Abstract
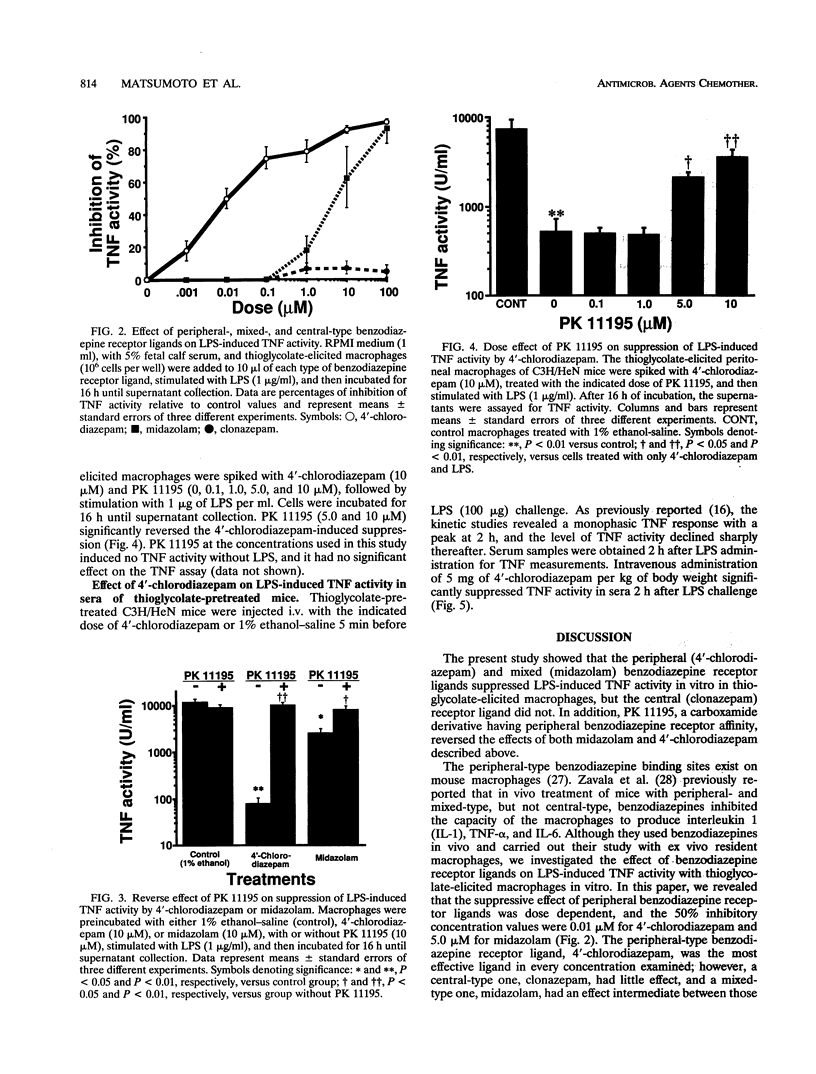
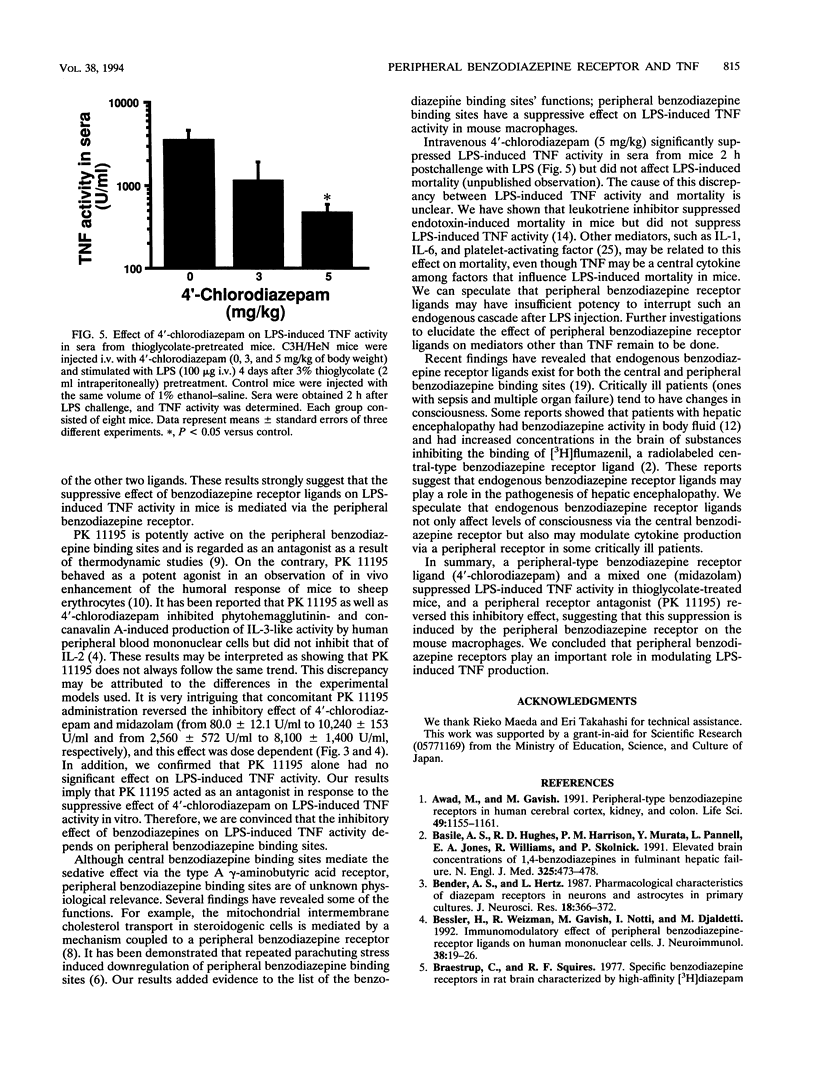
To investigate the effect of peripheral and central benzodiazepine receptor ligands on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity in mouse macrophages, three types of ligands, 4'-chlorodiazepam (pure peripheral), midazolam (mixed), and clonazepam (pure central), were compared. Midazolam and 4'-chlorodiazepam significantly suppressed LPS (1-microgram/ml)-induced TNF activity in thioglycolate-elicited mouse macrophages. In every concentration examined (0.001 to 100 microM), 4'-chlorodiazepam was the most effective agent, clonazepam was the least effective agent, and midazolam had an effect intermediate between those of the other two ligands. The peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands had a dose-dependent suppressive effect, and the 50% inhibitory concentrations were 0.01 microM for 4'-chlorodiazepam and 5 microM for midazolam. Concomitant use of PK 11195 (10 microM), an antagonist of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor, reversed this suppressive effect with 4'-chlorodiazepam (10 microM) or midazolam (10 microM). PK 11195 showed this antagonistic effect in a dose-dependent manner. Intravenous 4'-chlorodiazepam (5 mg/kg of body weight) significantly suppressed LPS (100-micrograms)-induced TNF activity of sera (2 h postchallenge with LPS) from thioglycolate-treated mice. The present findings suggest that the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor plays an important role in modulating LPS-induced TNF activity in mouse macrophages.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Awad M., Gavish M. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in human cerebral cortex, kidney, and colon. Life Sci. 1991;49(16):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90562-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basile A. S., Hughes R. D., Harrison P. M., Murata Y., Pannell L., Jones E. A., Williams R., Skolnick P. Elevated brain concentrations of 1,4-benzodiazepines in fulminant hepatic failure. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 15;325(7):473–478. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108153250705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A. S., Hertz L. Pharmacological characteristics of diazepam receptors in neurons and astrocytes in primary cultures. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18(2):366–372. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490180215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessler H., Weizman R., Gavish M., Notti I., Djaldetti M. Immunomodulatory effect of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands on human mononuclear cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 May;38(1-2):19–25. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90086-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dar D. E., Weizman A., Karp L., Grinshpoon A., Bidder M., Kotler M., Tyano S., Bleich A., Gavish M. Platelet peripheral benzodiazepine receptors in repeated stress. Life Sci. 1991;48(4):341–346. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90554-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giroir B. P. Mediators of septic shock: new approaches for interrupting the endogenous inflammatory cascade. Crit Care Med. 1993 May;21(5):780–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger K. E., Papadopoulos V. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors mediate translocation of cholesterol from outer to inner mitochondrial membranes in adrenocortical cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15015–15022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Fur G., Vaucher N., Perrier M. L., Flamier A., Benavides J., Renault C., Dubroeucq M. C., Guérémy C., Uzan A. Differentiation between two ligands for peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites, [3H]RO5-4864 and [3H]PK 11195, by thermodynamic studies. Life Sci. 1983 Aug 1;33(5):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenfant M., Haumont J., Zavala F. In vivo immunomodulating activity of PK 1195, a structurally unrelated ligand for "peripheral" benzodiazepine binding sites--I. Potentiation in mice of the humoral response to sheep red blood cells. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1986;8(7):825–828. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(86)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullen K. D., Szauter K. M., Kaminsky-Russ K. "Endogenous" benzodiazepine activity in body fluids of patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet. 1990 Jul 14;336(8707):81–83. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91594-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möhler H., Okada T. Benzodiazepine receptor: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science. 1977 Nov 25;198(4319):849–851. doi: 10.1126/science.918669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F. Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1987 Feb;79(2):319–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI112815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Matsumoto T., Kamochi M., Yoshida S. I., Mizuguchi Y., Shigematsu A. Protective effects of a leukotriene inhibitor and a leukotriene antagonist on endotoxin-induced mortality in carrageenan-pretreated mice. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2432–2437. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2432-2437.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Matsumoto T., Koga K., Takenaka I., Kamochi M., Sata T., Yoshida S., Shigematsu A. An antagonist of platelet-activating factor suppresses endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor and mortality in mice pretreated with carrageenan. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):699–704. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.699-704.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata M., Yoshida S., Kamochi M., Shigematsu A., Mizuguchi Y. Enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in mice by carrageenan pretreatment. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):679–683. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.679-683.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M. R., Gifford G. E. Purification and physico-chemical characterization of rabbit tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1671–1677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker H., Bliss M., Yamamura H. I. Specific high-affinity saturable binding of [3H] R05-4864 to benzodiazepine binding sites in the rat cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):173–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90405-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., McEnery M. W., Verma A. Molecular mechanisms of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors. Neurochem Res. 1990 Feb;15(2):119–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00972201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Werner P., Seeburg P. H., Mukhin A. G., Santi M. R., Grayson D. R., Guidotti A., Krueger K. E. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA encoding a peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20415–20421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires R. F., Brastrup C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature. 1977 Apr 21;266(5604):732–734. doi: 10.1038/266732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka I., Ogata M., Koga K., Matsumoto T., Shigematsu A. Ketamine suppresses endotoxin-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha production in mice. Anesthesiology. 1994 Feb;80(2):402–408. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199402000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Wang J. K., Spector S. Properties of [3H] diazepam binding to rat peritoneal mast cells. Life Sci. 1980 Jul 14;27(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90460-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Wang J. K., Spector S. [3H]Diazepam binding sites on rat heart and kidney. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Feb 15;31(4):589–590. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Cerami A. Pleiotropic effects of TNF in infection and neoplasia: beneficial, inflammatory, catabolic, or injurious. Immunol Ser. 1992;56:431–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Taniguchi T., Spector S. Properties of [3H]diazepam binding sites on rat blood platelets. Life Sci. 1980 Nov 17;27(20):1881–1888. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90434-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavala F., Haumont J., Lenfant M. Interaction of benzodiazepines with mouse macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 27;106(3):561–566. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavala F., Taupin V., Descamps-Latscha B. In vivo treatment with benzodiazepines inhibits murine phagocyte oxidative metabolism and production of interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Nov;255(2):442–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



