Abstract
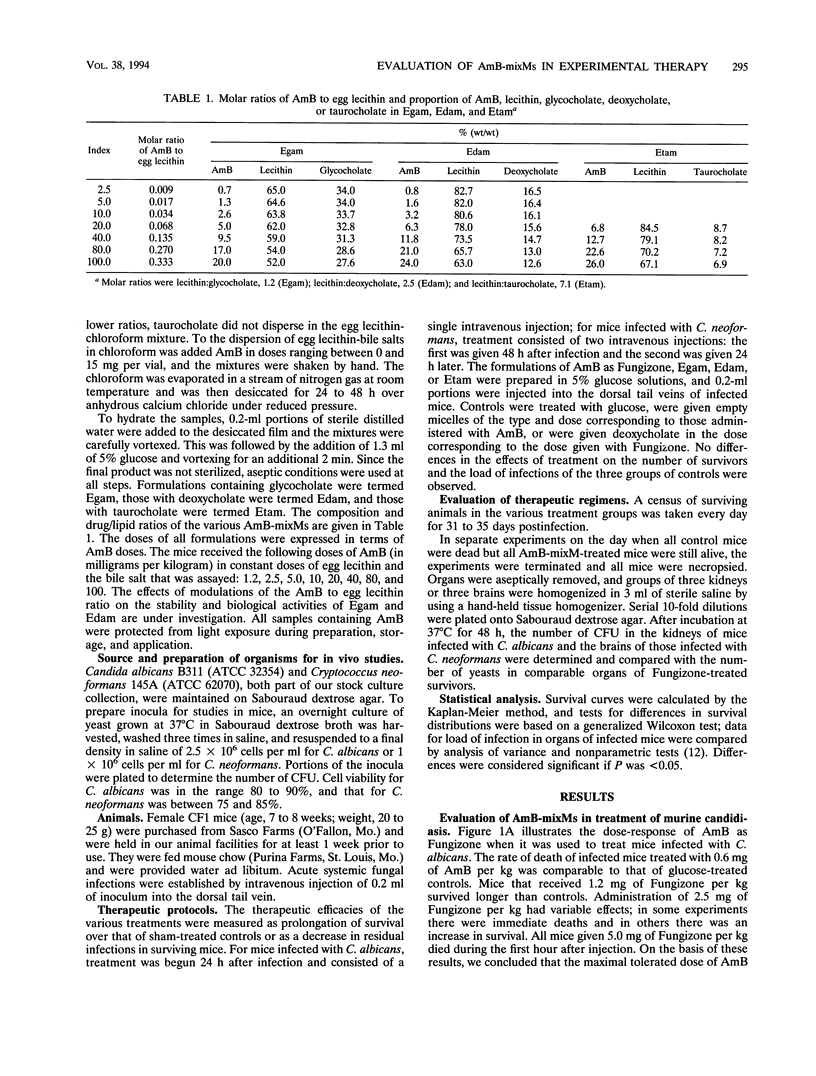
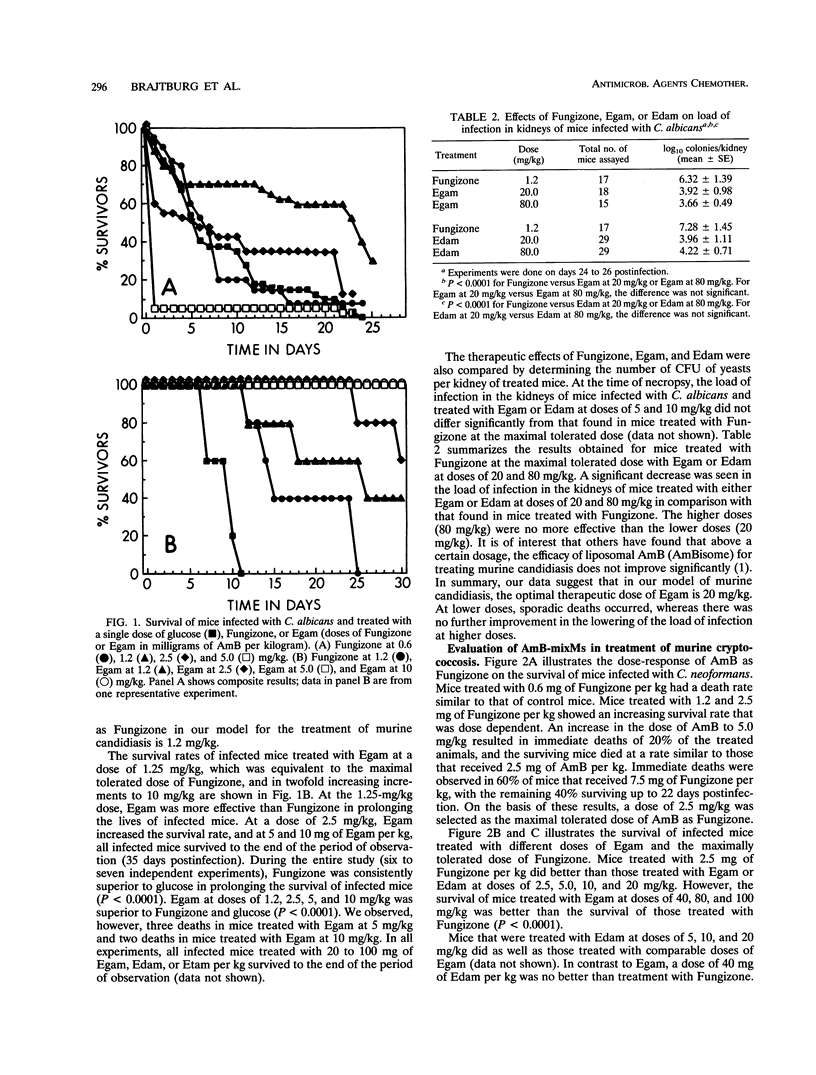
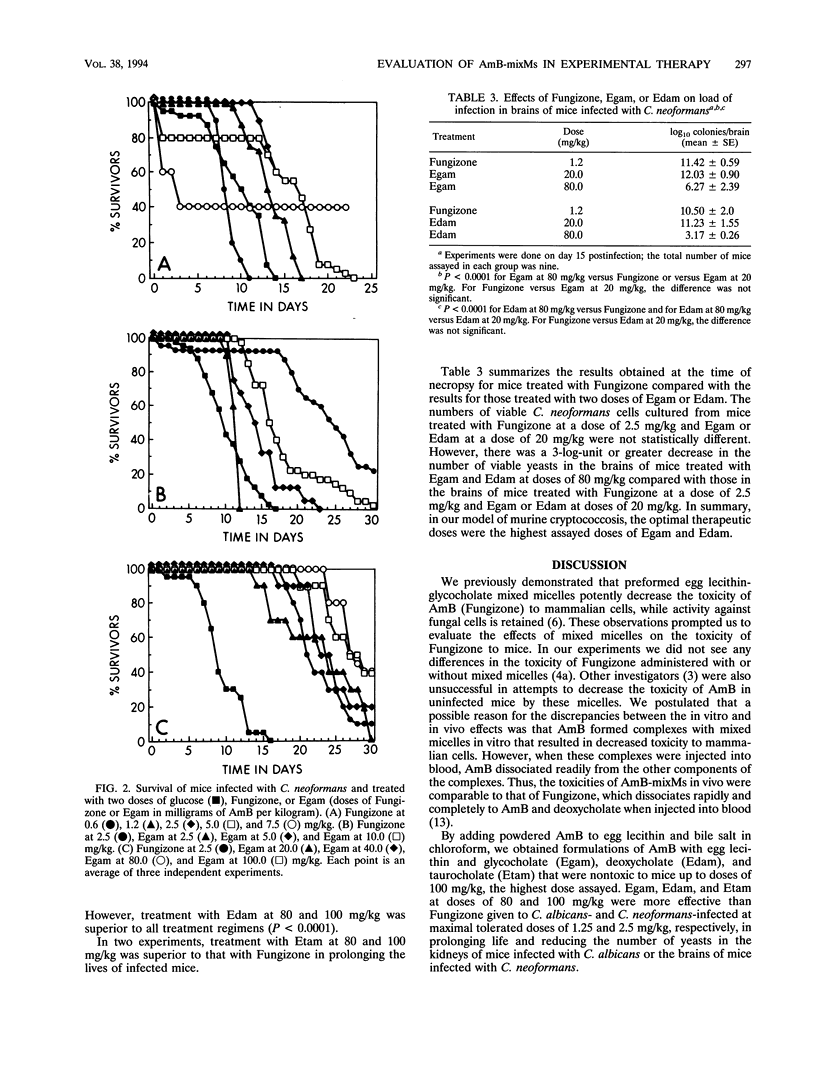
Amphotericin B (AmB) with deoxycholate (Fungizone) and AmB incorporated into mixed micelles (AmB-mixMs) composed of egg lecithin with glycocholate, deoxycholate, or taurocholate were compared as treatments for murine infections. For mice infected with Candida albicans, treatment consisted of a single intravenous injection; for mice infected with Cryptococcus neoformans, treatment consisted of two intravenous injections. The maximal tolerated doses of AmB as Fungizone were 1.25 mg/kg of body weight in mice with candidiasis and 2.5 mg/kg of body weight in mice with cryptococcosis. The AmB-mixMs were nontoxic to mice at doses of 80 and 100 mg/kg of body weight and were therapeutically more active than the maximal tolerated dose of Fungizone in both models of infection. However, when Fungizone or AmB-mixMs were administered at equivalent doses of AmB, AmB-mixMs were more active in treating murine candidiasis, whereas Fungizone was more active in treating murine cryptococcosis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler-Moore J. P., Chiang S. M., Satorius A., Guerra D., McAndrews B., McManus E. J., Proffitt R. T. Treatment of murine candidosis and cryptococcosis with a unilamellar liposomal amphotericin B formulation (AmBisome). J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Oct;28 (Suppl B):63–71. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.suppl_b.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangham A. D. Liposomes: realizing their promise. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 1992 Dec 15;27(12):51-6, 61-2. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1992.11705537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barwicz J., Christian S., Gruda I. Effects of the aggregation state of amphotericin B on its toxicity to mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Oct;36(10):2310–2315. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.10.2310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolard J., Legrand P., Heitz F., Cybulska B. One-sided action of amphotericin B on cholesterol-containing membranes is determined by its self-association in the medium. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 11;30(23):5707–5715. doi: 10.1021/bi00237a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Elberg S., Kobayashi G. S., Bolard J. Amphotericin B incorporated into egg lecithin-bile salt mixed micelles: molecular and cellular aspects relevant to therapeutic efficacy in experimental mycoses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Feb;38(2):300–306. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brajtburg J., Elberg S., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Inhibition of amphotericin B (Fungizone) toxicity to cells by egg lecithin-glycocholic acid mixed micelles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2415–2416. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Whitney R. R., Olsen S. J., George R. J., Swerdel M. R., Kunselman L., Bonner D. P. Amphotericin B lipid complex therapy of experimental fungal infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):615–621. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. S., Jr, Peacock J. E., Jr Amphotericin B revisited: reassessment of toxicity. Am J Med. 1990 May;88(5N):22N–27N. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemons K. V., Stevens D. A. Comparative efficacy of amphotericin B colloidal dispersion and amphotericin B deoxycholate suspension in treatment of murine coccidioidomycosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1829–1833. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds L. C., Davidson L., Bertino J. S., Jr Solubility and stability of amphotericin B in human serum. Ther Drug Monit. 1989;11(3):323–326. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198905000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gondal J. A., Swartz R. P., Rahman A. Therapeutic evaluation of free and liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic candidiasis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1544–1548. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Craven P. C., Taylor R. L., Williams D. M., Magee W. E. Treatment of murine cryptococcosis with liposome-associated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1982 May;145(5):748–752. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson L. H., Stevens D. A. Comparison of antifungal activity of amphotericin B deoxycholate suspension with that of amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate colloidal dispersion. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):486–488. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Mehta R., Lopez-Berestein G., Fainstein V., Juliano R. L. In vitro antifungal activities of amphotericin B and liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):387–389. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetler J. S., Clemons K. V., Hanson L. H., Stevens D. A. Efficacy and safety of amphotericin B colloidal dispersion compared with those of amphotericin B deoxycholate suspension for treatment of disseminated murine cryptococcosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2656–2660. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A. S. Lipids, liposomes, and rational drug design. Lab Invest. 1992 Jun;66(6):655–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsh R., Goldstein R., Tarloff J., Parris D., Hook J., Hanna N., Bugelski P., Poste G. An emulsion formulation of amphotericin B improves the therapeutic index when treating systemic murine candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1065–1070. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasic D. D. Mixed micelles in drug delivery. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):279–280. doi: 10.1038/355279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrand P., Romero E. A., Cohen B. E., Bolard J. Effects of aggregation and solvent on the toxicity of amphotericin B to human erythrocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2518–2522. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. J., Walsh T. J., Martinez A., Eichacker P. Q., Lopez-Berestein G., Natanson C. Cardiopulmonary toxicity after liposomal amphotericin B infusion. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Apr 15;114(8):664–666. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-8-664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Berestein G., Mehta R., Hopfer R. L., Mills K., Kasi L., Mehta K., Fainstein V., Luna M., Hersh E. M., Juliano R. Treatment and prophylaxis of disseminated infection due to Candida albicans in mice with liposome-encapsulated amphotericin B. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):939–945. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. P., el-Hariri L. M., Marriott C. Bile salt- and lysophosphatidylcholine-induced membrane damage in human erythrocytes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;44(8):646–650. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1992.tb05486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph E. D., Khazindar A. M., Barber K. R., Grant C. W. Comparative in vitro effects of liposomal amphotericin B, amphotericin B-deoxycholate, and free amphotericin B against fungal strains determined by using MIC and minimal lethal concentration susceptibility studies and time-kill curves. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):188–191. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaunak S., Cohen J. Clinical management of fungal infection in patients with AIDS. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Jul;28 (Suppl A):67–82. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.suppl_a.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Son K., Alkan H. Liposomes prepared dynamically by interactions between bile salt and phospholipid molecules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jun 6;981(2):288–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson C. E., Popescu M. C., Ginsberg R. S. Preparation and use of liposomes in the treatment of microbial infections. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988;15 (Suppl 1):S1–31. doi: 10.3109/10408418809104463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay C., Barza M., Fiore C., Szoka F. Efficacy of liposome-intercalated amphotericin B in the treatment of systemic candidiasis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):170–173. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyvoda O. S., Coleman R., Holdsworth G. Effects of different bile salts upon the composition and morphology of a liver plasma membrane preparation. Deoxycholate is more membrane damaging than cholate and its conjugates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 14;465(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90356-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



