Abstract
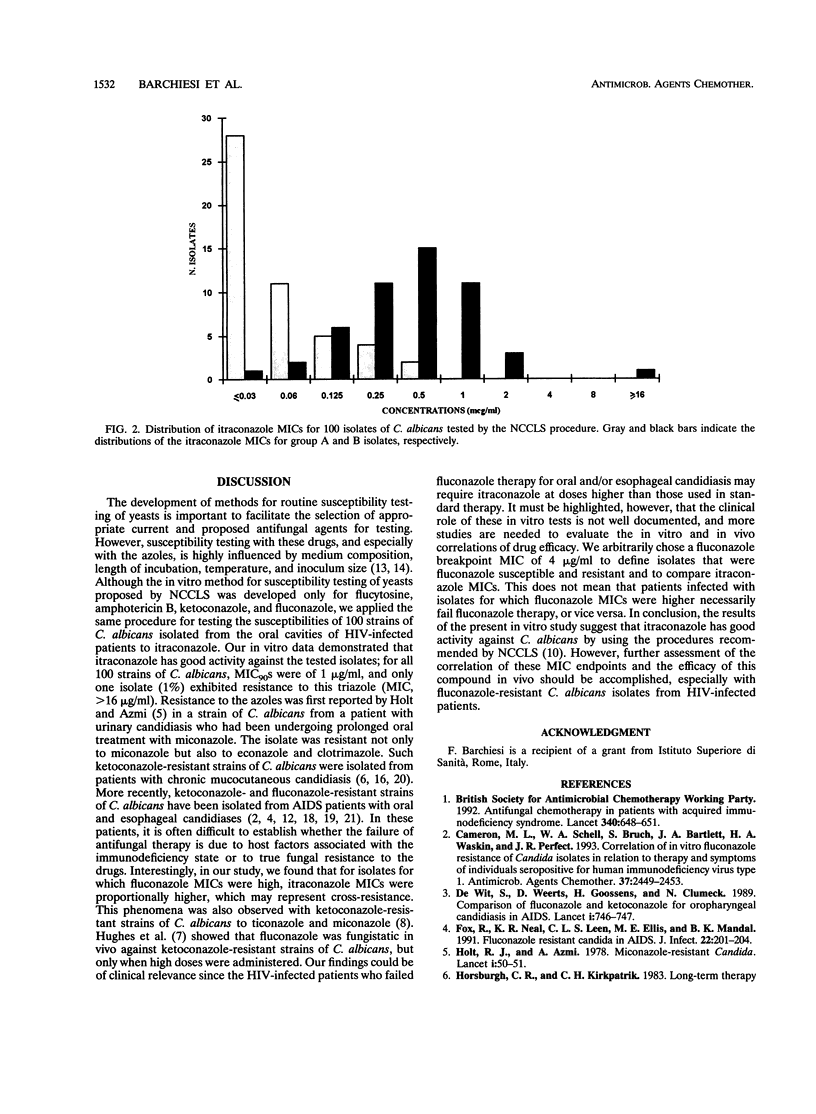
A broth macrodilution technique, which was performed by following the recommendations provided by the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (document M27-P), was applied to study the in vitro activity of itraconazole against fluconazole-susceptible and -resistant Candida albicans isolates from the oral cavities of 100 patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. The in vitro data demonstrated that itraconazole had good activity against the tested isolates; for 90% of all strains of C. albicans, MICs were 1 microgram/ml, and only one isolate was highly resistant to this triazole (MIC, > 16 micrograms/ml). However, the itraconazole MICs for the fluconazole-susceptible isolates were significantly lower than those for the fluconazole-resistant isolates; the MICs for 50 and 90% of the isolates tested were < or = 0.03 and 0.25 microgram/ml, respectively, for the fluconazole-susceptible isolates and 0.5 and 1 microgram/ml, respectively, for the fluconazole-resistant isolates (P = 0.00001). Our findings could be of clinical relevance because human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients who fail fluconazole therapy for oral and/or esophageal candidiasis may require itraconazole at doses higher than those used in standard therapy.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cameron M. L., Schell W. A., Bruch S., Bartlett J. A., Waskin H. A., Perfect J. R. Correlation of in vitro fluconazole resistance of Candida isolates in relation to therapy and symptoms of individuals seropositive for human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2449–2453. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wit S., Weerts D., Goossens H., Clumeck N. Comparison of fluconazole and ketoconazole for oropharyngeal candidiasis in AIDS. Lancet. 1989 Apr 8;1(8641):746–748. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92572-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R., Neal K. R., Leen C. L., Ellis M. E., Mandal B. K. Fluconazole resistant candida in AIDS. J Infect. 1991 Mar;22(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(91)91767-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt R. J., Azmi A. Miconazole-resistant Candida. Lancet. 1978 Jan 7;1(8054):50–51. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90403-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Kirkpatrick C. H. Long-term therapy of chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis with ketoconazole: experience with twenty-one patients. Am J Med. 1983 Jan 24;74(1B):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. E., Bennett R. L., Tuna I. C., Beggs W. H. Activities of fluconazole (UK 49,858) and ketoconazole against ketoconazole-susceptible and -resistant Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Feb;32(2):209–212. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Richardson M. D., Warnock D. W. In-vitro resistance to imidazole antifungals in Candida albicans. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Jun;13(6):547–558. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.6.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen R. A. Azoles and AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):727–730. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Burmeister L., Bartlett M. S., Rinaldi M. G. Multicenter evaluation of four methods of yeast inoculum preparation. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1437–1441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1437-1441.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaller M. A., Rhine-Chalberg J., Redding S. W., Smith J., Farinacci G., Fothergill A. W., Rinaldi M. G. Variations in fluconazole susceptibility and electrophoretic karyotype among oral isolates of Candida albicans from patients with AIDS and oral candidiasis. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jan;32(1):59–64. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.1.59-64.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rex J. H., Pfaller M. A., Rinaldi M. G., Polak A., Galgiani J. N. Antifungal susceptibility testing. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Oct;6(4):367–381. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.4.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi M. G. Laboratory evaluation of antifungal agents: a brief overview. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14 (Suppl 1):S130–S133. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.supplement_1.s130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryley J. F., Wilson R. G., Barrett-Bee K. J. Azole resistance in Candida albicans. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(1):53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samaranayake L. P., Holmstrup P. Oral candidiasis and human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Oral Pathol Med. 1989 Dec;18(10):554–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1989.tb01552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandven P., Bjørneklett A., Maeland A. Susceptibilities of Norwegian Candida albicans strains to fluconazole: emergence of resistance. The Norwegian Yeast Study Group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2443–2448. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavitian A., Raufman J. P., Rosenthal L. E., Weber J., Webber C. A., Dincsoy H. P. Ketoconazole-resistant Candida esophagitis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1986 Feb;90(2):443–445. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90946-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnock D. W., Johnson E. M., Richardson M. D., Vickers C. F. Modified response to ketoconazole of Candida albicans from a treatment failure. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):642–643. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91809-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willocks L., Leen C. L., Brettle R. P., Urquhart D., Russell T. B., Milne L. J. Fluconazole resistance in AIDS patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Dec;28(6):937–939. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.6.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



