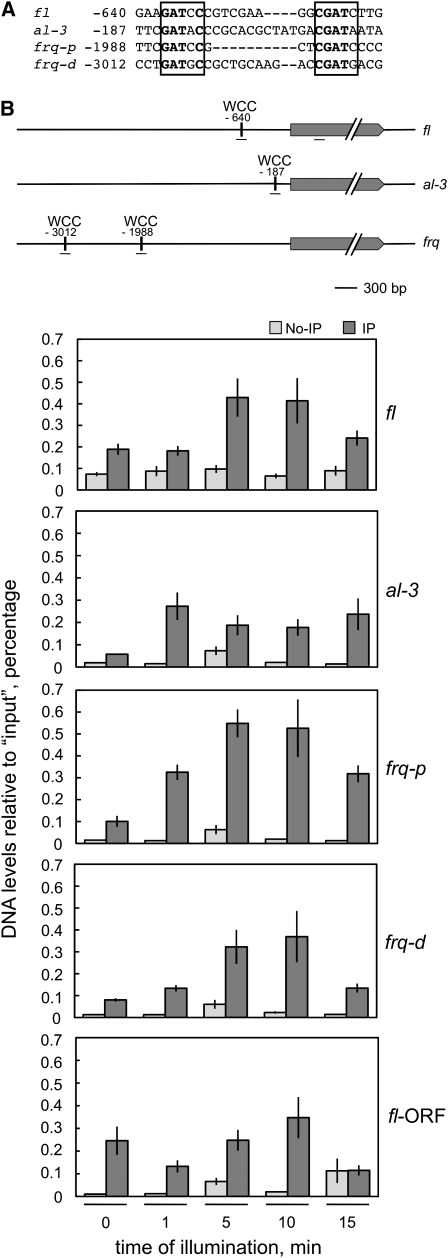
Figure 3.—
The WCC binds transiently to the promoter of fl. (A) A putative WCC binding site in the fl promoter. The WCC binding sites in the promoters of the light-regulated genes frq (proximal site, frq-p; distal site, frq-d) and al-3 (in the complementary strand) (He and Liu 2005) are compared to a putative WCC binding site in the fl promoter. Conserved nucleotides are shown in boldface type, and the putative WCC binding sites are boxed. The nucleotide position is shown relative to the initiator ATG. (B) Chromatin immunoprecipation assays. Wild-type mycelia were exposed to white light (the active blue-light component was 1 W/m2 blue light) for the indicated times and chromatin immunoprecipitated with an antibody against WC-2 (IP) or treated without any antibody (no-IP) as a control. After immunoprecipiation, the amount of DNA around the WCC binding site of fl, al-3, frq-p, and frq-d was measured by quantitative PCR and plotted relative to the amount obtained in each corresponding “input” sample. As a control, we assayed the amount of DNA of a segment located within the fl ORF. A scheme showing the relative position of each putative WCC binding site and the corresponding ORF is included. The short horizontal lines under each gene indicate the position of the DNA segments amplified by PCR. The plot shows the average and standard error of the mean in three experiments. Each DNA sample was quantified in three PCR experiments and averaged.