Abstract
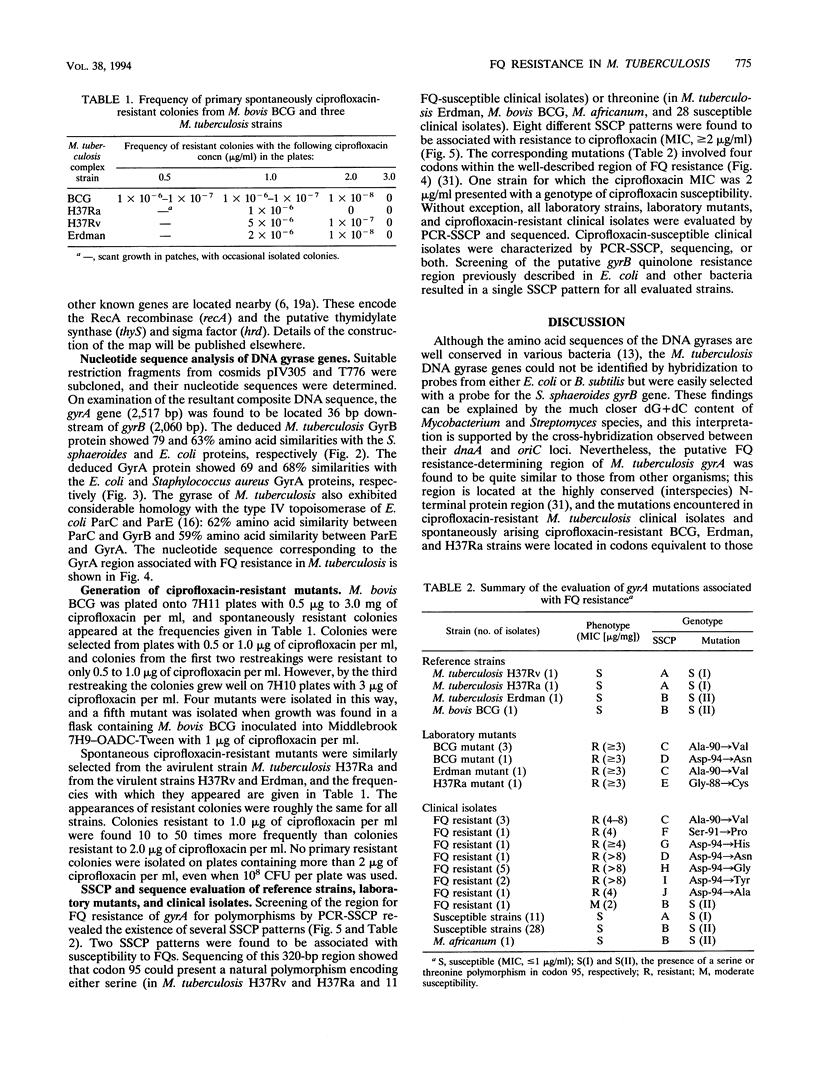
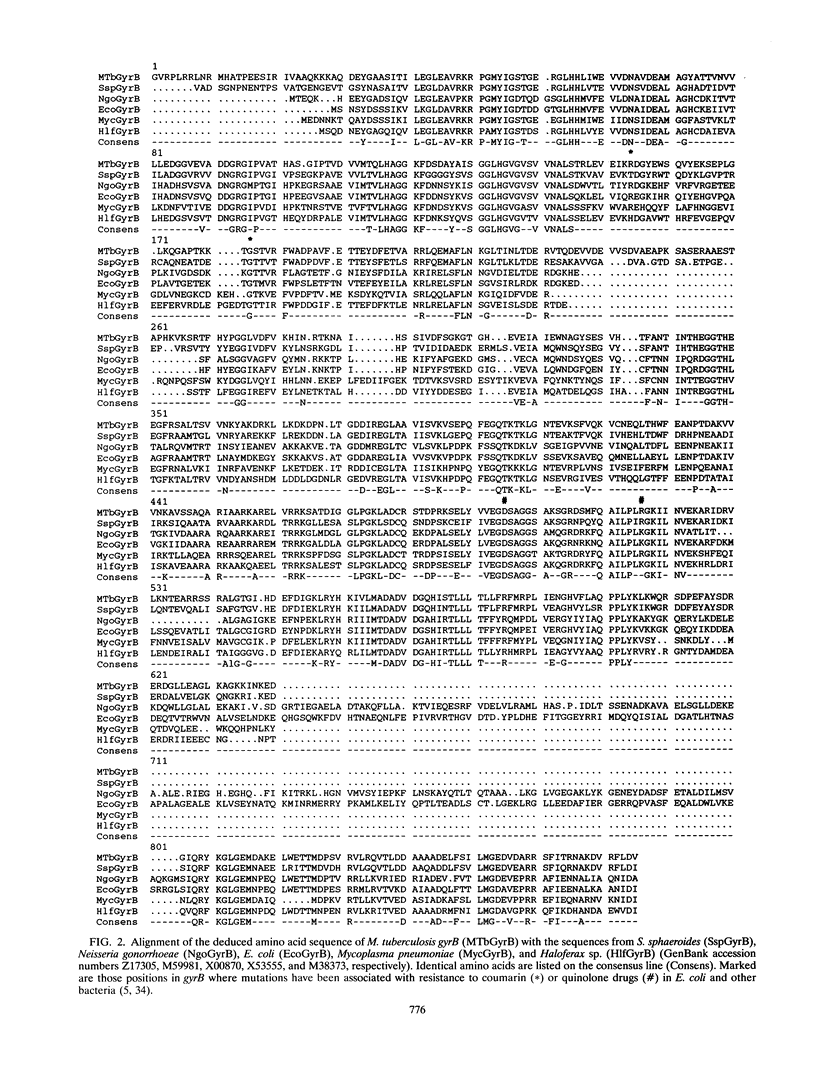
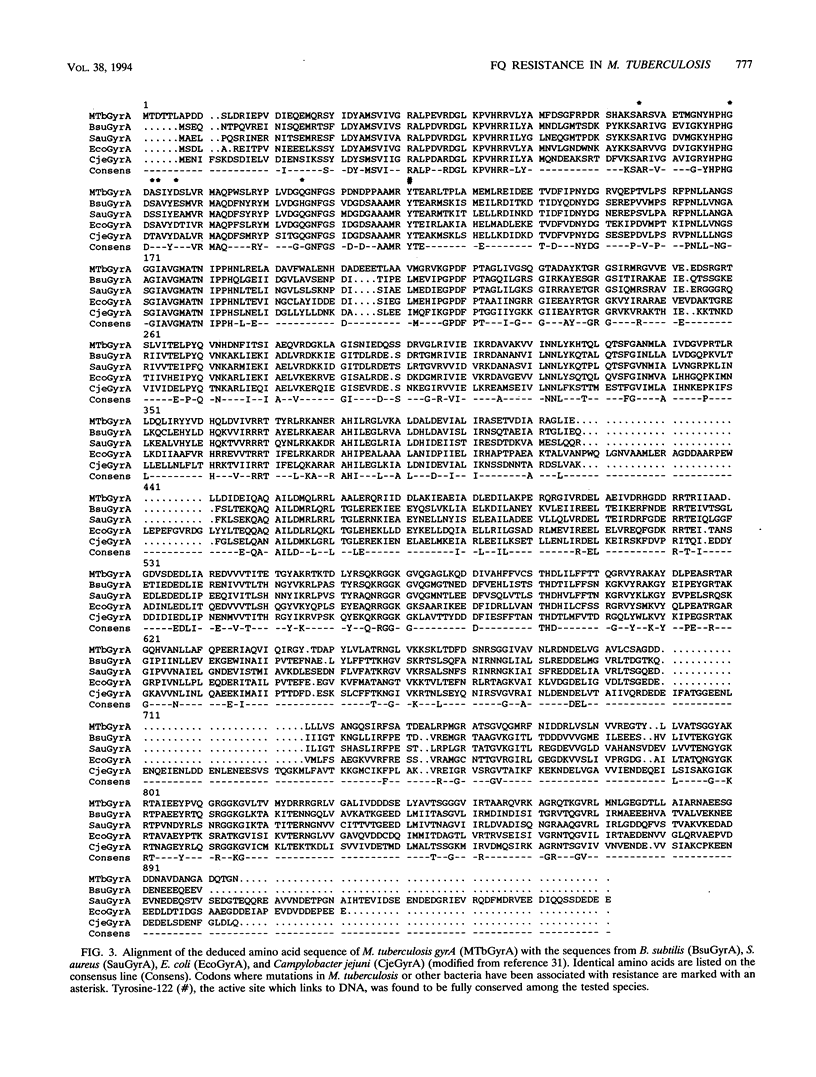
The emergence of multidrug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis has resulted in increased interest in the fluoroquinolones (FQs) as antituberculosis agents. To investigate the frequency and mechanisms of FQ resistance in M. tuberculosis, we cloned and sequenced the wild-type gyrA and gyrB genes, which encode the A and B subunits of the DNA gyrase, respectively; DNA gyrase is the main target of the FQs. On the basis of the sequence information, we performed DNA amplification for sequencing and single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis to examine the presumed quinolone resistance regions of gyrA and gyrB from reference strains (n = 4) and clinical isolates (n = 55). Mutations in codons of gyrA analogous to those described in other FQ-resistant bacteria were identified in all isolates (n = 14) for which the ciprofloxacin MIC was > 2 micrograms/ml. In addition, we selected ciprofloxacin-resistant mutants of Mycobacterium bovis BCG and M. tuberculosis Erdman and H37ra. Spontaneously resistant mutants developed at a frequency of 1 in 10(7) to 10(8) at ciprofloxacin concentrations of 2 micrograms/ml, but no primary resistant colonies were selected at higher ciprofloxacin concentrations. Replating of those first-step mutants selected for mutants with high levels of resistance which harbored gyrA mutations similar to those found among clinical FQ-resistant isolates. The gyrA and gyrB sequence information will facilitate analysis of the mechanisms of resistance to drugs which target the gyrase and the implementation of rapid strategies for the estimation of FQ susceptibility in clinical M. tuberculosis isolates.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry A. L., Jones R. N. Cross-resistance among cinoxacin, ciprofloxacin, DJ-6783, enoxacin, nalidixic acid, norfloxacin, and oxolinic acid after in vitro selection of resistant populations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):775–777. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calcutt M. J., Schmidt F. J. Conserved gene arrangement in the origin region of the Streptomyces coelicolor chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3220–3226. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3220-3226.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Shih J. F., Lindholm-Levy P. J., Heifets L. B. Minimal inhibitory concentrations of rifabutin, ciprofloxacin, and ofloxacin against Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolated before treatment of patients in Taiwan. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):987–989. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Maxwell A. gyrB mutations which confer coumarin resistance also affect DNA supercoiling and ATP hydrolysis by Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(12):1617–1624. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00886.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Sedgwick S. G., Colston M. J. Novel structure of the recA locus of Mycobacterium tuberculosis implies processing of the gene product. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5653–5662. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5653-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Daikos G. L., Uttamchandani R. B., Poblete R. B., Moreno J. N., Reyes R. R., Boota A. M., Thompson L. M., Cleary T. J., Oldham S. A. Clinical presentation and outcome of patients with HIV infection and tuberculosis caused by multiple-drug-resistant bacilli. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Aug 1;117(3):184–190. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-3-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswitz J. J., Willard K. E., Fasching C. E., Peterson L. R. Detection of gyrA gene mutations associated with ciprofloxacin resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: analysis by polymerase chain reaction and automated direct DNA sequencing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1166–1169. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heifets L. B., Lindholm-Levy P. J. MICs and MBCs of Win 57273 against Mycobacterium avium and M. tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):770–774. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisig P., Schedletzky H., Falkenstein-Paul H. Mutations in the gyrA gene of a highly fluoroquinolone-resistant clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):696–701. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori S., Ohshita Y., Utsui Y., Hiramatsu K. Sequential acquisition of norfloxacin and ofloxacin resistance by methicillin-resistant and -susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2278–2284. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. R., Jr, Kalpana G. V., Cirillo J. D., Pascopella L., Snapper S. B., Udani R. A., Jones W., Barletta R. G., Bloom B. R. Genetic systems for mycobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:537–555. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04027-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Nishimura Y., Imamura R., Niki H., Hiraga S., Suzuki H. New topoisomerase essential for chromosome segregation in E. coli. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90172-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalande V., Truffot-Pernot C., Paccaly-Moulin A., Grosset J., Ji B. Powerful bactericidal activity of sparfloxacin (AT-4140) against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):407–413. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limb D. I., Dabbs D. J., Spencer R. C. In-vitro selection of bacteria resistant to the 4-quinolone agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jan;19(1):65–71. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram M., Fisher L. M. 4-Quinolone resistance mutations in the DNA gyrase of Escherichia coli clinical isolates identified by using the polymerase chain reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):387–389. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqi S. H., Libonati J. P., Middlebrook G. Evaluation of rapid radiometric method for drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):908–912. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.908-912.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S., Oram M., Jensen B., Peterson L. R., Fisher L. M. DNA gyrase gyrA mutations in ciprofloxacin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus: close similarity with quinolone resistance mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7260–7262. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7260-7262.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenti A., Imboden P., Marchesi F., Lowrie D., Cole S., Colston M. J., Matter L., Schopfer K., Bodmer T. Detection of rifampicin-resistance mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lancet. 1993 Mar 13;341(8846):647–650. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90417-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenti A., Imboden P., Marchesi F., Schmidheini T., Bodmer T. Direct, automated detection of rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis by polymerase chain reaction and single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Oct;37(10):2054–2058. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.10.2054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenti A., Marchesi F., Balz M., Bally F., Böttger E. C., Bodmer T. Rapid identification of mycobacteria to the species level by polymerase chain reaction and restriction enzyme analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):175–178. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.175-178.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiara A. S., Cundliffe E. Cloning and characterization of a DNA gyrase B gene from Streptomyces sphaeroides that confers resistance to novobiocin. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2255–2259. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03065.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trucksis M., Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. A novel locus conferring fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5854–5860. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5854-5860.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Bedsole G., Sumter G., Sanders C. V., Steele L. C., Brown B. A., Smith J., Graham D. R. Activities of ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin against rapidly growing mycobacteria with demonstration of acquired resistance following single-drug therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):65–70. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Huang W. M., Taylor D. E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Campylobacter jejuni gyrA gene and characterization of quinolone resistance mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):457–463. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Bacterial resistance to quinolones: mechanisms and clinical importance. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11 (Suppl 5):S960–S968. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_5.s960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura M., Nakamura S. Quinolone resistance-determining region in the DNA gyrase gyrA gene of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1271–1272. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura M., Yamanaka L. M., Nakamura S. Quinolone resistance-determining region in the DNA gyrase gyrB gene of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Aug;35(8):1647–1650. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.8.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakrzewska-Czerwińska J., Schrempf H. Characterization of an autonomously replicating region from the Streptomyces lividans chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2688–2693. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2688-2693.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., Cave M. D., Crawford J. T., Dale J. W., Eisenach K. D., Gicquel B., Hermans P., Martin C., McAdam R., Shinnick T. M. Strain identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by DNA fingerprinting: recommendations for a standardized methodology. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Feb;31(2):406–409. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.2.406-409.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




