Abstract
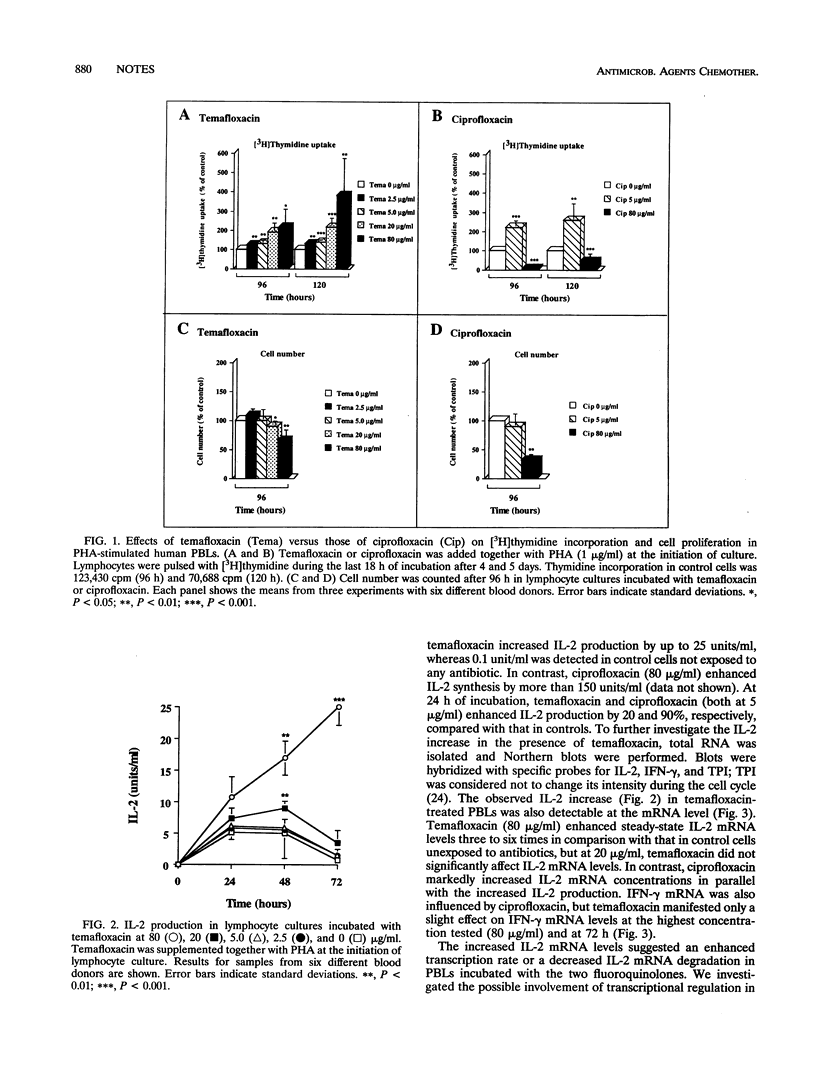
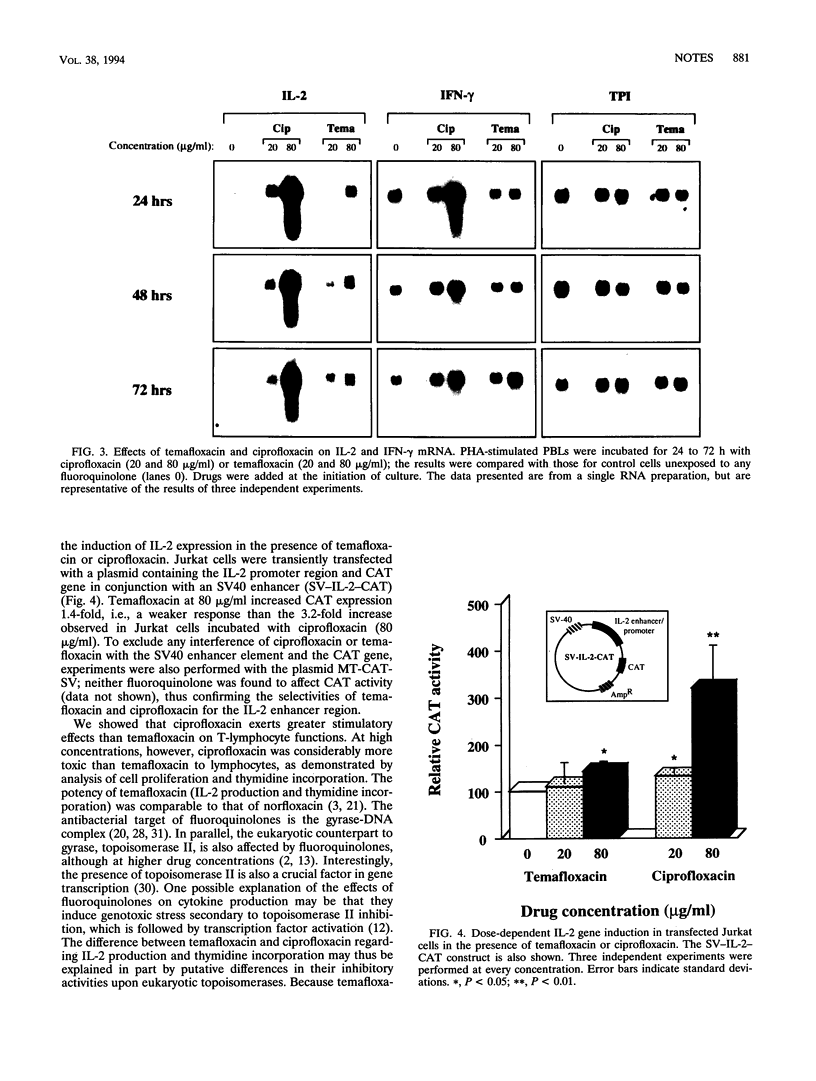
Temafloxacin increased interleukin-2 production and mRNA levels and enhanced thymidine incorporation in stimulated lymphocyte cultures. Gamma interferon mRNA levels were unaffected. Temafloxacin also stimulated interleukin-2 gene induction, as revealed in a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene system. However, temafloxacin exerted significantly weaker effects in these respects than did ciprofloxacin.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai S., Gohara Y., Akashi A., Kuwano K., Nishimoto M., Yano T., Oizumi K., Takeda K., Yamaguchi T. Effects of new quinolones on Mycoplasma pneumoniae-infected hamsters. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Feb;37(2):287–292. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredberg A., Brant M., Jaszyk M. Ciprofloxacin-induced inhibition of topoisomerase II in human lymphoblastoid cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):448–450. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredberg A., Brant M., Riesbeck K., Azou Y., Forsgren A. 4-Quinolone antibiotics: positive genotoxic screening tests despite an apparent lack of mutation induction. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar;211(1):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(89)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey P., McDonald T. Postmarketing surveillance of quinolones, 1990 to 1992. Drugs. 1993;45 (Suppl 3):46–53. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199300453-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N. A review of the pharmacokinetic profile of temafloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Dec;28 (Suppl 100):55–64. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.suppl_c.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Bergh A. K., Brandt M., Hansson G. Quinolones affect thymidine incorporation into the DNA of human lymphocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):506–508. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Bredberg A., Pardee A. B., Schlossman S. F., Tedder T. F. Effects of ciprofloxacin on eucaryotic pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis and cell growth. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):774–779. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Schlossman S. F., Tedder T. F. 4-Quinolone drugs affect cell cycle progression and function of human lymphocytes in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):768–773. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gooding B. B., Erwin M. E., Barrett M. S., Johnson D. M., Jones R. N. Antimicrobial activities of two investigational fluoroquinolones (CI-960 and E4695) against over 100 Legionella sp. isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Sep;36(9):2049–2050. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.9.2049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn T., Barak Y., Liebovich E., Malach L., Dagan O., Rubinstein E. Ciprofloxacin inhibits human hematopoietic cell growth: synergism with tumor necrosis factor and interferon. Exp Hematol. 1991 Mar;19(3):157–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Fornace A. J., Jr Response to adversity: molecular control of gene activation following genotoxic stress. New Biol. 1991 Sep;3(9):825–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussy P., Maass G., Tümmler B., Grosse F., Schomburg U. Effect of 4-quinolones and novobiocin on calf thymus DNA polymerase alpha primase complex, topoisomerases I and II, and growth of mammalian lymphoblasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1073–1078. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletter Y., Riklis I., Shalit I., Fabian I. Enhanced repopulation of murine hematopoietic organs in sublethally irradiated mice after treatment with ciprofloxacin. Blood. 1991 Oct 1;78(7):1685–1691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson I. L., Leanderson T. Regulation of interleukin 2 gene expression: discrepancy between enhancer activity and endogenous gene expression. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jan;19(1):145–149. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby S. R., Lietman P. S. Safety and tolerability of fluoroquinolones. Drugs. 1993;45 (Suppl 3):59–64. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199300453-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye K., Shi Y. G., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Wise R. The in-vitro activity, pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of temafloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Sep;24(3):415–424. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palù G., Valisena S., Ciarrocchi G., Gatto B., Palumbo M. Quinolone binding to DNA is mediated by magnesium ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9671–9675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesbeck K., Andersson J., Gullberg M., Forsgren A. Fluorinated 4-quinolones induce hyperproduction of interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2809–2813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesbeck K., Forsgren A. Selective enhancement of synthesis of interleukin-2 in lymphocytes in the presence of ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;9(6):409–413. doi: 10.1007/BF01979471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Kohlbrenner W. E., Weigl D., Baranowski J. Mechanism of quinolone inhibition of DNA gyrase. Appearance of unique norfloxacin binding sites in enzyme-DNA complexes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stünkel K. G., Hewlett G., Zeiler H. J. Ciprofloxacin enhances T cell function by modulating interleukin activities. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Dec;86(3):525–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb02964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases: why so many? J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6659–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmott C. J., Maxwell A. A single point mutation in the DNA gyrase A protein greatly reduces binding of fluoroquinolones to the gyrase-DNA complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jan;37(1):126–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehavi-Willner T., Shalit I. Enhancement of interleukin-2 production in human lymphocytes by two new quinolone derivatives. Lymphokine Res. 1989 Spring;8(1):35–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



