Abstract
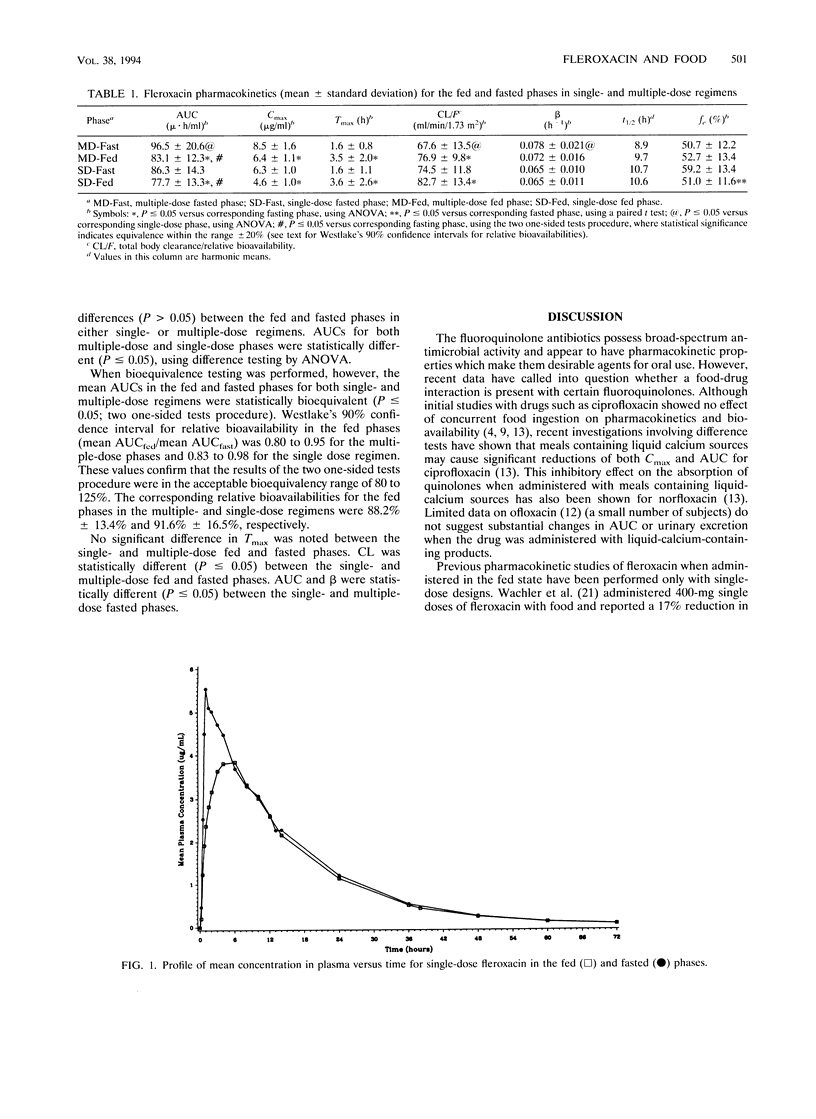
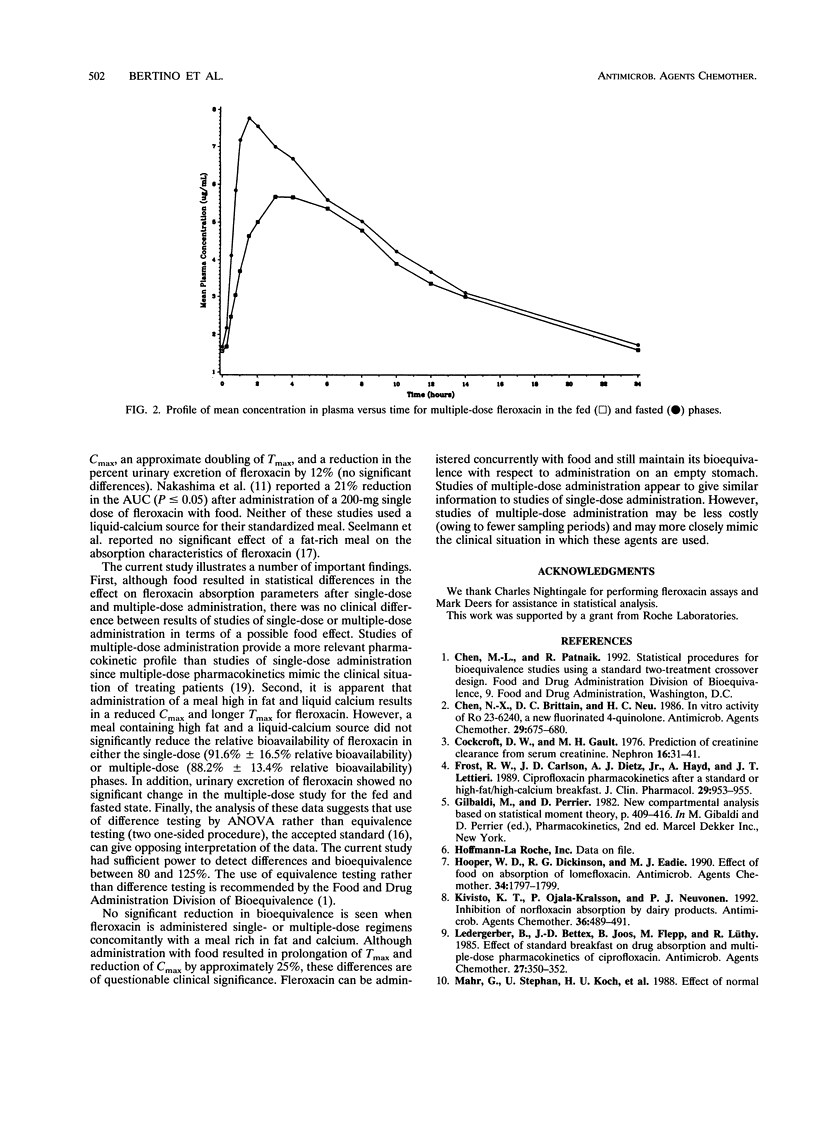
The effect of a fat- and liquid-calcium-rich meal on the pharmacokinetics of single and multiple doses of fleroxacin in 20 healthy men and women was investigated in a randomized crossover fashion. Fleroxacin was administered as 400 mg daily for 3 days and as a single 400 mg dose. Concurrent administration of fleroxacin with food resulted in a statistically significant (P < or = 0.05) decrease in the area under the curve (13.9% for multiple-dose administration, 10% for single-dose administration) and in the peak concentration (25.9% for multiple-dose administration, 27% for single-dose administration) and a lengthening of the time to peak (more than doubled for single- and multiple-dose phases). In addition, by using an equivalence criteria of 80 to 125%, the two one-sided tests procedure indicated that the mean areas under the curves for fleroxacin administered in a fed and a fasted state were statistically bioequivalent (P < or = 0.05) for both the single- and multiple-dose regimens. Although a meal high in fat and containing liquid calcium reduces the peak concentration by approximately 25%, a minimal effect on bioavailability is seen with concomitant food administration. In addition, multiple-dose bioavailability studies appear to give similar information to single-dose studies while representing the clinical setting more closely.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin N. X., Brittain D. C., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of Ro 23-6240, a new fluorinated 4-quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):675–680. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Gault M. H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41. doi: 10.1159/000180580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost R. W., Carlson J. D., Dietz A. J., Jr, Heyd A., Lettieri J. T. Ciprofloxacin pharmacokinetics after a standard or high-fat/high-calcium breakfast. J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;29(10):953–955. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1989.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper W. D., Dickinson R. G., Eadie M. J. Effect of food on absorption of lomefloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1797–1799. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivistö K. T., Ojala-Karlsson P., Neuvonen P. J. Inhibition of norfloxacin absorption by dairy products. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Feb;36(2):489–491. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.2.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledergerber B., Bettex J. D., Joos B., Flepp M., Lüthy R. Effect of standard breakfast on drug absorption and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):350–352. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima M., Kanamaru M., Uematsu T., Takiguchi A., Mizuno A., Itaya T., Kawahara F., Ooie T., Saito S., Uchida H. Clinical pharmacokinetics and tolerance of fleroxacin in healthy male volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Oct;22 (Suppl 500):133–144. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.supplement_d.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Kivistö K. T., Lehto P. Interference of dairy products with the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Nov;50(5 Pt 1):498–502. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1991.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Kivistö K. T. Milk and yoghurt do not impair the absorption of ofloxacin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;33(3):346–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. H., Reeves D. S. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Microbiology, pharmacokinetics and clinical use. Drugs. 1988 Aug;36(2):193–228. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198836020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuirmann D. J. A comparison of the two one-sided tests procedure and the power approach for assessing the equivalence of average bioavailability. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1987 Dec;15(6):657–680. doi: 10.1007/BF01068419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi A. A., Bochner F., Keal J. A., Rolan P. E., Smith M. Effect of food on enoxacin absorption. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):638–639. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinijans V. W., Hauschke D., Jonkman J. H. Controversies in bioequivalence studies. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1992 Apr;22(4):247–253. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199222040-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verho M., Malerczyk V., Dagrosa E., Korn A. The effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin. Curr Med Res Opin. 1986;10(3):166–171. doi: 10.1185/03007998609110436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



