Abstract
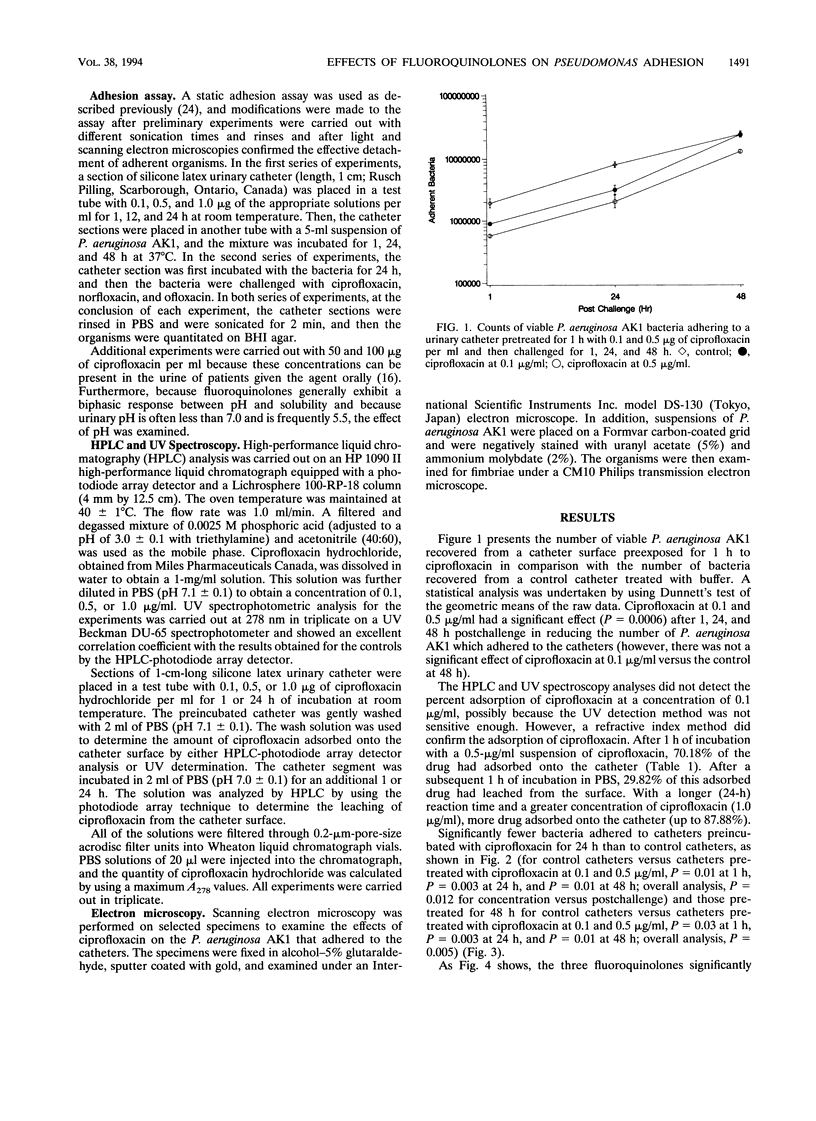
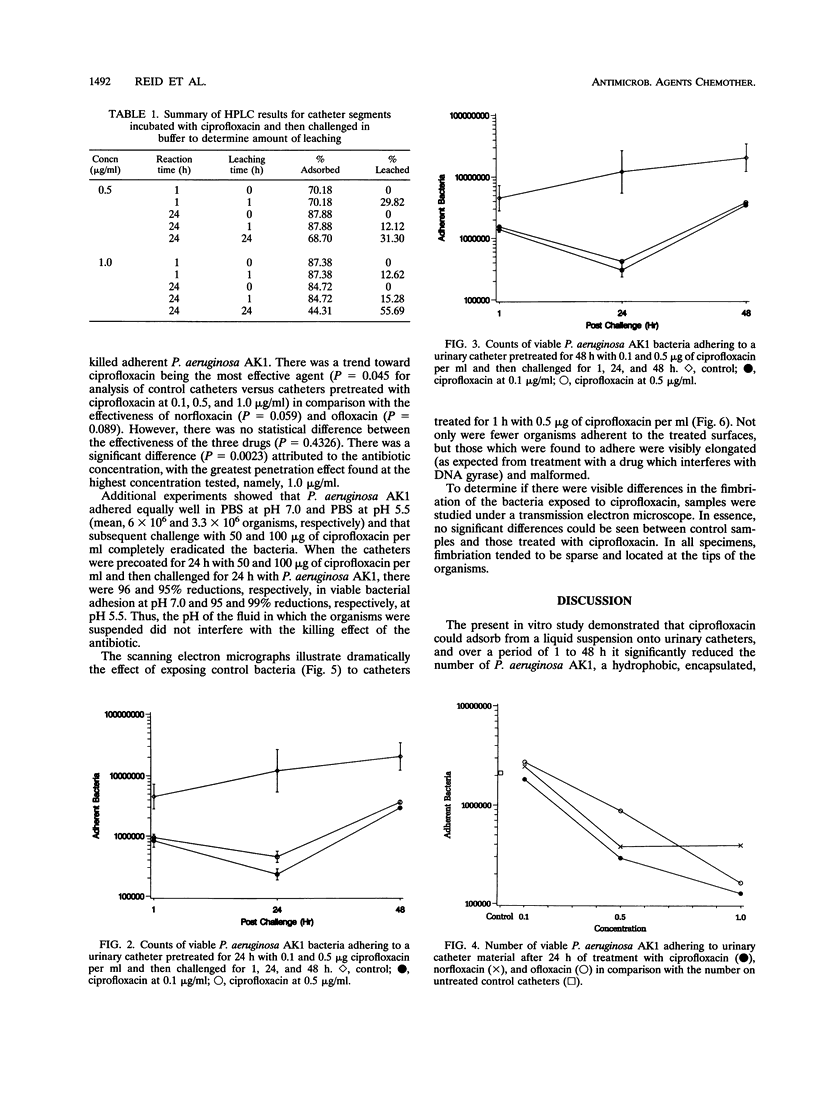
Pretreatment of urinary silicone latex catheters in vitro with 0.1 and 0.5 microgram of ciprofloxacin per ml for 1, 24, and 48 h significantly reduced the adhesion and survival of the clinical isolate Pseudomonas aeruginosa AK1. UV spectroscopy and high-performance liquid chromatography confirmed the presence of ciprofloxacin adsorbed onto the catheters and showed that up to 56% of the drug leached into the surrounding fluid within 24 h. Scanning electron microscopy demonstrated that the adherent organisms were malformed and elongated after exposure to ciprofloxacin. Transmission electron microscopy showed the presence of fimbriae on the bacterial surfaces, but there was no conclusive evidence of changes in the fimbriae upon exposure to ciprofloxacin. It was found that a significant eradication of 24-h Pseudomonas biofilms could be achieved with ciprofloxacin as well as with ofloxacin and norfloxacin. Preincubation of catheters with 50- and 100-micrograms/ml concentrations of ciprofloxacin resulted in up to a 99% reduction in the number of adherent bacteria in comparison with the reduction on control catheters. In addition, adherent biofilms were eradicated by 24 h of challenge with 50 and 100 micrograms of ciprofloxacin per ml at pH 7.0 and 5.5. Results of these in vitro studies suggest that there could be a clinical role for fluoroquinolones in preventing and treating urinary tract infections associated with P. aeruginosa adherence to prosthetic devices.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar H., Dasgupta M. K., Costerton J. W. Testing the susceptibility of bacteria in biofilms to antibacterial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2043–2046. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwar H., Dasgupta M., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Tobramycin resistance of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm grown under iron limitation. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Nov;24(5):647–655. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.5.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Eisenstein B. I., Ofek I. Sublethal concentrations of antibiotics and bacterial adhesion. Ciba Found Symp. 1981;80:288–305. doi: 10.1002/9780470720639.ch18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. T., Fernandes P. B. Structure-activity relationships of the fluoroquinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Feb;33(2):131–135. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.2.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig P., Todd T., Sastry P. A., Lee K. K., Hodges R. S., Paranchych W., Irvin R. T. Role of pili in adhesion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to human respiratory epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1641-1646.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber B. F., Wolff A. G. The use of salicylic acid to prevent the adherence of Escherichia coli to silastic catheters. J Urol. 1993 Mar;149(3):667–670. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüttinger K. J., Rudi H., Bomar M. T. Influence of surface chemistry of the substrate on the adsorption of Escherichia coli. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1987 Aug;184(6):538–547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen B., Kristinsson K. G., Jansen S., Peters G., Pulverer G. In-vitro efficacy of a central venous catheter complexed with iodine to prevent bacterial colonization. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Aug;30(2):135–139. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. R., Roberts P. L., Olsen R. J., Moyer K. A., Stamm W. E. Prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract infection with a silver oxide-coated urinary catheter: clinical and microbiologic correlates. J Infect Dis. 1990 Nov;162(5):1145–1150. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.5.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Butrus S. I., Misra R. P., Osato M. S. The contribution of bacterial surface hydrophobicity to the process of adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to hydrophilic contact lenses. Curr Eye Res. 1989 Feb;8(2):195–202. doi: 10.3109/02713688908995192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liedberg H., Ekman P., Lundeberg T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: adherence to and growth on different urinary catheter coatings. Int Urol Nephrol. 1990;22(5):487–492. doi: 10.1007/BF02549783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Martinez L., Pascual A., Perea E. J. Kinetics of adherence of mucoid and non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to plastic catheters. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Jan;34(1):7–12. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-1-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. J., Ahearn D. G. Adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to hydrophilic contact lenses and other substrata. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1392–1397. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1392-1397.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Ruseska I., Wright J. B., Costerton J. W. Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfau A., Sacks T. G. Single dose quinolone treatment in acute uncomplicated urinary tract infection in women. J Urol. 1993 Mar;149(3):532–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phaneuf M. D., Ozaki C. K., Bide M. J., Quist W. C., Alessi J. M., Tannenbaum G. A., LoGerfo F. W. Application of the quinolone antibiotic ciprofloxacin to Dacron utilizing textile dyeing technology. J Biomed Mater Res. 1993 Feb;27(2):233–237. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820270213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Bruce A. W., Taylor M. Influence of three-day antimicrobial therapy and lactobacillus vaginal suppositories on recurrence of urinary tract infections. Clin Ther. 1992 Jan-Feb;14(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Charbonneau-Smith R., Lam D., Kang Y. S., Lacerte M., Hayes K. C. Bacterial biofilm formation in the urinary bladder of spinal cord injured patients. Paraplegia. 1992 Oct;30(10):711–717. doi: 10.1038/sc.1992.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Denstedt J. D., Kang Y. S., Lam D., Nause C. Microbial adhesion and biofilm formation on ureteral stents in vitro and in vivo. J Urol. 1992 Nov;148(5):1592–1594. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Kang Y. S., Lacerte M., Tieszer C., Hayes K. C. Bacterial biofilm formation on the bladder epithelium of spinal cord injured patients. II. Toxic outcome on cell viability. Paraplegia. 1993 Aug;31(8):494–499. doi: 10.1038/sc.1993.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen T. The fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents. Prog Med Chem. 1990;27:235–295. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70293-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer A. J., Story K. O., Johnson S. M. Effect of silver oxide/trichloroisocyanuric acid antimicrobial urinary drainage system on catheter-associated bacteriuria. J Urol. 1988 Jan;139(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)42295-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. P., Maki D. G. Bacteriuria in the catheterized patient. What quantitative level of bacteriuria is relevant? N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 30;311(9):560–564. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408303110903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M. J. Therapeutic focus. Ciprofloxacin. Br J Clin Pract. 1988 Nov;42(11):469–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wall E., Verkooyen R. P., Mintjes-de Groot J., Oostinga J., van Dijk A., Hustinx W. N., Verbrugh H. A. Prophylactic ciprofloxacin for catheter-associated urinary-tract infection. Lancet. 1992 Apr 18;339(8799):946–951. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91529-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





