Abstract
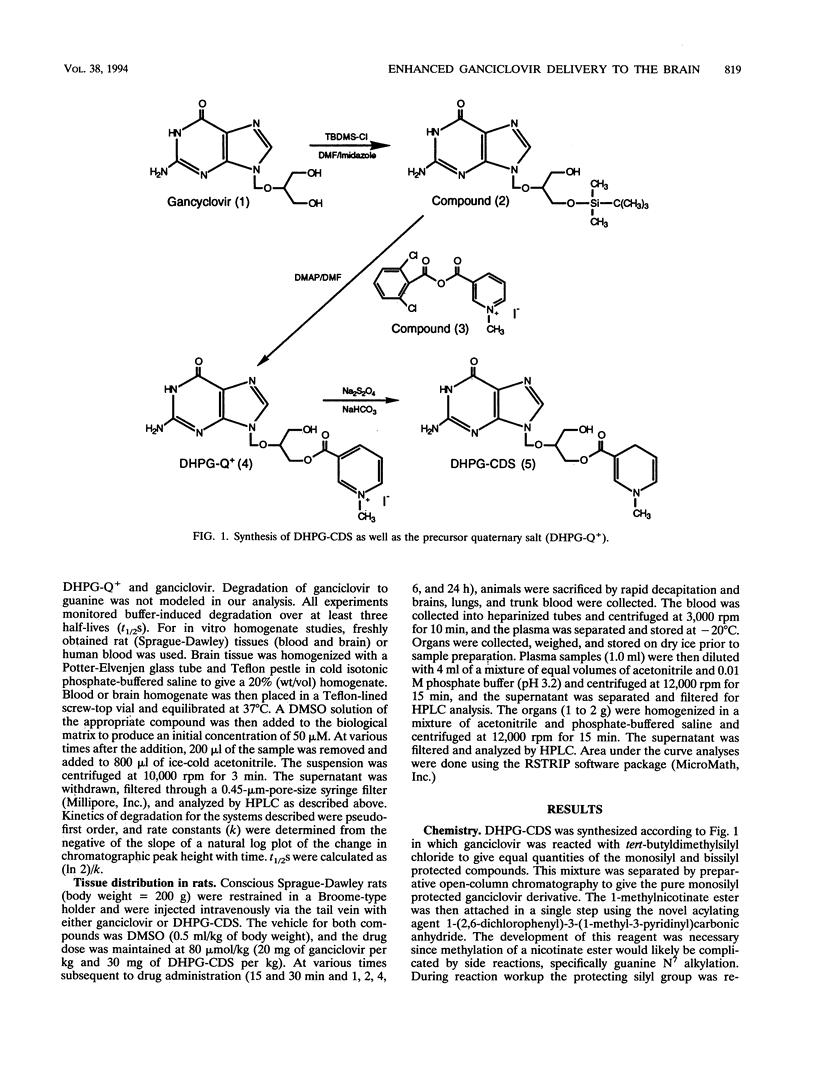
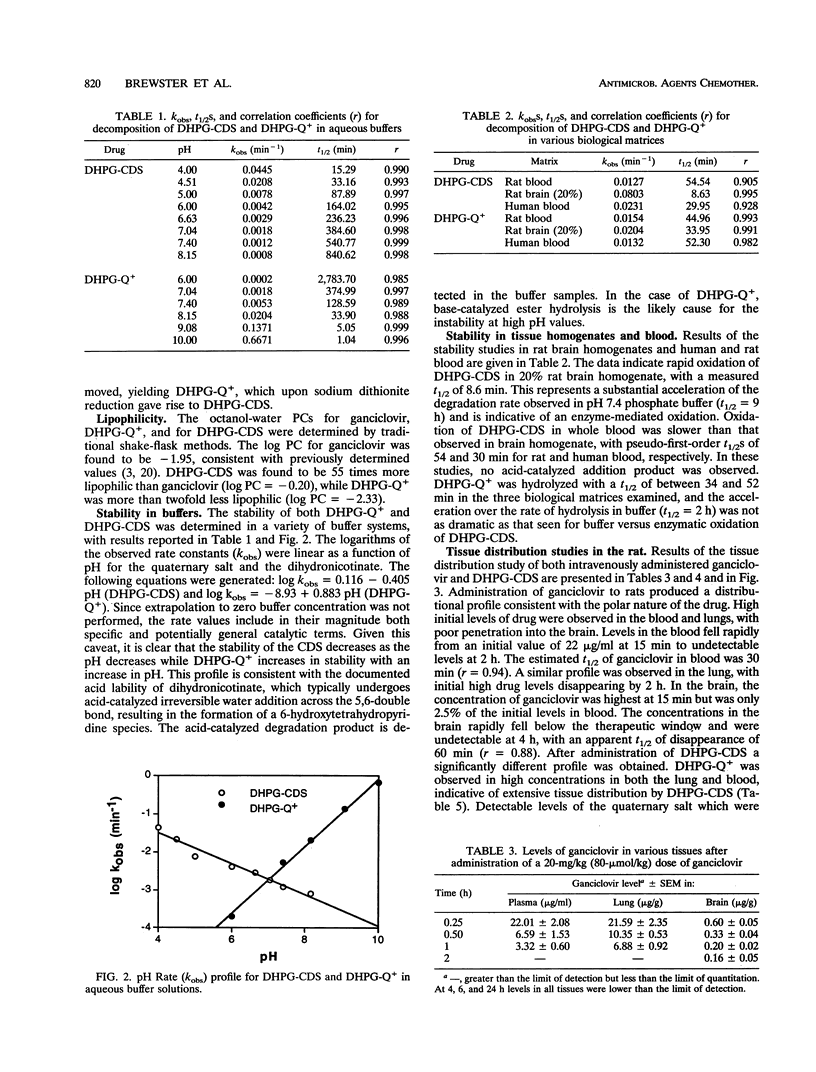
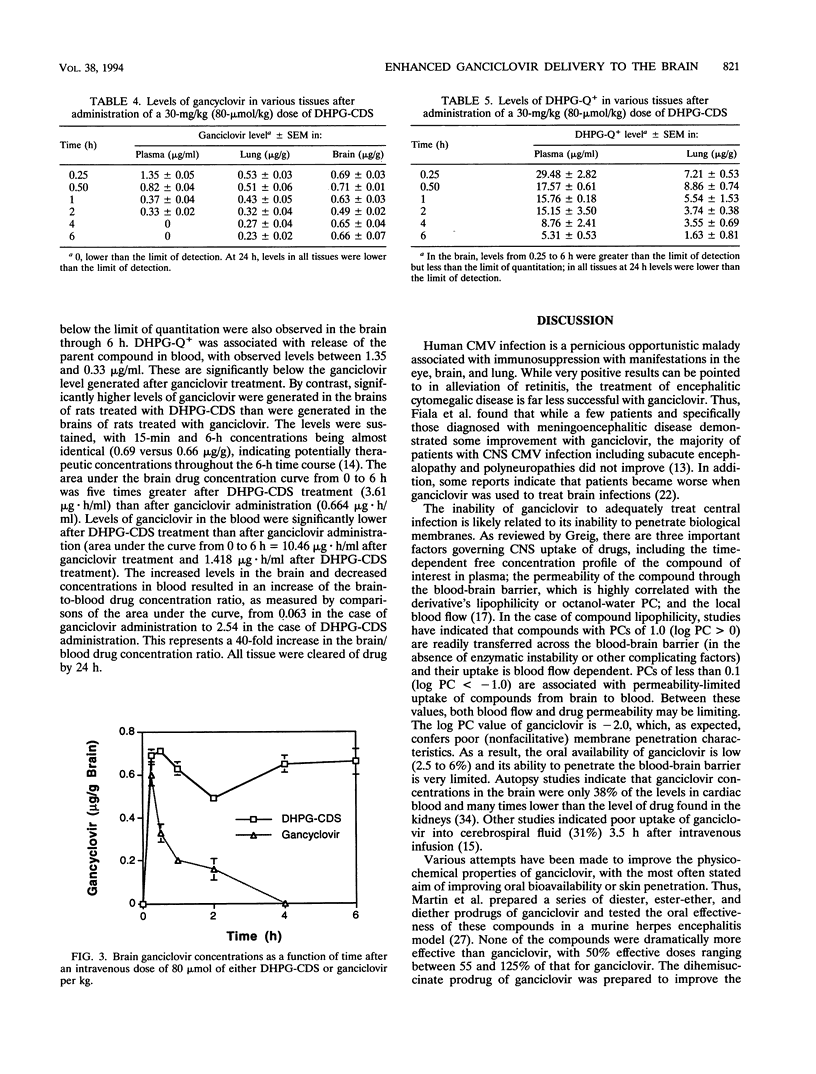
Enhanced delivery of ganciclovir to the brain was demonstrated by a redox-based chemical delivery system. A ganciclovir monoester in which a 1-methyl-1,4-dihydronicotinate was covalently attached to one of the hydroxymethyl functions was prepared. The stability of the ganciclovir chemical delivery system (DHPG-CDS) was evaluated in aqueous buffers and organ homogenates. In vivo distribution studies in the rat indicated that while ganciclovir poorly penetrated into the central nervous system and was rapidly eliminated, DHPG-CDS provided for therapeutically relevant (2.7 microM) and sustained levels of the parent compound through 6 h. An analysis of the area under the concentration curve indicated that the chemical delivery system delivered five times more ganciclovir than that of the parent drug. The high levels in the brain and reduced levels in the blood gave a brain-to-blood drug concentration ratio of 2.54 for ganciclovir when delivered by the chemical delivery system, compared to a ratio of 0.063 when the parent drug was administered. These data suggest that DHPG-CDS could be a useful adjunct for the treatment of cytomegalovirus encephalitis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal S. K., Gogu S. R., Rangan S. R., Agrawal K. C. Synthesis and biological evaluation of prodrugs of zidovudine. J Med Chem. 1990 May;33(5):1505–1510. doi: 10.1021/jm00167a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton W. T., Karkas J. D., Field A. K., Tolman R. L. Activation by thymidine kinase and potent antiherpetic activity of 2'-nor-2'-deoxyguanosine (2'NDG). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 29;108(4):1716–1721. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(82)80109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin E. J., Firestone B. A., Bergstrom R., Fass M., Massey I., Tsina I., Lin Y. Y. Selection of a derivative of the antiviral agent 9-[(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)-methyl]guanine (DHPG) with improved oral absorption. Pharm Res. 1987 Apr;4(2):120–125. doi: 10.1023/a:1016462801968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodor N., Farag H. H., Brewster M. E., 3rd Site-specific, sustained release of drugs to the brain. Science. 1981 Dec 18;214(4527):1370–1372. doi: 10.1126/science.7313698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodor N. Redox drug delivery systems for targeting drugs to the brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;507:289–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb45809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster M. E., Anderson W., Bodor N. Brain, blood, and cerebrospinal fluid distribution of a zidovudine chemical delivery system in rabbits. J Pharm Sci. 1991 Sep;80(9):843–846. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600800908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster M. E., Bodor N. Redox approaches to drug delivery to the central nervous system. NIDA Res Monogr. 1992;120:169–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu C. K., Bhadti V. S., Doshi K. J., Etse J. T., Gallo J. M., Boudinot F. D., Schinazi R. F. Brain targeting of anti-HIV nucleosides: synthesis and in vitro and in vivo studies of dihydropyridine derivatives of 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxyuridine and 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine. J Med Chem. 1990 Aug;33(8):2188–2192. doi: 10.1021/jm00170a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L., Buhles W., Erlich K. S. Herpesvirus infections (cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus). How to use ganciclovir (DHPG) and acyclovir. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):495–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulds D., Heel R. C. Ganciclovir. A review of its antiviral activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic efficacy in cytomegalovirus infections. Drugs. 1990 Apr;39(4):597–638. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199039040-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Cone L. A., Cohen N., Patel D., Williams K., Casareale D., Shapshak P., Tourtelotte W. Responses of neurologic complications of AIDS to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine and 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl) guanine. I. Clinical features. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Mar-Apr;10(2):250–256. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Davies M. E., DeWitt C., Perry H. C., Liou R., Germershausen J., Karkas J. D., Ashton W. T., Johnston D. B., Tolman R. L. 9-([2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine: a selective inhibitor of herpes group virus replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4139–4143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Sawchuk R., Chinnock B., de Miranda P., Balfour H. H., Jr Human pharmacokinetics of the antiviral drug DHPG. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Sep;40(3):281–286. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francavilla A., Di Leo A., Polimeno L., Conte D., Barone M., Fanizza G., Chiumarulo C., Rizzo G., Rubino M. Nuclear and cytosolic estrogen receptors in human colon carcinoma and in surrounding noncancerous colonic tissue. Gastroenterology. 1987 Dec;93(6):1301–1306. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig N. H. Optimizing drug delivery to brain tumors. Cancer Treat Rev. 1987 Mar;14(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0305-7372(87)90048-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. A., Schaefer J. F., Schulz D. M., Muller J. Cytomegalovirus encephalitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Dec;80(6):874–877. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.6.874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffries D. J. The spectrum of cytomegalovirus infection and its management. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Jun;23 (Suppl E):1–10. doi: 10.1093/jac/23.suppl_e.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E., Bundgaard H. Synthesis, enzymatic hydrolysis and physico-chemical properties of N-substituted 4-(aminomethyl)benzoate diester prodrugs of ganciclovir. Acta Pharm Nord. 1991;3(4):243–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. C. Latent infection and the elusive cytomegalovirus. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):205–215. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin O. L., Cederberg D. M., Mills J., Eron L. J., Mildvan D., Spector S. A. Ganciclovir for the treatment and suppression of serious infections caused by cytomegalovirus. Am J Med. 1987 Aug;83(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90685-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupia R. H., Ferencz N., Lertora J. J., Aggarwal S. K., George W. J., Agrawal K. C. Comparative pharmacokinetics of two prodrugs of zidovudine in rabbits: enhanced levels of zidovudine in brain tissue. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):818–824. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. C., Dvorak C. A., Smee D. F., Matthews T. R., Verheyden J. P. 9-[(1,3-Dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]guanine: a new potent and selective antiherpes agent. J Med Chem. 1983 May;26(5):759–761. doi: 10.1021/jm00359a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. C., Tippie M. A., McGee D. P., Verheyden J. P. Synthesis and antiviral activity of various esters of 9-[(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxy)methyl]guanine. J Pharm Sci. 1987 Feb;76(2):180–184. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600760221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. F., Felton C. P., Garay S. M., Gottlieb M. S., Hopewell P. C., Stover D. E., Teirstein A. S. Pulmonary complications of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Report of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute workshop. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 21;310(25):1682–1688. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406213102529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Cho E. S., Petito C. K., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):525–535. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palestine A. G. Clinical aspects of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 3):S515–S521. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.supplement_3.s515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell M. F., Magill A., Chu N., Hama K., Mau C. I., Foster L., Bergstrom R. Chemical and enzymatic degradation of ganciclovir prodrugs: enhanced stability of the diadamantoate prodrug under acid conditions. Pharm Res. 1991 Nov;8(11):1418–1423. doi: 10.1023/a:1015809408908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Masur H., Rook A. H., Armstrong G., Frederick W. R., Epstein J., Manischewitz J. F., Macher A. M., Jackson L., Ames J. Herpesvirus infections in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. JAMA. 1984 Jul 6;252(1):72–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepp D. H., Dandliker P. S., de Miranda P., Burnette T. C., Cederberg D. M., Kirk L. E., Meyers J. D. Activity of 9-[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxymethyl]guanine in the treatment of cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Sep;103(3):368–373. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-3-368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D., Simpson D. M., Nielsen S., Gold J. W., Metroka C. E., Posner J. B. Neurological complications of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: analysis of 50 patients. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):403–418. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stella V. J., Himmelstein K. J. Prodrugs and site-specific drug delivery. J Med Chem. 1980 Dec;23(12):1275–1282. doi: 10.1021/jm00186a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelmann E., Winkler I., Rolly H., Rösner M., Jähne G. New prodrugs of acyclic nucleosides with antiviral activity. Arzneimittelforschung. 1988 Nov;38(11):1545–1548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler I., Winkelmann E., Scholl T., Rösner M., Jähne G., Helsberg M. Antiviral activity and pharmacokinetics of HOE 602, an acyclic nucleoside, in animal models. Antiviral Res. 1990 Aug;14(2):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(90)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



