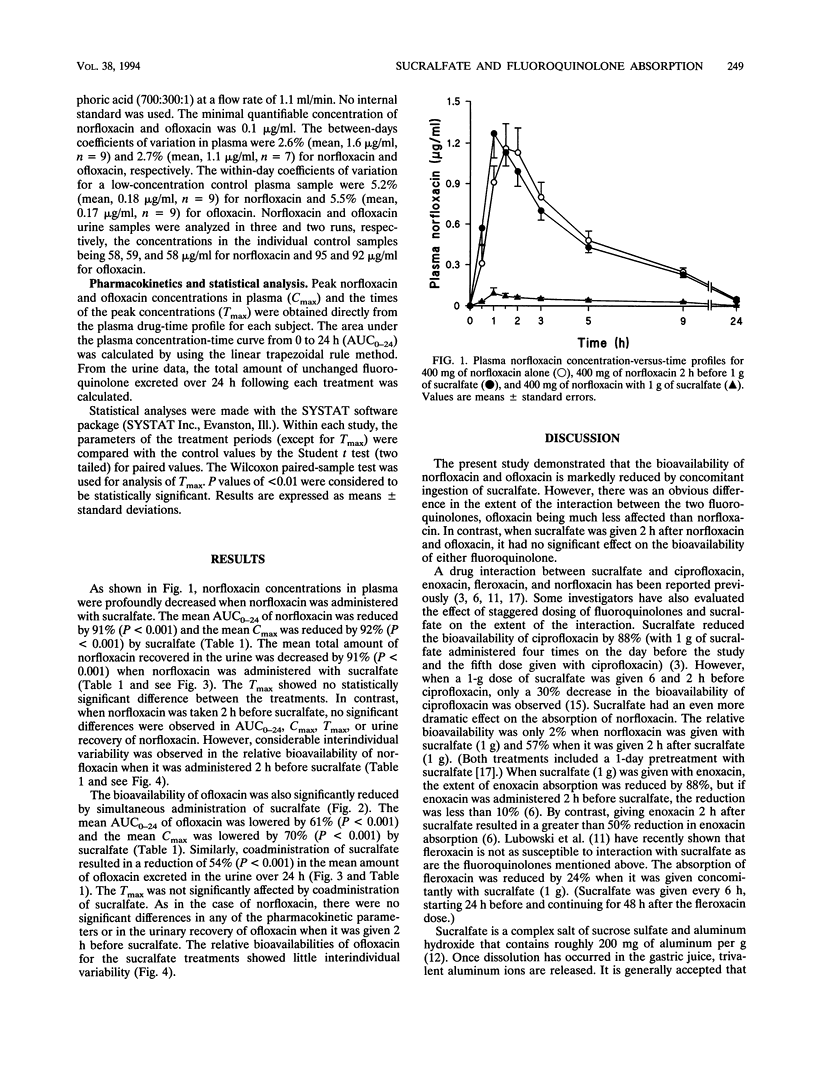
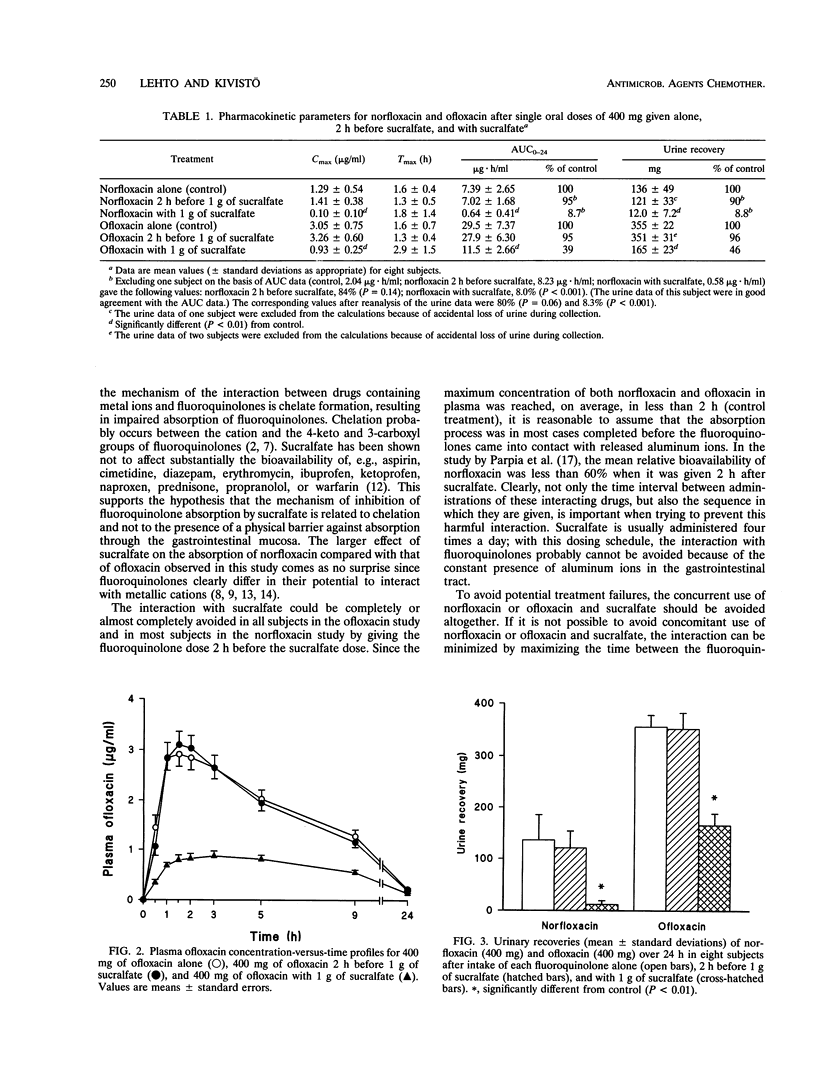
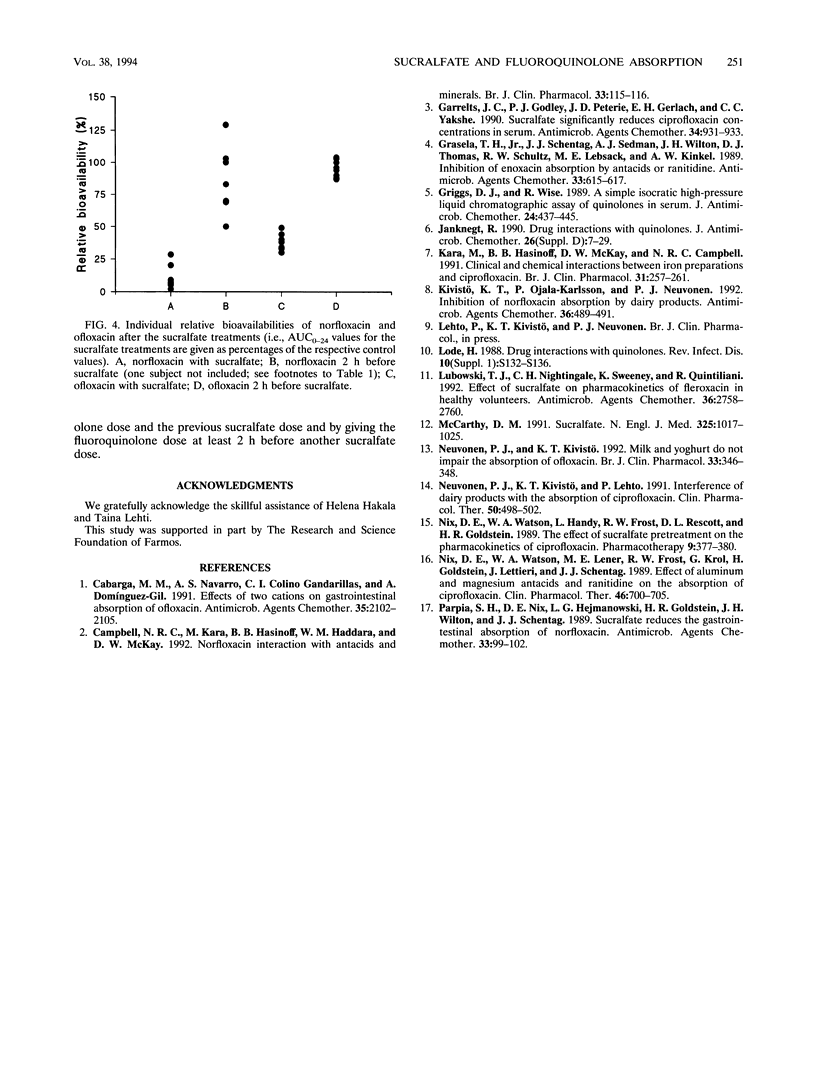
The effect of sucralfate on the pharmacokinetics of norfloxacin and ofloxacin was assessed in two separate crossover studies with healthy volunteers. In both studies, eight subjects were randomized to one of the following three regimens: a 400-mg dose of norfloxacin or ofloxacin alone, norfloxacin or ofloxacin given simultaneously with sucralfate (1 g), or norfloxacin or ofloxacin given 2 h before sucralfate. Coadministration of sucralfate reduced the bioavailability of norfloxacin and ofloxacin by 91% (P < 0.001) and 61% (P < 0.001), respectively. However, when norfloxacin and ofloxacin were given 2 h before sucralfate, there were no significant alterations in the pharmacokinetics of either fluoroquinolone. Similar results were obtained when the cumulative amount of each fluoroquinolone recovered in the urine was used to calculate bioavailability. To avoid these interactions and potential therapeutic failures, norfloxacin and ofloxacin should not be used concurrently with sucralfate. The interaction can be minimized by maximizing the time between the fluoroquinolone dose and the previous sucralfate dose and giving the fluoroquinolone at least 2 h before another sucralfate dose.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell N. R., Kara M., Hasinoff B. B., Haddara W. M., McKay D. W. Norfloxacin interaction with antacids and minerals. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;33(1):115–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrelts J. C., Godley P. J., Peterie J. D., Gerlach E. H., Yakshe C. C. Sucralfate significantly reduces ciprofloxacin concentrations in serum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):931–933. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grasela T. H., Jr, Schentag J. J., Sedman A. J., Wilton J. H., Thomas D. J., Schultz R. W., Lebsack M. E., Kinkel A. W. Inhibition of enoxacin absorption by antacids or ranitidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):615–617. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griggs D. J., Wise R. A simple isocratic high-pressure liquid chromatographic assay of quinolones in serum. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Sep;24(3):437–445. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.3.437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknegt R. Drug interactions with quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Nov;26 (Suppl 500):7–29. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.suppl_d.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara M., Hasinoff B. B., McKay D. W., Campbell N. R. Clinical and chemical interactions between iron preparations and ciprofloxacin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;31(3):257–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivistö K. T., Ojala-Karlsson P., Neuvonen P. J. Inhibition of norfloxacin absorption by dairy products. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):489–491. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H. Drug interactions with quinolones. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10 (Suppl 1):S132–S136. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.supplement_1.s132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubowski T. J., Nightingale C. H., Sweeney K., Quintiliani R. Effect of sucralfate on pharmacokinetics of fleroxacin in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2758–2760. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Cabarga M., Sánchez Navarro A., Colino Gandarillas C. I., Domínguez-Gil A. Effects of two cations on gastrointestinal absorption of ofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Oct;35(10):2102–2105. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.10.2102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy D. M. Sucralfate. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 3;325(14):1017–1025. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110033251407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Kivistö K. T., Lehto P. Interference of dairy products with the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Nov;50(5 Pt 1):498–502. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1991.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Kivistö K. T. Milk and yoghurt do not impair the absorption of ofloxacin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;33(3):346–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., Watson W. A., Handy L., Frost R. W., Rescott D. L., Goldstein H. R. The effect of sucralfate pretreatment on the pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin. Pharmacotherapy. 1989;9(6):377–380. doi: 10.1002/j.1875-9114.1989.tb04152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix D. E., Watson W. A., Lener M. E., Frost R. W., Krol G., Goldstein H., Lettieri J., Schentag J. J. Effects of aluminum and magnesium antacids and ranitidine on the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Dec;46(6):700–705. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parpia S. H., Nix D. E., Hejmanowski L. G., Goldstein H. R., Wilton J. H., Schentag J. J. Sucralfate reduces the gastrointestinal absorption of norfloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):99–102. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


