Abstract
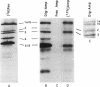
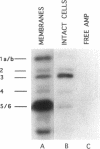
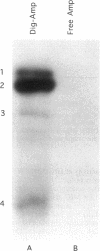
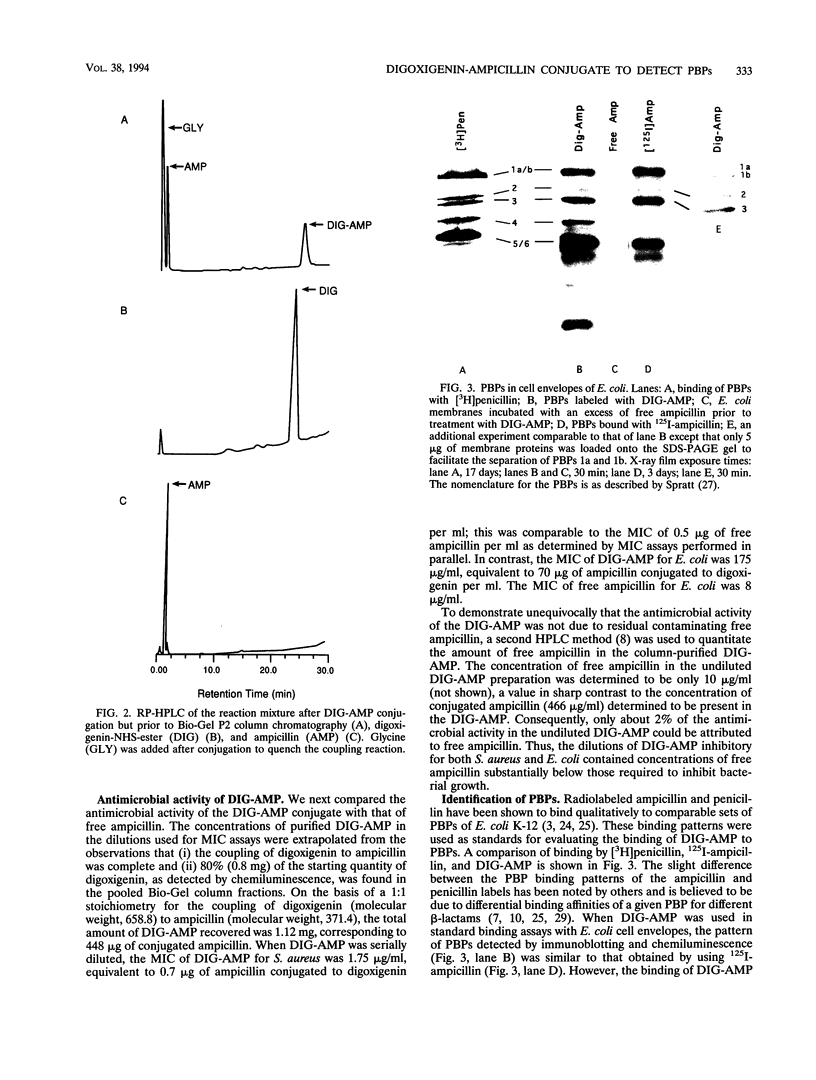
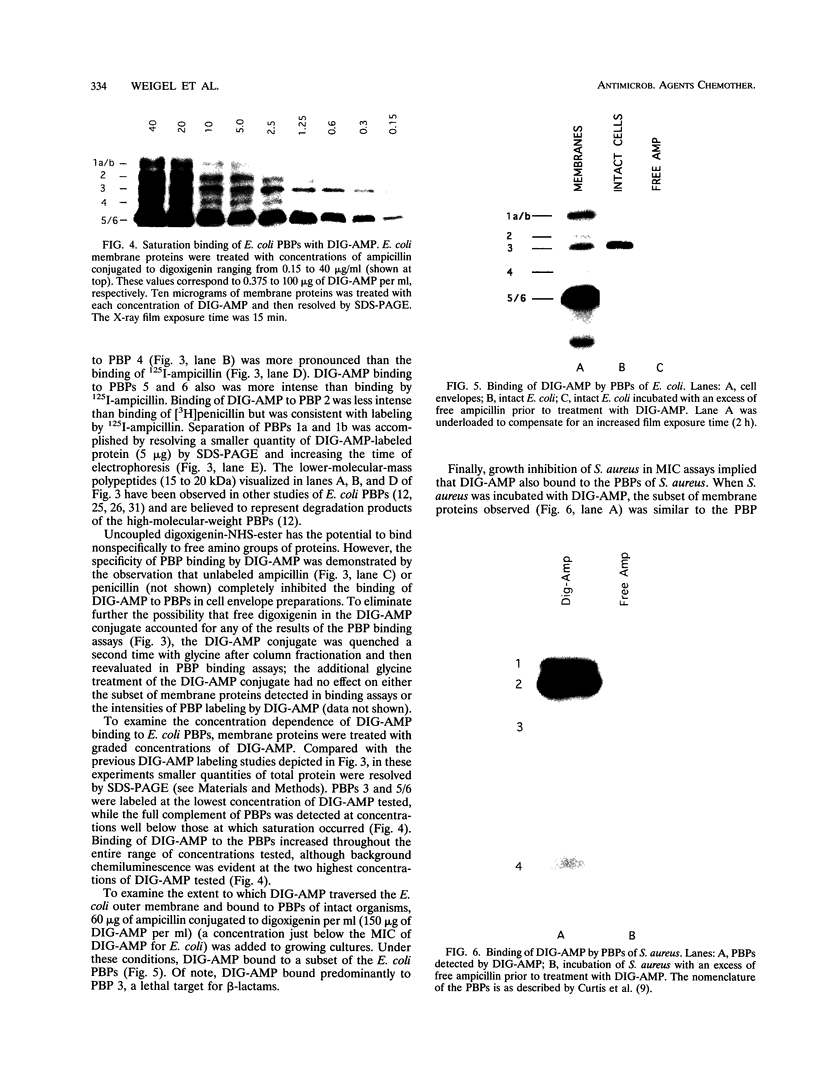
This paper describes a highly sensitive new method for the identification of penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) that is based on the use of an ampicillin-digoxigenin conjugate (DIG-AMP conjugate) which is detected by immunoblotting and chemiluminescence. The sensitivity of chemiluminescence permitted X-ray film exposure times to be decreased to minutes, as opposed to the days or weeks which are requisite when conventionally radiolabeled beta-lactams are used. Coupling of ampicillin to digoxigenin yielded a product containing digoxigenin (detected by chemiluminescence) which also was inhibitory for Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Unconjugated digoxigenin at concentrations of up to 100 micrograms/ml was not inhibitory for either organism. For S. aureus the MICs of DIG-AMP (0.7 microgram of conjugated ampicillin per ml) and of free ampicillin (0.5 microgram/ml) were comparable, indicating that ampicillin retained its bioactivity when coupled to digoxigenin. However, for E. coli the MICs of DIG-AMP (70 micrograms of conjugated ampicillin per ml) and of free ampicillin (8 micrograms/ml) were widely disparate, suggesting that the DIG-AMP conjugate was too large and/or hydrophobic to traverse the E. coli outer membrane via porins. DIG-AMP binding assays with E. coli and S. aureus cell envelopes revealed profiles of PBPs similar to those detected with 125I-ampicillin or [3H]penicillin. DIG-AMP binding to PBPs was completely inhibited in competition experiments with free ampicillin or penicillin, supporting the specificity of the DIG-AMP conjugate for PBPs. DIG-AMP thus represents an advantageous alternative to radioactive beta-lactams for the identification and analysis of PBPs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botta G. A., Park J. T. Evidence for involvement of penicillin-binding protein 3 in murein synthesis during septation but not during cell elongation. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):333–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.333-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowler L. D., Spratt B. G. Membrane topology of penicillin-binding protein 3 of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1277–1286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain A., White S., Bawdon R., Thomas S., Larsen B. Pharmacokinetics of ampicillin and sulbactam in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Feb;168(2):667–673. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90515-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galleni M., Lakaye B., Lepage S., Jamin M., Thamm I., Joris B., Frère J. M. A new, highly sensitive method for the detection and quantification of penicillin-binding proteins. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):19–21. doi: 10.1042/bj2910019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Binding of beta-lactam antibiotics to penicillin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):834–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Penicillin-binding proteins in bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):148–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltke H. J., Sagner G., Kessler C., Schmitz G. Sensitive chemiluminescent detection of digoxigenin-labeled nucleic acids: a fast and simple protocol and its applications. Biotechniques. 1992 Jan;12(1):104–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler C., Höltke H. J., Seibl R., Burg J., Mühlegger K. Non-radioactive labeling and detection of nucleic acids. I. A novel DNA labeling and detection system based on digoxigenin: anti-digoxigenin ELISA principle (digoxigenin system). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Oct;371(10):917–927. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.2.917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlegger K., Huber E., von der Eltz H., Rüger R., Kessler C. Non-radioactive labeling and detection of nucleic acids. IV. Synthesis and properties of digoxigenin-modified 2'-deoxyuridine-5'-triphosphates and a photoactivatable analog of digoxigenin (photodigoxigenin). Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Oct;371(10):953–965. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.2.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisabarro A. G., Prats R., Váquez D., Rodríguez-Tébar A. Activity of penicillin-binding protein 3 from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):199–206. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.199-206.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plésiat P., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria are permeable to steroid probes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1323–1333. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats R., Gomez M., Pla J., Blasco B., Ayala J. A. A new beta-lactam-binding protein derived from penicillin-binding protein 3 of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5194–5198. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5194-5198.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Moomaw C., Slaughter C. A., Norgard M. V. Penicillin-binding proteins and peptidoglycan of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1248-1254.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. E., Brown D. F. Penicillin-binding proteins of beta-lactam-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Effect of growth conditions. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):28–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F., Ayala J. A., de la Rosa E. J., de Pedro M. A., Arán V., Berenguer J., Vázquez D. Binding of 125I-labeled beta-lactam antibiotics to the penicillin binding proteins of Escherichia coli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Apr;37(4):389–393. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Cromie K. D. Penicillin-binding proteins of gram-negative bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):699–711. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Pardee A. B. Penicillin-binding proteins and cell shape in E. coli. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):516–517. doi: 10.1038/254516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wientjes F. B., Olijhoek T. J., Schwarz U., Nanninga N. Labeling pattern of major penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli during the division cycle. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1287–1293. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1287-1293.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]