Abstract
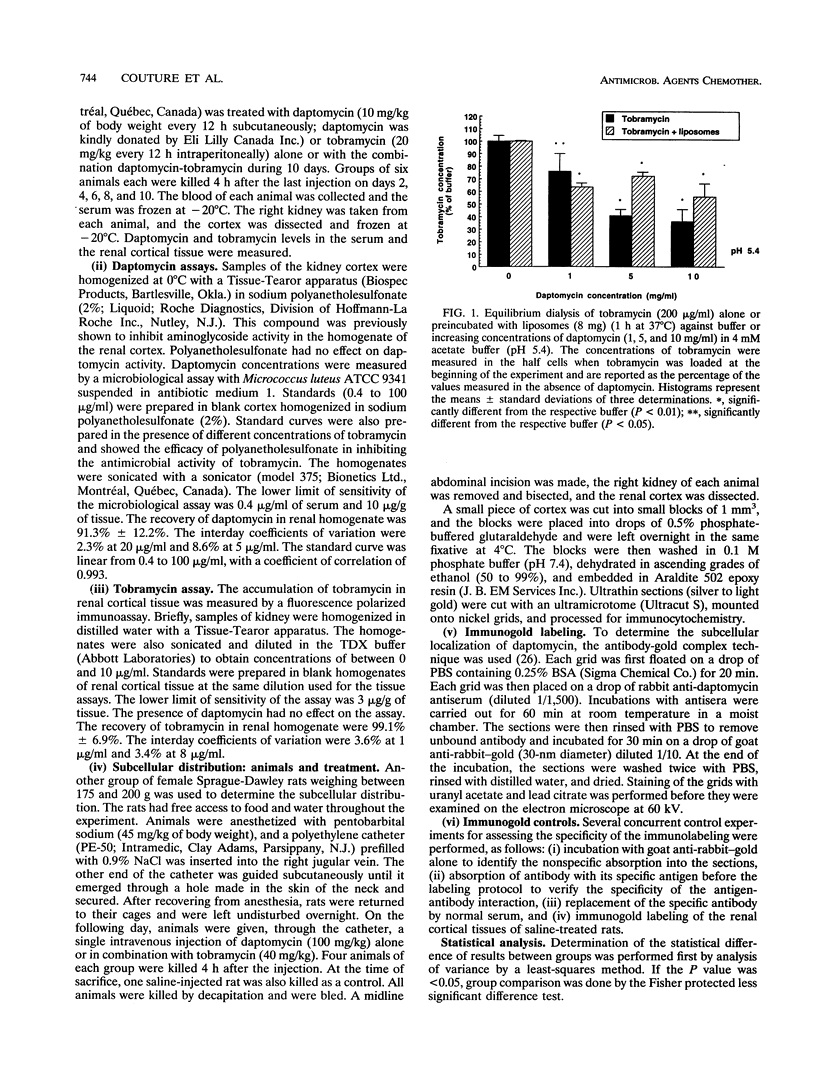
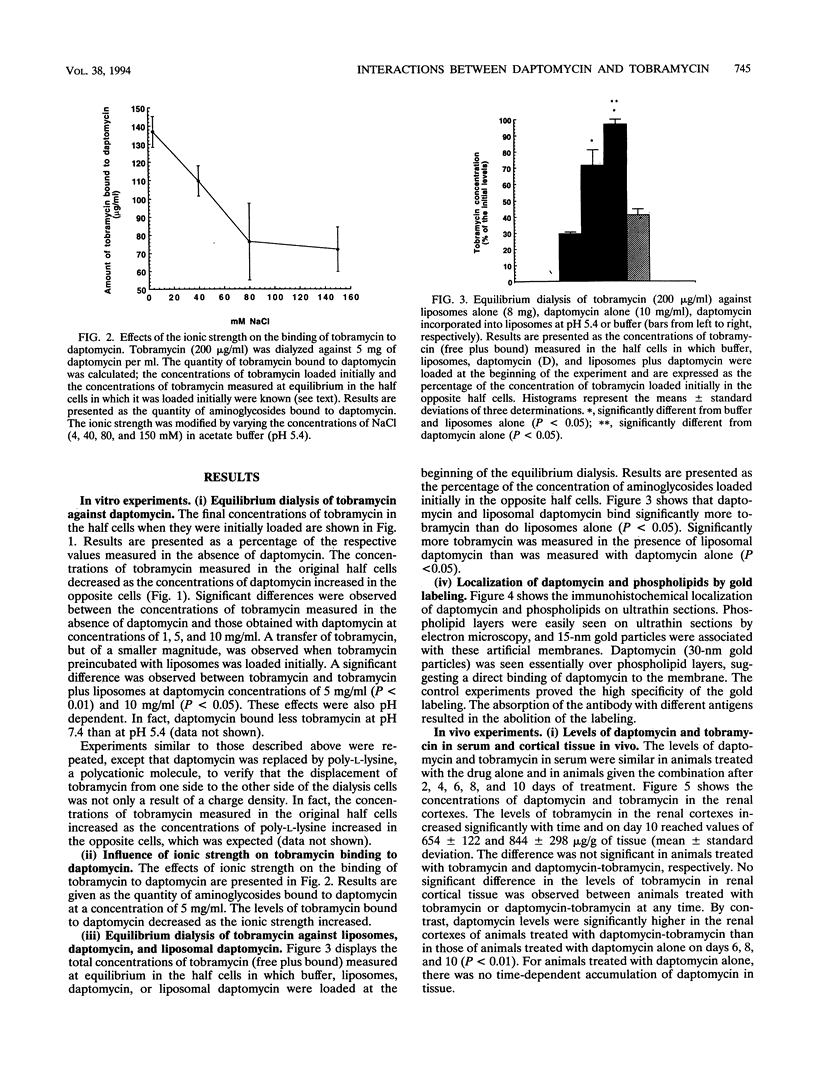
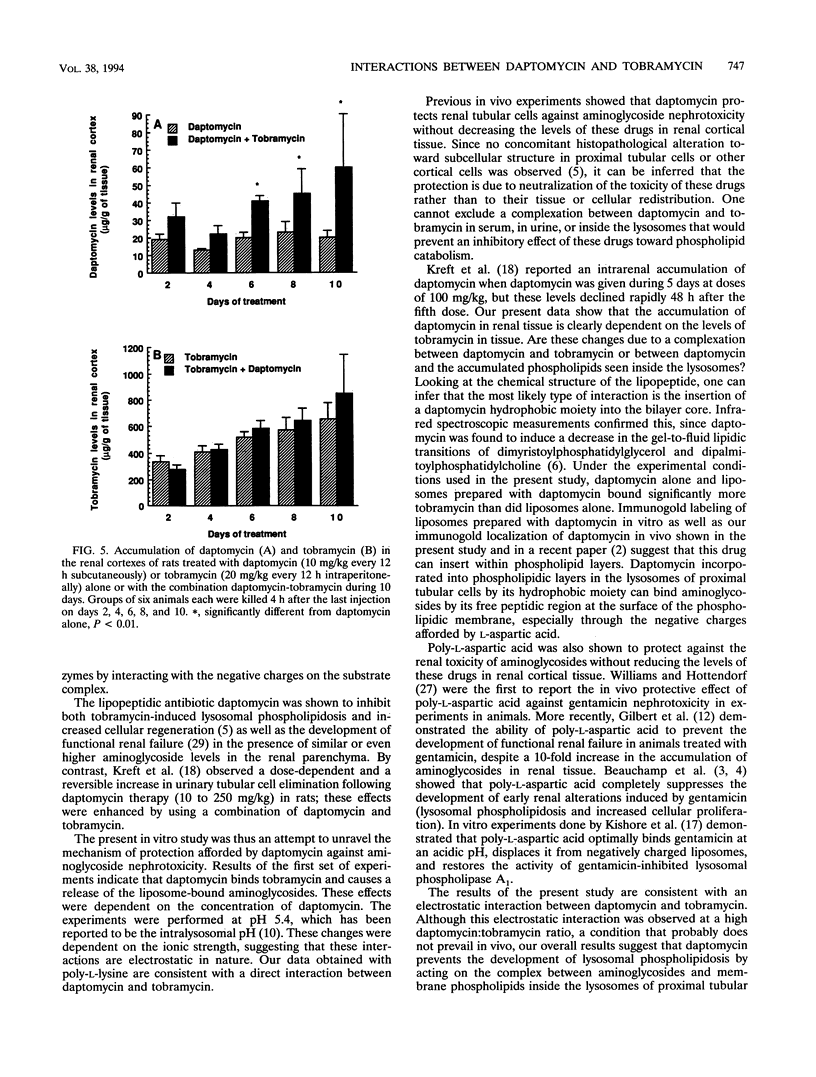
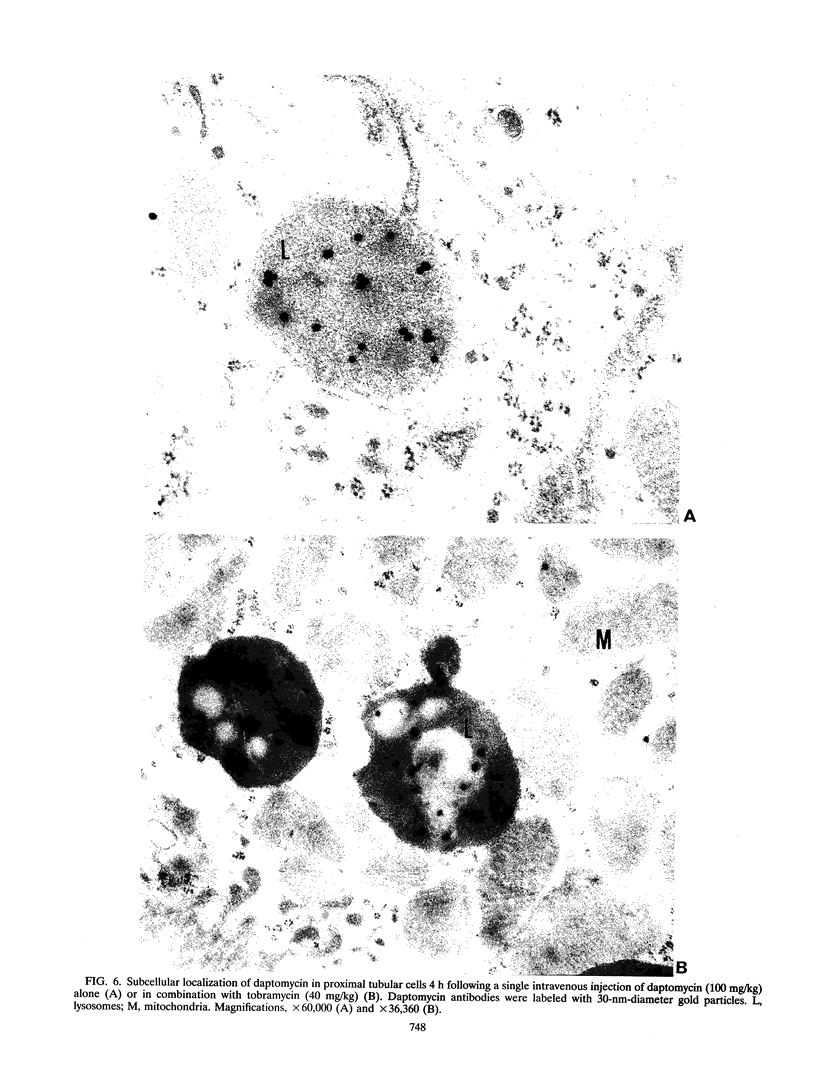
The lipopeptidic antibiotic daptomycin is reported to reduce experimental tobramycin nephrotoxicity (D. Beauchamp, M. Pellerin, P. Gourde, M. Pettigrew and M. G. Bergeron, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34:139-147, 1990; C. A. Wood, H. C. Finkbeiner, S. J. Kohlhepp, P. W. Kohnen, and D. C. Gilbert, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 33:1280-1285, 1989). In an attempt to explain these results, the in vivo and in vitro interactions between daptomycin and tobramycin were studied. Tobramycin alone and preincubated with negatively charged phospholipid bilayers (liposomes) was dialyzed against increasing concentrations of daptomycin in buffer at pH 5.4. A significant drop in the concentration of tobramycin was observed when daptomycin was added to the opposite half cells. Furthermore, daptomycin induced a concentration-dependent release of lipid-bound tobramycin. Gold labeling experiments showed that daptomycin could be incorporated into phospholipid layers. Female Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with daptomycin alone, with tobramycin alone, or with the combination over 2 to 10 days. Levels of daptomycin and tobramycin in serum were similar in all groups. The levels of tobramycin in the renal cortex increased significantly with time and, on day 10, reached values of 654 +/- 122 and 844 +/- 298 micrograms/g of tissue (mean +/- standard deviation; not significant) in animals treated with tobramycin and the combination of daptomycin-tobramycin, respectively. No significant difference was observed in the levels of tobramycin in the kidneys between animals treated with tobramycin or the daptomycin-tobramycin combination at any time. By contrast, daptomycin levels were significantly higher in the renal cortexes of animals treated with daptomycin-tobramycin in comparison with those in the renal cortexes of animals treated with daptomycin alone on days 6,8, and 10 (P < 0.01). For immunogold labeling studies, animals were killed 4 h after a single injection of daptomycin alone or daptomycin in combination with tobramycin. Daptomycin was found throughout the matrixes of the lysosomes of proximal tubular cells of animals treated with daptomycin alone. In animals treated with the combination of daptomycin and tobramycin, daptomycin was associated with intralysosomal myeloid bodies. Our results suggest that daptomycin might attenuate experimental aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity by interacting with the aminoglycoside, perhaps electrostatically, and thereby protecting intracellular targets of toxicity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beauchamp D., Gourde P., Bergeron M. G. Subcellular distribution of gentamicin in proximal tubular cells, determined by immunogold labeling. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Nov;35(11):2173–2179. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.11.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Gourde P., Simard M., Bergeron M. G. Subcellular distribution of daptomycin given alone or with tobramycin in renal proximal tubular cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Feb;38(2):189–194. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Laurent G., Maldague P., Abid S., Kishore B. K., Tulkens P. M. Protection against gentamicin-induced early renal alterations (phospholipidosis and increased DNA synthesis) by coadministration of poly-L-aspartic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):858–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Laurent G., Maldague P., Tulkens P. M. Reduction of gentamicin nephrotoxicity by the concomitant administration of poly-l-aspartic acid and poly-l-asparagine in rats. Arch Toxicol Suppl. 1986;9:306–309. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71248-7_52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp D., Pellerin M., Gourde P., Pettigrew M., Bergeron M. G. Effects of daptomycin and vancomycin on tobramycin nephrotoxicity in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):139–147. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. M., Elliott W. C., Houghton D. C., Gilbert D. N., DeFehr J., McCarron D. A. Reduction of experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats by dietary calcium loading. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):508–512. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasseur R., Laurent G., Ruysschaert J. M., Tulkens P. Interactions of aminoglycoside antibiotics with negatively charged lipid layers. Biochemical and conformational studies. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Feb 15;33(4):629–637. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A., Kan F. W., Bendayan M. Introduction of a high-resolution cytochemical method for studying the distribution of phospholipids in biological tissues. Eur J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;46(3):564–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Wood C. A., Kohlhepp S. J., Kohnen P. W., Houghton D. C., Finkbeiner H. C., Lindsley J., Bennett W. M. Polyaspartic acid prevents experimental aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):945–953. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giurgea-Marion L., Toubeau G., Laurent G., Heuson-Stiennon J. A., Tulkens P. M. Impairment of lysosome-pinocytic vesicle fusion in rat kidney proximal tubules after treatment with gentamicin at low doses. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;86(2):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(86)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes H. D., Sastrasinh M., Weinberg J. M. Calcium is a competitive inhibitor of gentamicin-renal membrane binding interactions and dietary calcium supplementation protects against gentamicin nephrotoxicity. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):134–147. doi: 10.1172/JCI111184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Just M., Erdmann G., Habermann E. The renal handling of polybasic drugs. 1. Gentamicin and aprotinin in intact animals. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;300(1):57–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00505080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kacew S. Inhibition of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity by pyridoxal-5'-phosphate in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jan;248(1):360–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreft B., de Wit C., Krech R., Marre R., Schulz E., Sack K. Experimental studies on nephrotoxicity and pharmacokinetics of LY 146032 (daptomycin) in rats. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Apr;25(4):635–643. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.4.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Carlier M. B., Rollman B., Van Hoof F., Tulkens P. Mechanism of aminoglycoside-induced lysosomal phospholipidosis: in vitro and in vivo studies with gentamicin and amikacin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 1;31(23):3861–3870. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Maldague P., Carlier M. B., Tulkens P. M. Increased renal DNA synthesis in vivo after administration of low doses of gentamicin to rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Oct;24(4):586–593. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.4.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. M., Michael U. F. The protective effect of nitrendipine on gentamicin acute renal failure in rats. Exp Mol Pathol. 1985 Aug;43(1):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(85)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mingeot-Leclercq M. P., Laurent G., Tulkens P. M. Biochemical mechanism of aminoglycoside-induced inhibition of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis by lysosomal phospholipases. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 15;37(4):591–599. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsammy L. S., Josepovitz C., Lane B. P., Kaloyanides G. J. Polyaspartic acid protects against gentamicin nephrotoxicity in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jul;250(1):149–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastrasinh M., Knauss T. C., Weinberg J. M., Humes H. D. Identification of the aminoglycoside binding site in rat renal brush border membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Aug;222(2):350–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverblatt F. J., Kuehn C. Autoradiography of gentamicin uptake by the rat proximal tubule cell. Kidney Int. 1979 Apr;15(4):335–345. doi: 10.1038/ki.1979.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapia F. J., Varndell I. M., Probert L., De Mey J., Polak J. M. Double immunogold staining method for the simultaneous ultrastructural localization of regulatory peptides. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jul;31(7):977–981. doi: 10.1177/31.7.6189888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught J. L., Carson J. R., Carmosin R. J., Blum P. S., Persico F. J., Hageman W. E., Shank R. P., Raffa R. B. Antinociceptive action of McN-5195 in rodents: a structurally novel (indolizine) analgesic with a nonopioid mechanism of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. D., Hottendorf G. H., Bennett D. B. Inhibition of renal membrane binding and nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):919–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. D., Hottendorf G. H. Inhibition of renal membrane binding and nephrotoxicity of gentamicin by polyasparagine and polyaspartic acid in the rat. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;47(2):317–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. A., Finkbeiner H. C., Kohlhepp S. J., Kohnen P. W., Gilbert D. N. Influence of daptomycin on staphylococcal abscesses and experimental tobramycin nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1280–1285. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]