Abstract
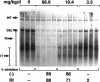
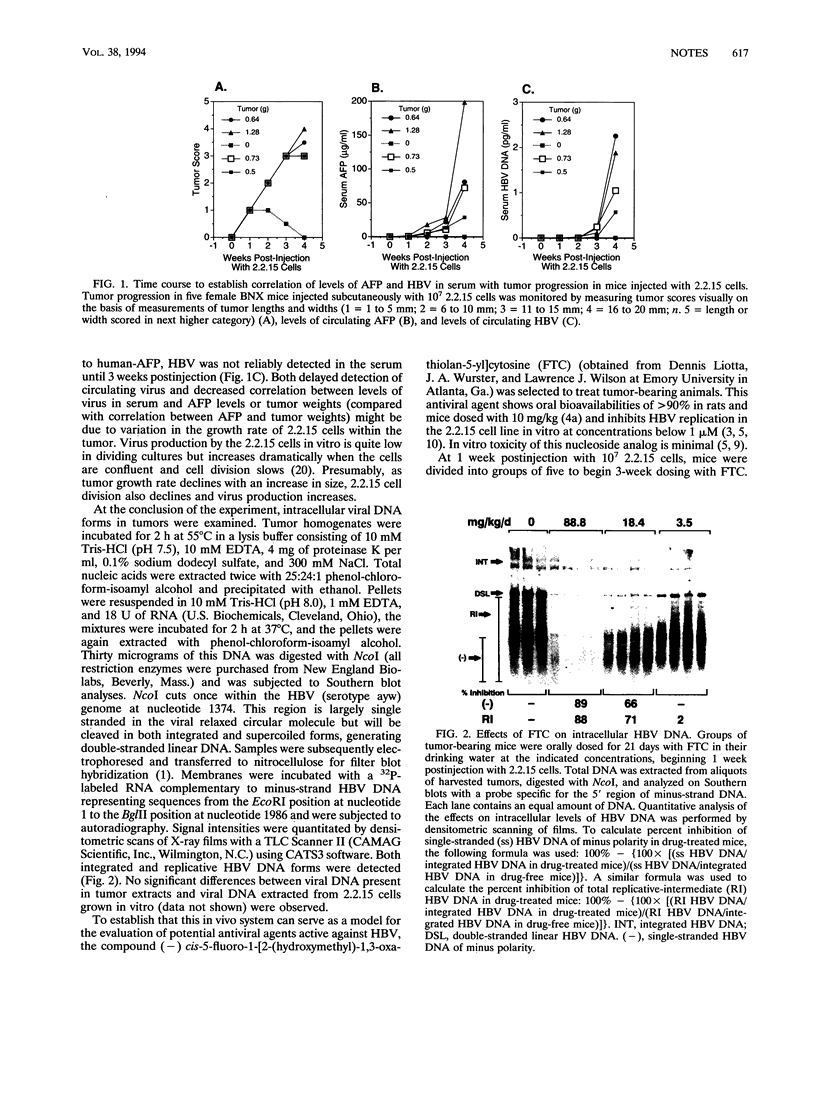
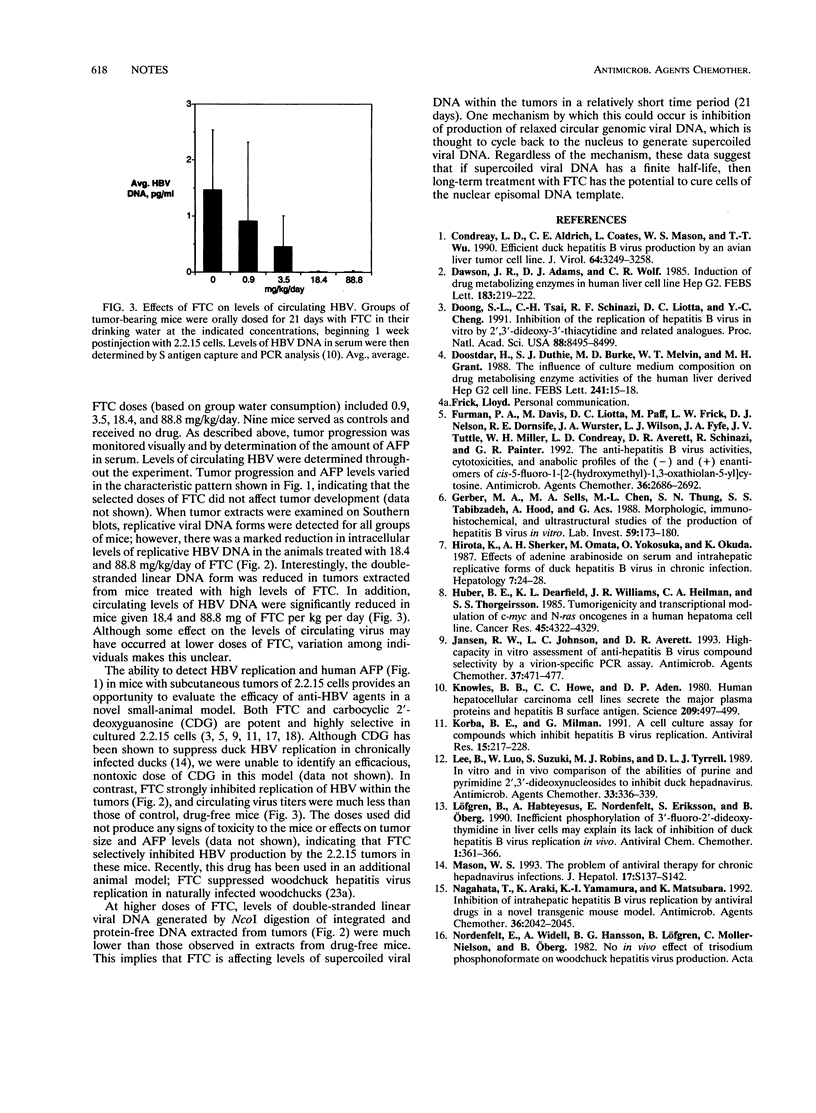
A murine model was developed to investigate the in vivo activity of anti-hepatitis B virus (HBV) agents. Mice with subcutaneous tumors of HBV-producing 2.2.15 cells showed reductions in levels of HBV in serum and in intracellular levels of HBV when the mice were orally dosed with (-) cis-5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]cytosine (FTC). No effects on tumor size or alpha-fetoprotein levels were observed. FTC can selectively inhibit HBV replication at nontoxic doses.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Condreay L. D., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Mason W. S., Wu T. T. Efficient duck hepatitis B virus production by an avian liver tumor cell line. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3249–3258. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3249-3258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. R., Adams D. J., Wolf C. R. Induction of drug metabolizing enzymes in human liver cell line Hep G2. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80780-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doong S. L., Tsai C. H., Schinazi R. F., Liotta D. C., Cheng Y. C. Inhibition of the replication of hepatitis B virus in vitro by 2',3'-dideoxy-3'-thiacytidine and related analogues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8495–8499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doostdar H., Duthie S. J., Burke M. D., Melvin W. T., Grant M. H. The influence of culture medium composition on drug metabolising enzyme activities of the human liver derived Hep G2 cell line. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):15–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Davis M., Liotta D. C., Paff M., Frick L. W., Nelson D. J., Dornsife R. E., Wurster J. A., Wilson L. J., Fyfe J. A. The anti-hepatitis B virus activities, cytotoxicities, and anabolic profiles of the (-) and (+) enantiomers of cis-5-fluoro-1-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-oxathiolan-5-yl]cytosine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2686–2692. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber M. A., Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Thung S. N., Tabibzadeh S. S., Hood A., Acs G. Morphologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural studies of the production of hepatitis B virus in vitro. Lab Invest. 1988 Aug;59(2):173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota K., Sherker A. H., Omata M., Yokosuka O., Okuda K. Effects of adenine arabinoside on serum and intrahepatic replicative forms of duck hepatitis B virus in chronic infection. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):24–28. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber B. E., Dearfield K. L., Williams J. R., Heilman C. A., Thorgeirsson S. S. Tumorigenicity and transcriptional modulation of c-myc and N-ras oncogenes in a human hepatoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1985 Sep;45(9):4322–4329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korba B. E., Milman G. A cell culture assay for compounds which inhibit hepatitis B virus replication. Antiviral Res. 1991 Mar-Apr;15(3):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(91)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Luo W. X., Suzuki S., Robins M. J., Tyrrell D. L. In vitro and in vivo comparison of the abilities of purine and pyrimidine 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides to inhibit duck hepadnavirus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):336–339. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S. The problem of antiviral therapy for chronic hepadnavirus infections. J Hepatol. 1993;17 (Suppl 3):S137–S142. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80439-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahata T., Araki K., Yamamura K., Matsubara K. Inhibition of intrahepatic hepatitis B virus replication by antiviral drugs in a novel transgenic mouse model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Sep;36(9):2042–2045. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.9.2042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. M., Banerjee R., Acs G. Inhibition of the replication of hepatitis B virus by the carbocyclic analogue of 2'-deoxyguanosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8541–8544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. M., Banerjee R., Jeffrey A. M., Acs G. The mechanism of inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by the carbocyclic analog of 2'-deoxyguanosine. Hepatology. 1992 Jul;16(1):8–12. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Zelent A. Z., Shvartsman M., Acs G. Replicative intermediates of hepatitis B virus in HepG2 cells that produce infectious virions. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2836–2844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2836-2844.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherker A. H., Hirota K., Omata M., Okuda K. Foscarnet decreases serum and liver duck hepatitis B virus DNA in chronically infected ducks. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):818–824. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90681-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shouval D., Schuger L., Levij I. S., Reid L. M., Neeman Z., Shafritz D. A. Comparative morphology and tumourigenicity of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines in athymic rats and mice. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;412(6):595–606. doi: 10.1007/BF00844296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Knight S. S., Duke A. E., Robinson W. S., Matthews T. R., Marion P. L. Activities of arabinosyladenine monophosphate and 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine against ground squirrel hepatitis virus in vivo as determined by reduction in serum virion-associated DNA polymerase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):277–279. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Lee B., Luo W., Tovell D., Robins M. J., Tyrrell D. L. Inhibition of duck hepatitis B virus replication by purine 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 15;156(3):1144–1151. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80752-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]