Abstract
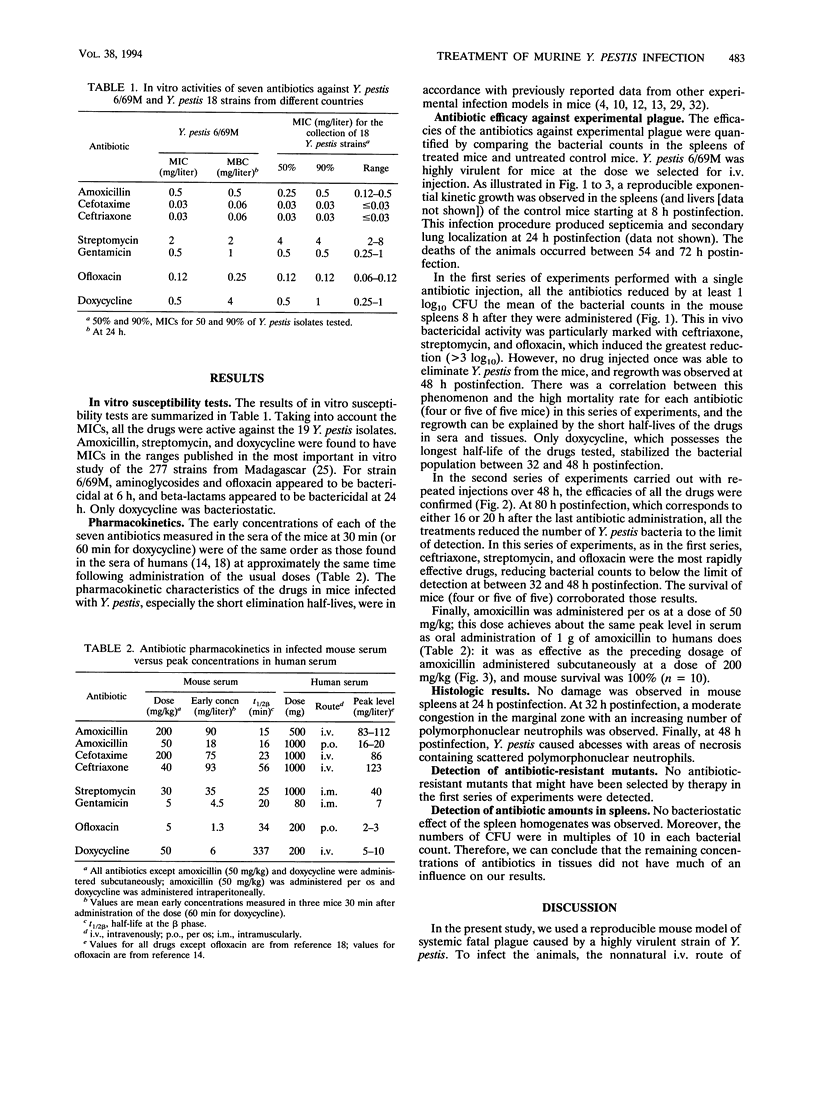
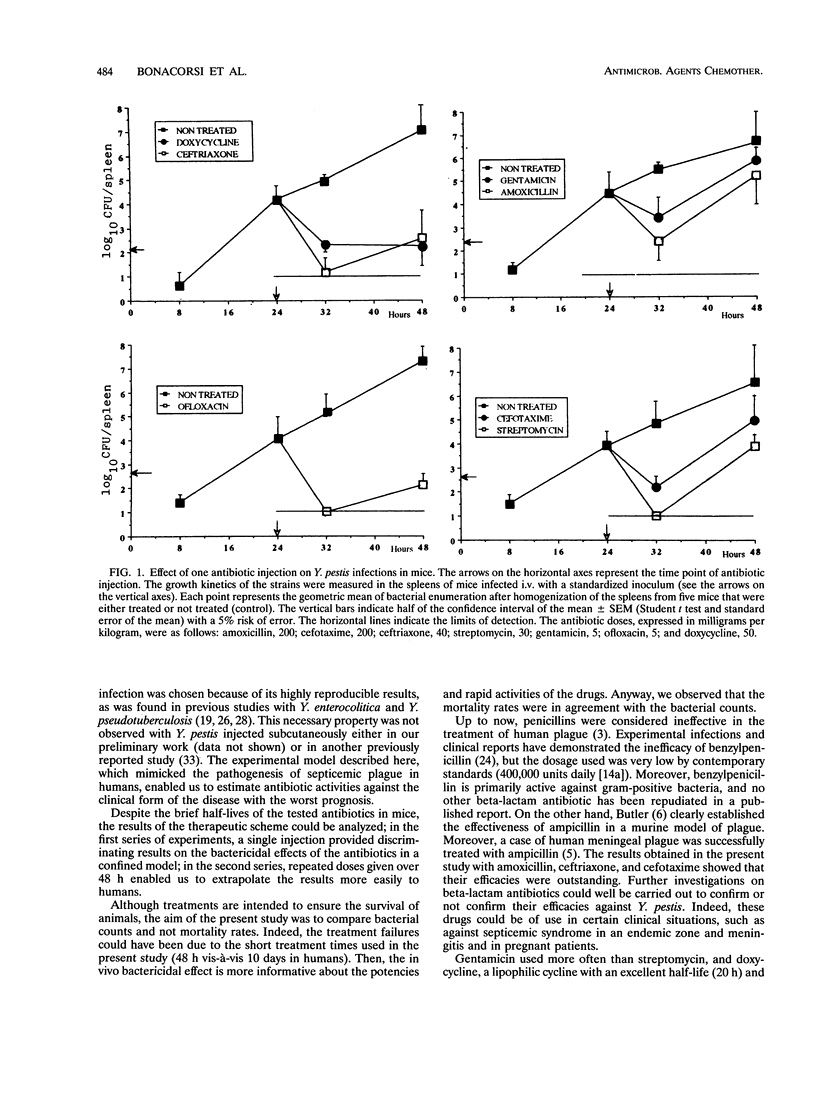
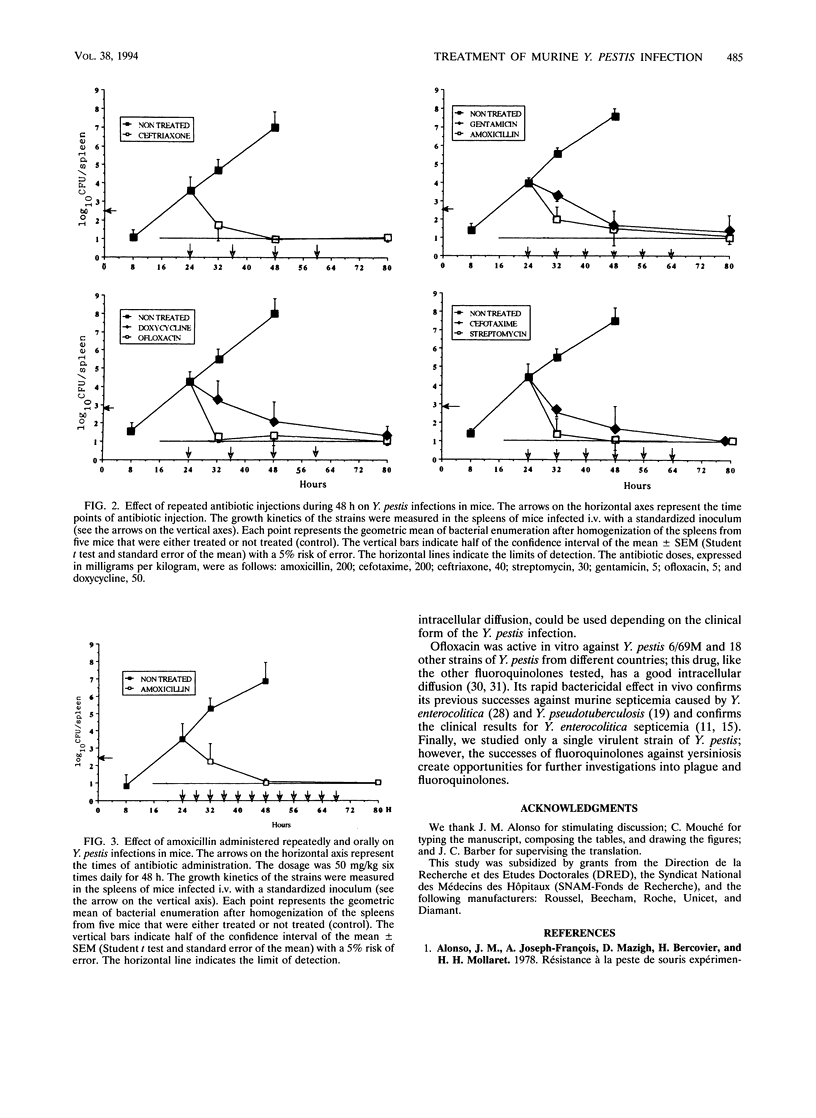
Amoxicillin, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, gentamicin, doxycycline, and ofloxacin were active in vitro, like the reference drug streptomycin, against the virulent strain Yersinia pestis 6/69M. The comparative efficacies of these drugs in vivo were evaluated in a standardized and reproducible mouse model of systemic infection. Each antibiotic was injected intravenously once, at 24 h postinfection, and then repeatedly during 48 h. In vivo results were measured by counting the viable bacteria recovered from the whole spleens of mice sacrificed at selected times. All the drugs were manifestly successful; ceftriaxone, ofloxacine, and the reference drug were the most effective. Therefore, gentamicin and doxycycline could be used, depending on the clinical forms of the Y. pestis infection. Further investigations on beta-lactams, especially those used in the present study, could be carried out to confirm or not confirm their activities against Y. pestis. Ofloxacin appeared to be as active and to perform as rapidly as streptomycin in the treatment of murine Y. pestis infection, which is in agreement with the previous successes obtained with the use of fluoroquinolones in the treatment of murine infections caused by other pathogenic yersiniae.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alsofrom D. J., Mettler F. A., Jr, Mann J. M. Radiographic manifestations of plaque in New Mexico, 1975-1980. A review of 42 proved cases. Radiology. 1981 Jun;139(3):561–565. doi: 10.1148/radiology.139.3.7232721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale A. S., Gisby J., Sutherland R. Efficacy of amoxycillin/clavulanic acid in experimental Bacteroides fragilis/Escherichia coli mixed infections. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Apr;21(4):451–459. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker T. M., Poland J. D., Quan T. J., White M. E., Mann J. M., Barnes A. M. Plague meningitis--a retrospective analysis of cases reported in the United States, 1970-1979. West J Med. 1987 Nov;147(5):554–557. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carniel E., Guiyoule A., Mercereau-Puijalon O., Mollaret H. H. Chromosomal marker for the 'high pathogenicity' phenotype in Yersinia. Contrib Microbiol Immunol. 1991;12:192–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frimodt-Møller N., Bentzon M. W., Thomsen V. F. Experimental infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae in mice: correlation of in vitro activity and pharmacokinetic parameters with in vivo effect for 14 cephalosporins. J Infect Dis. 1986 Sep;154(3):511–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.3.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gayraud M., Scavizzi M. R., Mollaret H. H., Guillevin L., Hornstein M. J. Antibiotic treatment of Yersinia enterocolitica septicemia: a retrospective review of 43 cases. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Sep;17(3):405–410. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.3.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Brugger H. P., Feller C., Stritzko T., Stalder B. Antibiotic therapy of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in normal and granulocytopenic mice: comparison of murine and human pharmacokinetics. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):90–97. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisby J., Wightman B. J., Beale A. S. Comparative efficacies of ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, and cefaclor against experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae respiratory infections in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):831–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guay D. R., Opsahl J. A., McMahon F. G., Vargas R., Matzke G. R., Flor S. Safety and pharmacokinetics of multiple doses of intravenous ofloxacin in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):308–312. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HADDAD C., VALERO A. Streptomycin in bubonic plague. Br Med J. 1948 May 29;1(4560):1026–1026. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4560.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogkamp-Korstanje J. A. The possible role of quinolones in yersiniosis. Drugs. 1987;34 (Suppl 1):134–138. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198700341-00029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornstein M. J., Jupeau A. M., Scavizzi M. R., Philippon A. M., Grimont P. A. In vitro susceptibilities of 126 clinical isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica to 21 beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):806–811. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull H. F., Montes J. M., Mann J. M. Septicemic plague in New Mexico. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):113–118. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre B. C., Mazigh D. A., Scavizzi M. R. Failure of beta-lactam antibiotics and marked efficacy of fluoroquinolones in treatment of murine Yersinia pseudotuberculosis infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1785–1790. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER K. F. Modern therapy of plague. J Am Med Assoc. 1950 Nov 18;144(12):982–985. doi: 10.1001/jama.1950.02920120006003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall J. D., Jr, Joy R. J., Ai N. V., Quy D. V., Stockard J. L., Gibson F. L. Plague in Vietnam 1965-1966. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 Nov;86(3):603–616. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazigh D., Quilici M. L., Mollaret H. H. Role of the virulence-associated plasmids of Yersinia enterocolitica on its immunogenicity against Y. pestis. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Nov-Dec;135B(3):283–290. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello D. A. "In vitro" sensitivity of 100 strains of Pasteurella pestis from Northeastern Brazil to antibiotics and a compound sulphonamides. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1970 May-Jun;12(3):195–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasoamanana B., Coulanges P., Michel P., Rasolofonirina N. Sensibilité de Yersinia pestis aux antibiotiques: 277 souches isolées à Madagascar entre 1926 et 1989. Arch Inst Pasteur Madagascar. 1989;56(1):37–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scavizzi M. R., Alonso J. M., Philippon A. M., Jupeau-Vessieres A. M., Guiyoule A. Failure of newer beta-lactam antibiotics for murine Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):523–526. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasha B., Lang R., Rubinstein E. Therapy of experimental murine brucellosis with streptomycin, co-trimoxazole, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, pefloxacin, doxycycline, and rifampin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):973–976. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T., Osada Y. Penetrability of ofloxacin into cultured epithelial cells and macrophages. Arzneimittelforschung. 1988 Sep;38(9):1265–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Matsumoto T., Husson M. Intraphagocytic penetration of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Aug;22(2):185–192. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Leggett J., Turnidge J., Ebert S., Craig W. A. Correlation of antimicrobial pharmacokinetic parameters with therapeutic efficacy in an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):831–847. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER D. L., FOSTER L. E., CHEN T. H., LARSON A., MEYER K. F. Studies on immunization against plague. V. Multiplication and persistence of virulent and avirulent Pasteurella pestis in mice and guinea pigs. J Immunol. 1953 Mar;70(3):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welty T. K., Grabman J., Kompare E., Wood G., Welty E., Van Duzen J., Rudd P., Poland J. Nineteen cases of plague in Arizona. A spectrum including ecthyma gangrenosum due to plague and plague in pregnancy. West J Med. 1985 May;142(5):641–646. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



