Abstract
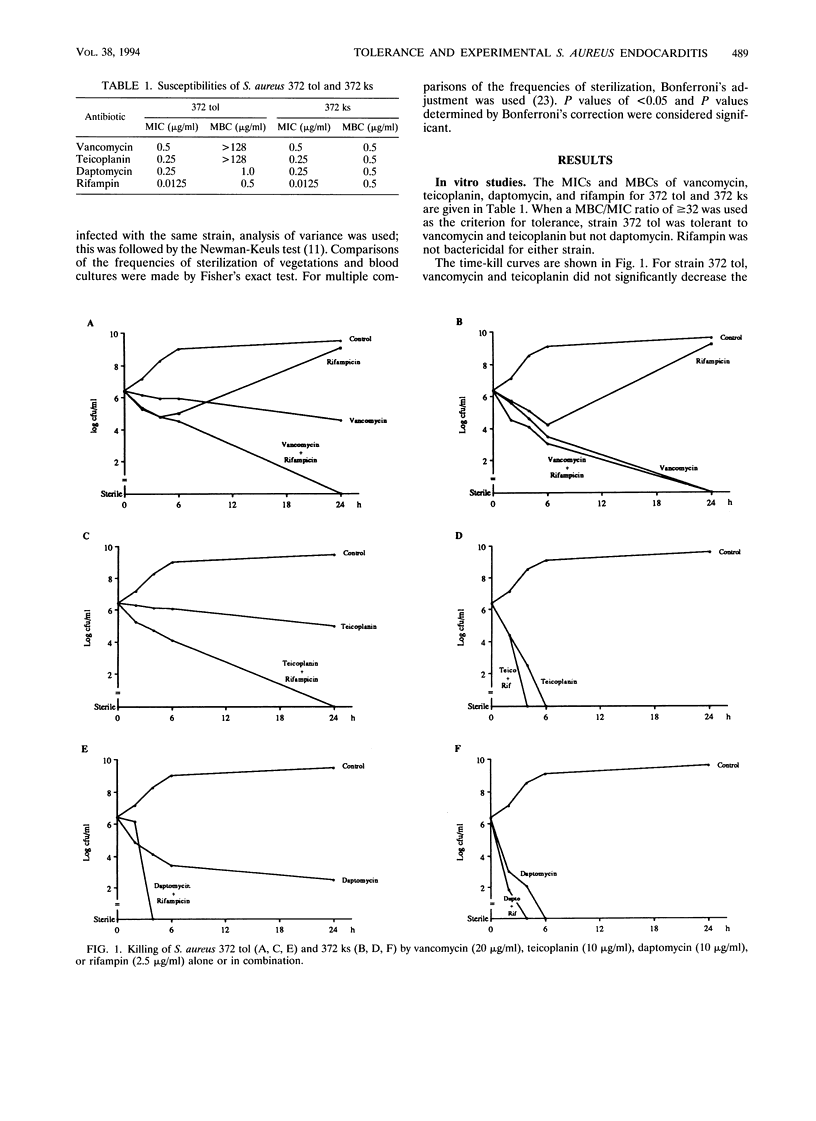
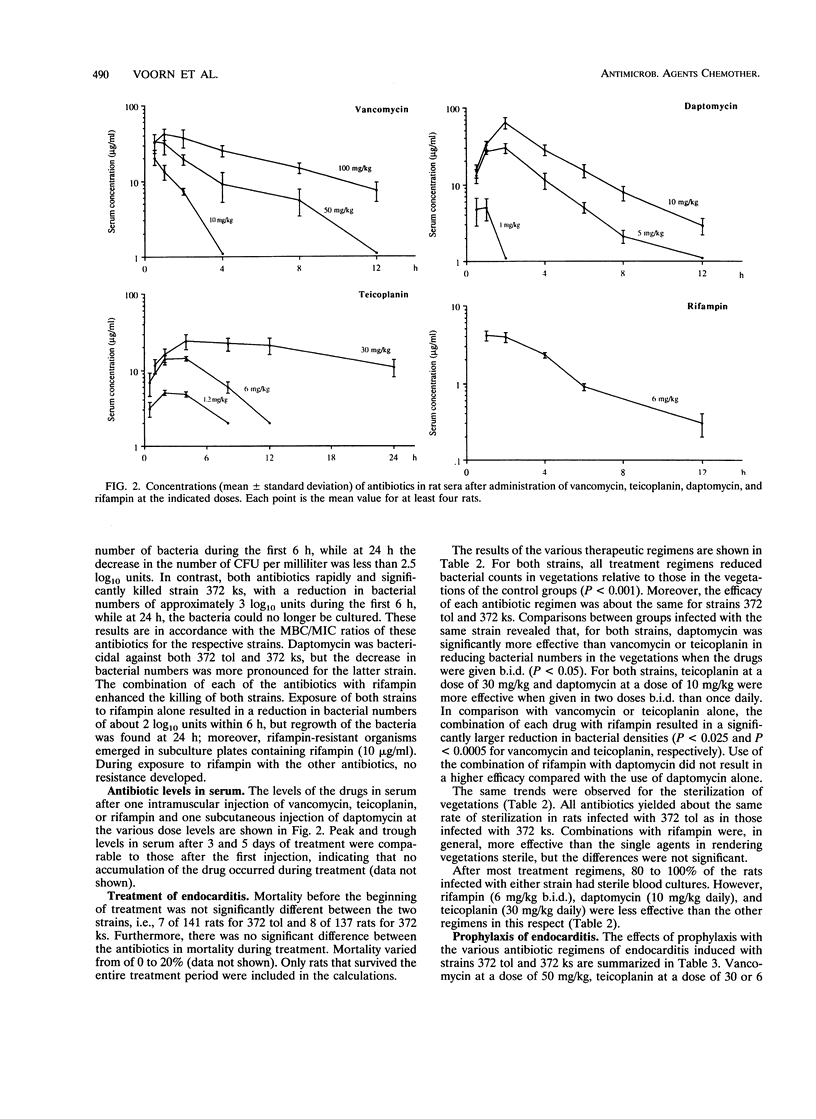
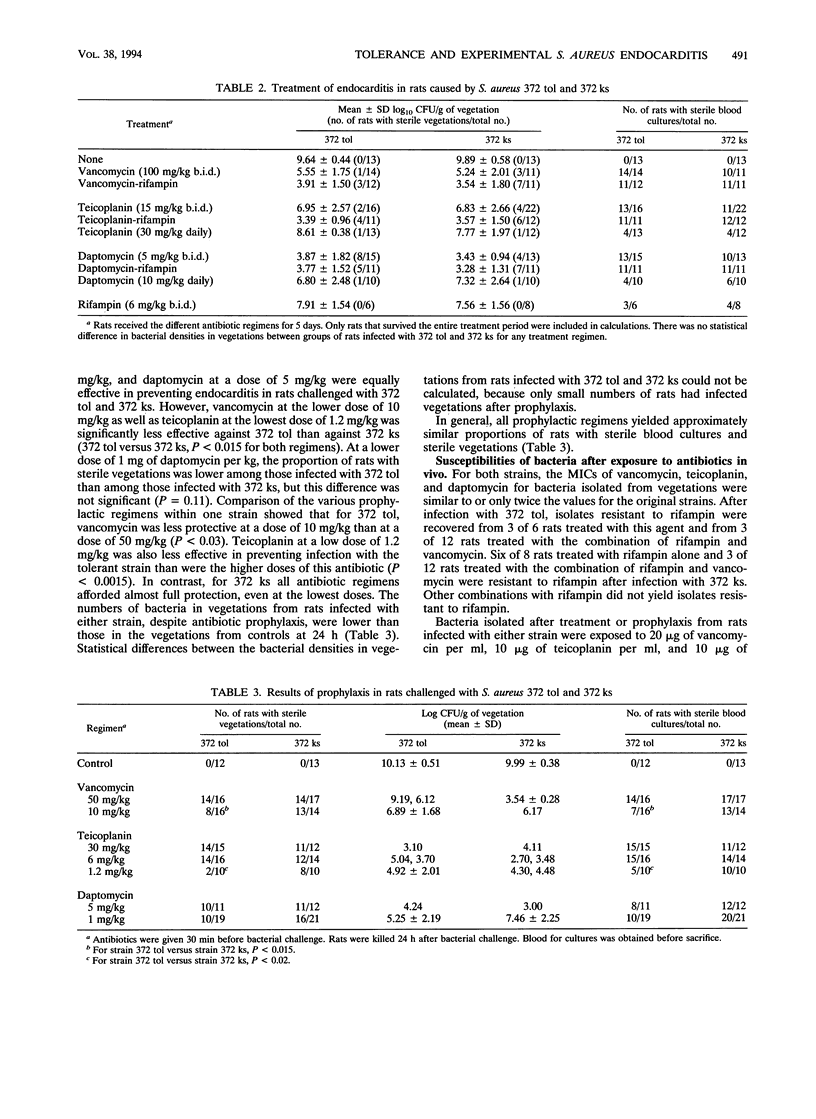
The role of Staphylococcus aureus tolerance in the treatment and prophylaxis of endocarditis in rats was investigated. The efficacies of vancomycin, teicoplanin, and daptomycin, alone and in combination with rifampin, were compared in rats with endocarditis infected with a tolerant strain of S. aureus and in rats with endocarditis infected with its nontolerant variant. In vitro the cloxacillin-tolerant strain was also tolerant to vancomycin and teicoplanin, but not to daptomycin. However, tolerance to these antibiotics did not influence the results of treatment of experimental S. aureus endocarditis. There was no difference in the bacterial densities in the vegetations of rats infected with either the tolerant or the nontolerant strain after 5 days of treatment with any of the antibiotic regimens. Of all antibiotics, daptomycin was the most effective in reducing bacterial numbers in vegetations. Combination of rifampin with vancomycin or teicoplanin improved the results of treatment for the tolerant as well as the nontolerant strains. Daptomycin was as effective alone as in combination with rifampin. In contrast, tolerance influenced the prophylactic effects of vancomycin and teicoplanin. The proportion of rats with sterile vegetations after prophylaxis with vancomycin or teicoplanin at a low dose was lower for those infected with the tolerant strain than for those infected with the nontolerant strain. A low dose of daptomycin was equally effective against the tolerant and the nontolerant strains. However, higher doses of all three antibiotics afforded almost full protection against both strains.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen N. E., Alborn W. E., Jr, Hobbs J. N., Jr Inhibition of membrane potential-dependent amino acid transport by daptomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2639–2642. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Lam K. Efficacy of vancomycin plus rifampin in experimental aortic-valve endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: in vitro-in vivo correlations. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):157–165. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard J. P., Francioli P., Glauser M. P. Vancomycin prophylaxis of experimental Streptococcus sanguis. Inhibition of bacterial adherence rather than bacterial killing. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1113–1116. doi: 10.1172/JCI110337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. O., Durack D. T. Therapeutic significance of penicillin tolerance in experimental streptococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):273–277. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantoni L., Glauser M. P., Bille J. Comparative efficacy of daptomycin, vancomycin, and cloxacillin for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in rats and role of test conditions in this determination. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2348–2353. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron F., Kitzis M. D., Gutmann L., Cremieux A. C., Maziere B., Vallois J. M., Saleh-Mghir A., Lemeland J. F., Carbon C. Daptomycin or teicoplanin in combination with gentamicin for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to a highly glycopeptide-resistant isolate of Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2611–2616. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremieux A. C., Maziere B., Vallois J. M., Ottaviani M., Azancot A., Raffoul H., Bouvet A., Pocidalo J. J., Carbon C. Evaluation of antibiotic diffusion into cardiac vegetations by quantitative autoradiography. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):938–944. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debbia E., Pesce A., Schito G. C. In vitro activity of LY146032 alone and in combination with other antibiotics against gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):279–281. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin R., Modin G., Kunz S., Rich R., Zak O., Sande M. Comparative efficacies of ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin, and vancomycin in combination with rifampin in a rat model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus chronic osteomyelitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1014–1016. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faville R. J., Jr, Zaske D. E., Kaplan E. L., Crossley K., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Combined therapy with vancomycin and rifampin. JAMA. 1978 Oct 27;240(18):1963–1965. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.18.1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey K. Statistics in practice. Comparing the means of several groups. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1450–1456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goessens W. H., Fontijne P., Michel M. F. Responses of tolerant and nontolerant Staphylococcus aureus strains to methicillin treatment in an experimental infection in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):829–832. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal V., Bisno A. L., Silverblatt F. J. Failure of vancomycin treatment in Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. In vivo and in vitro observations. JAMA. 1976 Oct 4;236(14):1604–1606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Tomasz A. Antibiotic tolerance among clinical isolates of bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):368–386. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J., Dankert J., Durack D. Significance of penicillin tolerance in vivo: prevention of experimental Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jun;11(6):555–564. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.6.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Héraïef E., Glauser M. P., Freedman L. R. Natural history of aortic valve endocarditis in rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):127–131. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.127-131.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Dorman N. J., Lerner S. A. Emergence of teicoplanin resistance during therapy of Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):103–108. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Reddy V. N., Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J. Daptomycin compared with teicoplanin and vancomycin for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2081–2085. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Bayer A. S. Significance of in-vitro penicillin tolerance in experimental enterococcal endocarditis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Apr;19(4):475–485. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.4.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leport C., Perronne C., Massip P., Canton P., Leclercq P., Bernard E., Lutun P., Garaud J. J., Vilde J. L. Evaluation of teicoplanin for treatment of endocarditis caused by gram-positive cocci in 20 patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):871–876. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. P., Fromm B. S., Reddy B. R. Slow response to vancomycin or vancomycin plus rifampin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Nov 1;115(9):674–680. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-9-674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacArthur R. D., Jackson G. G. An evaluation of the use of statistical methodology in the Journal of Infectious Diseases. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):349–354. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manquat G., Croize J., Stahl J. P., Meyran M., Hirtz P., Micoud M. Failure of teicoplanin treatment associated with an increase in MIC during therapy of Staphylococcus aureus septicaemia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Jun;29(6):731–732. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.6.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeson J., McColm A. A., Acred P., Greenwood D. Differential response to benzylpenicillin in vivo of tolerant and non-tolerant variants of Streptococcus sanguis II. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jan;25(1):103–109. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. F., van Leeuwen W. B. Degree and stability of tolerance to penicillin in Streptococcus pyogenes. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;8(3):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF01965265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujadas R., Escriva E., Jane J., Argimon J., Fernandez F., Fava P., Galera M., Garau J. Tolerance and efficacy of parenterally administered penicillin-streptomycin and orally administered amoxicillin or penicillin V for prophylaxis of experimentally induced streptococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):321–325. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. E. Structure, biochemistry and mechanism of action of glycopeptide antibiotics. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Nov;8(11):943–950. doi: 10.1007/BF01967563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrell T. C., Packham D. R., Shanker S., Foldes M., Munro R. Vancomycin therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):344–350. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton C. W., Liu C., Weeks L. S. Activity of LY146032 compared with that of methicillin, cefazolin, cefamandole, cefuroxime, ciprofloxacin, and vancomycin against staphylococci as determined by kill-kinetic studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Aug;31(8):1210–1215. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.8.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Albino A., Zanati E. Multiple antibiotic resistance in a bacterium with suppressed autolytic system. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):138–140. doi: 10.1038/227138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Miller H. Comparative in vitro activities of teichomycin and vancomycin alone and in combination with rifampin and aminoglycosides against staphylococci and enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):411–412. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon C. U., Washburn D. Teicoplanin and rifampicin singly and in combination in the treatment of experimental Staphylococcus epidermidis endocarditis in the rabbit model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Aug;20(2):233–237. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorn G. P., Thompson J., Goessens W. H., Schmal-Bauer W., Broeders P. H., Michel M. F. Role of tolerance in cloxacillin treatment of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):640–643. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorn G. P., Thompson J., Goessens W. H., Schmall-Bauer W., Broeders P. H., Michel M. F. Role of tolerance in cloxacillin prophylaxis of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jul;166(1):169–173. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.1.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C., Guerriero J. C. Interaction between vancomycin and rifampin against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1089–1091. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



