Abstract
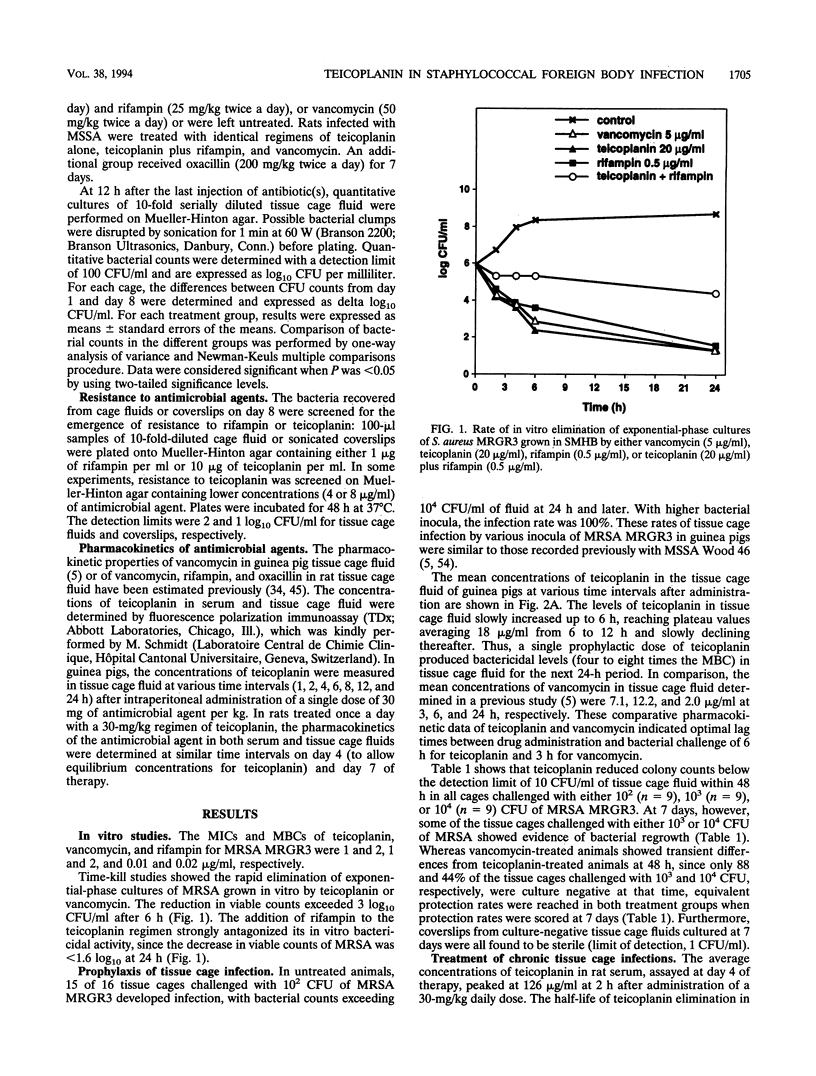
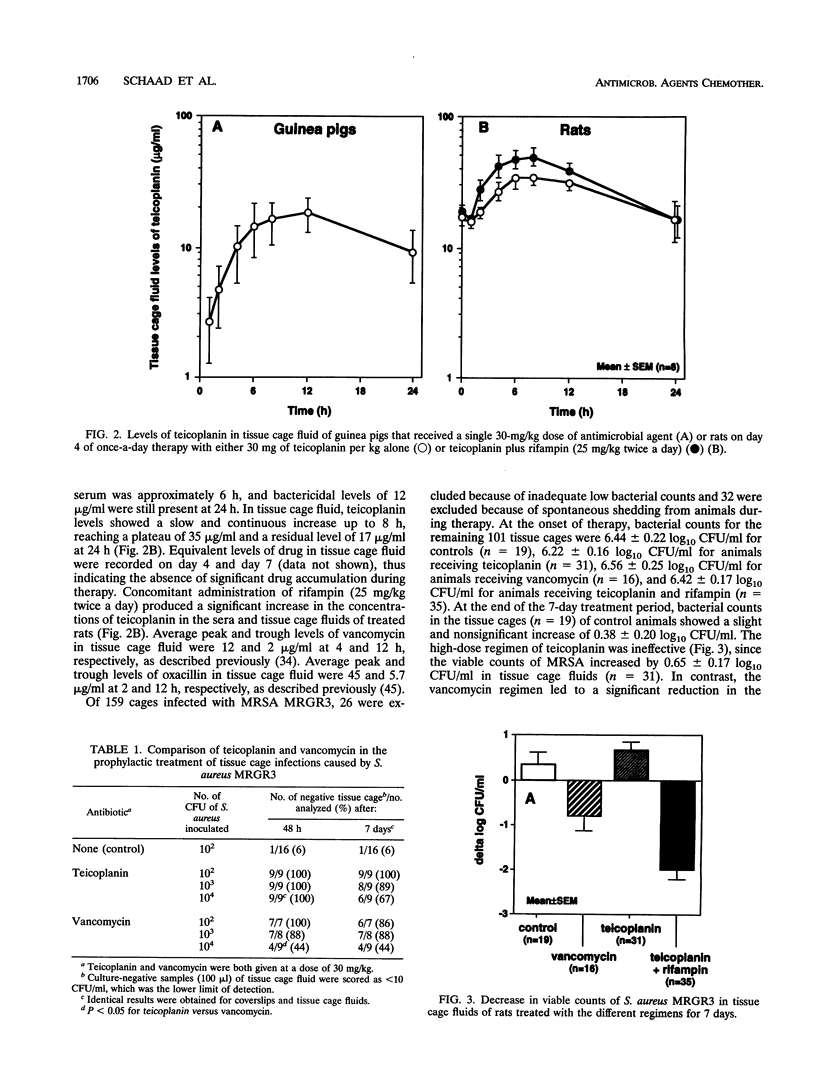
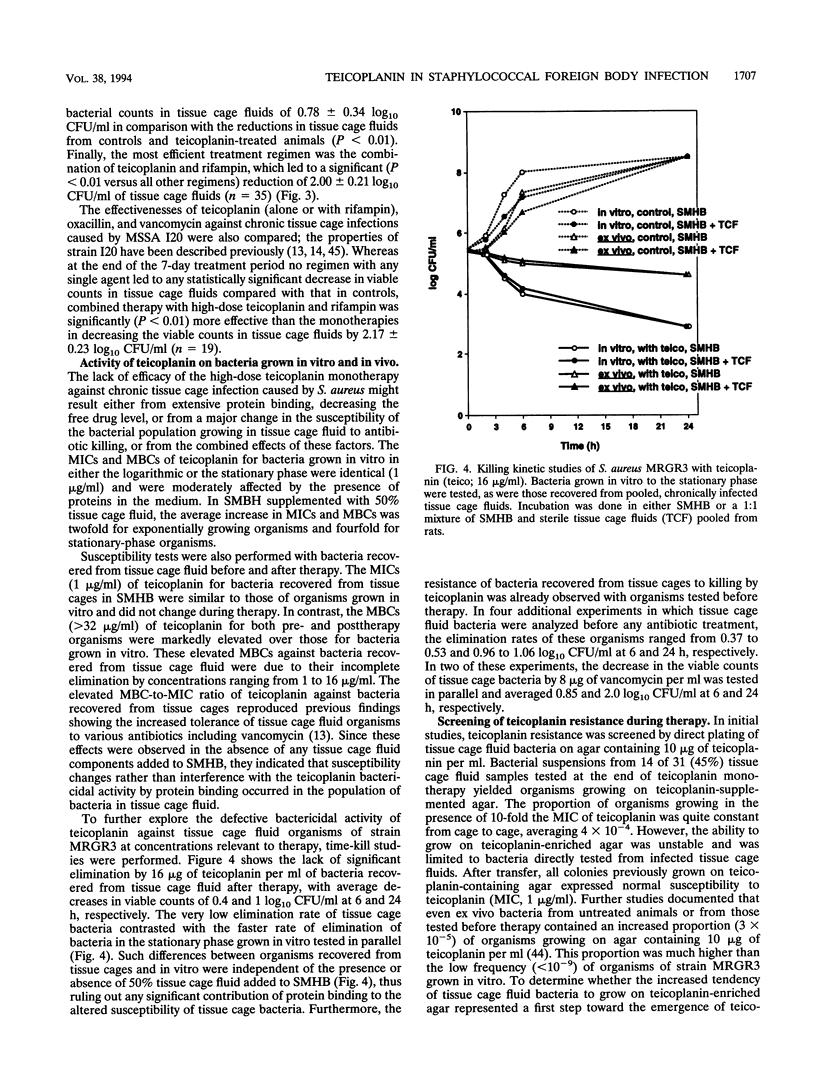
The prophylactic and therapeutic activities of teicoplanin were evaluated in two different experimental models of foreign body infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In a guinea pig model of prophylaxis, subcutaneously implanted tissue cages were infected at a > 90% rate by 10(2) CFU of MRSA in control animals. A single dose of 30 mg of teicoplanin per kg of body weight administered intraperitoneally 6 h before bacterial challenge was as effective as vancomycin in preventing experimental infection in tissue cages injected with either 10(2), 10(3), or 10(4) CFU of MRSA. In a rat model evaluating the therapy of chronic tissue cage infection caused by MRSA, the efficacy of a 7-day high-dose (30 mg/kg once daily) regimen of teicoplanin was compared with that of vancomycin (50 mg/kg twice daily). Whereas high levels of teicoplanin were found in tissue cage fluid, continuously exceeding its MBC for MRSA by 8- to 16-fold, no significant reduction in the viable counts of MRSA occurred during therapy. In contrast, either vancomycin alone or a combined regimen of high-dose teicoplanin plus rifampin (25 mg/kg twice daily) could significantly decrease the viable counts in tissue cage fluids. Whereas the bacteria recovered from tissue cage fluids during therapy showed no evidence of teicoplanin resistance, they failed to be killed even by high levels of this antimicrobial agent. The altered susceptibility of in vivo growing bacteria to teicoplanin killing might in part explain the defective activity of this antimicrobial agent when used as monotherapy against chronic S. aureus infections. These data may indicate the need for a combined regimen of teicoplanin with other agents such as rifampin to optimize the therapy of severe staphylococcal infections.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arioli V., Berti M., Candiani G. Activity of teicoplanin in localized experimental infections in rats. J Hosp Infect. 1986 Mar;7 (Suppl A):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(86)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J., Kaatz G. W. Comparative effect of protein binding on the killing activities of teicoplanin and vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jun;35(6):1089–1092. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.6.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Lam K. Efficacy of vancomycin plus rifampin in experimental aortic-valve endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: in vitro-in vivo correlations. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):157–165. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibler M. R., Frame P. T., Hagler D. N., Bode R. B., Staneck J. L., Thamlikitkul V., Harris J. E., Haregewoin A., Bullock W. E., Jr Clinical evaluation of efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety of teicoplanin for serious gram-positive infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):207–212. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouchenaki N., Vaudaux P. E., Huggler E., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Successful single-dose prophylaxis of Staphylococcus aureus foreign body infections in guinea pigs by fleroxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):21–24. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Williams P. Influence of substrate limitation and growth phase on sensitivity to antimicrobial agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15 (Suppl A):7–14. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.suppl_a.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calain P., Krause K. H., Vaudaux P., Auckenthaler R., Lew D., Waldvogel F., Hirschel B. Early termination of a prospective, randomized trial comparing teicoplanin and flucloxacillin for treating severe staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;155(2):187–191. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calain P., Waldvogel F. Clinical efficacy of teicoplanin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;9(2):127–129. doi: 10.1007/BF01963637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carper H. T., Sullivan G. W., Mandell G. L. Teicoplanin, vancomycin, rifampicin: in-vivo and in-vitro studies with Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 May;19(5):659–662. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.5.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Kennedy S. Effects of dosage, peak and trough concentrations in serum, protein binding, and bactericidal rate on efficacy of teicoplanin in a rabbit model of endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Apr;34(4):510–514. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.4.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Sande M. A. Teicoplanin versus nafcillin and vancomycin in the treatment of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):61–64. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuard C., Herrmann M., Vaudaux P., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Successful therapy of experimental chronic foreign-body infection due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by antimicrobial combinations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Dec;35(12):2611–2616. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.12.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuard C., Lucet J. C., Rohner P., Herrmann M., Auckenthaler R., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus recovered from infected foreign body in vivo to killing by antimicrobials. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1369–1373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuard C., Vaudaux P., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus growing on fibronectin-coated surfaces to bactericidal antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):625–632. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey P. G., Williams A. H. A review of the safety profile of teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Apr;27 (Suppl B):69–73. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.suppl_b.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey P. G., Williams A. H. Teicoplanin monotherapy of serious infections caused by gram-positive bacteria: a re-evaluation of patients with endocarditis or Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia from a European open trial. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Apr;27 (Suppl B):43–50. doi: 10.1093/jac/27.suppl_b.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Favero A., Menichetti F., Guerciolini R., Bucaneve G., Baldelli F., Aversa F., Terenzi A., Davis S., Pauluzzi S. Prospective randomized clinical trial of teicoplanin for empiric combined antibiotic therapy in febrile, granulocytopenic acute leukemia patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1126–1129. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faville R. J., Jr, Zaske D. E., Kaplan E. L., Crossley K., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Combined therapy with vancomycin and rifampin. JAMA. 1978 Oct 27;240(18):1963–1965. doi: 10.1001/jama.240.18.1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galetto D. W., Boscia J. A., Kobasa W. D., Kaye D. Teicoplanin compared with vancomycin for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Wood C. A., Kimbrough R. C. Failure of treatment with teicoplanin at 6 milligrams/kilogram/day in patients with Staphylococcus aureus intravascular infection. The Infectious Diseases Consortium of Oregon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Collier P. J., Brown M. R. Influence of growth rate on susceptibility to antimicrobial agents: biofilms, cell cycle, dormancy, and stringent response. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1865–1868. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glupczynski Y., Lagast H., Van der Auwera P., Thys J. P., Crokaert F., Yourassowsky E., Meunier-Carpentier F., Klastersky J., Kains J. P., Serruys-Schoutens E. Clinical evaluation of teicoplanin for therapy of severe infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):52–57. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N. Treatment of bone, joint, and vascular-access-associated gram-positive bacterial infections with teicoplanin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2392–2397. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood D. Microbiological properties of teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21 (Suppl A):1–13. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_a.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenthner S. H., Wenzel R. P. In vitro activities of teichomycin, fusidic acid, flucloxacillin, fosfomycin, and vancomycin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):268–269. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Tomasz A. Antibiotic tolerance among clinical isolates of bacteria. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):368–386. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. P., Uttley A. H., Woodford N., George R. C. Resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin: an emerging clinical problem. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):280–291. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Dorman N. J., Lerner S. A. Emergence of teicoplanin resistance during therapy of Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):103–108. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Reddy V. N., Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J. Daptomycin compared with teicoplanin and vancomycin for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2081–2085. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karchmer A. W. Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin: the sequel. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Nov 1;115(9):739–741. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-9-739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leport C., Perronne C., Massip P., Canton P., Leclercq P., Bernard E., Lutun P., Garaud J. J., Vilde J. L. Evaluation of teicoplanin for treatment of endocarditis caused by gram-positive cocci in 20 patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):871–876. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. P., Fromm B. S., Reddy B. R. Slow response to vancomycin or vancomycin plus rifampin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Nov 1;115(9):674–680. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-9-674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P., Garaud J. J., Parenti F. A multicentre open clinical trial of teicoplanin in infections caused by gram-positive bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21 (Suppl A):61–67. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_a.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucet J. C., Herrmann M., Rohner P., Auckenthaler R., Waldvogel F. A., Lew D. P. Treatment of experimental foreign body infection caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Dec;34(12):2312–2317. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.12.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manquat G., Croize J., Stahl J. P., Meyran M., Hirtz P., Micoud M. Failure of teicoplanin treatment associated with an increase in MIC during therapy of Staphylococcus aureus septicaemia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Jun;29(6):731–732. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.6.731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino P., Venditti M., Micozzi A., Brandimarte C., Gentile G., Santini C., Serra P. Teicoplanin in the treatment of gram-positive-bacterial endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1329–1334. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Niederreiter K., Shinners E. M. Treatment of experimental chronic osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus with teicoplanin. Infection. 1986 May-Jun;14(3):136–138. doi: 10.1007/BF01643479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Shaffer M. Treatment of experimental chronic osteomyelitis due to staphylococcus aureus with vancomycin and rifampin. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):352–357. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peetermans W. E., Hoogeterp J. J., Hazekamp-van Dokkum A. M., van den Broek P., Mattie H. Antistaphylococcal activities of teicoplanin and vancomycin in vitro and in an experimental infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1869–1874. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Shanholtzer C. J. Tests for bactericidal effects of antimicrobial agents: technical performance and clinical relevance. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1992 Oct;5(4):420–432. doi: 10.1128/cmr.5.4.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland M. Clinical pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1990 Mar;18(3):184–209. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199018030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. R., Cheesbrough J., Spearing R., Davies J. M. Randomized prospective study comparing vancomycin with teicoplanin in the treatment of infections associated with Hickman catheters. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1193–1197. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stille W., Sietzen W., Dieterich H. A., Fell J. J. Clinical efficacy and safety of teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21 (Suppl A):69–79. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_a.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Laethem Y., Hermans P., De Wit S., Goosens H., Clumeck N. Teicoplanin compared with vancomycin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: preliminary results. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21 (Suppl A):81–87. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.suppl_a.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Aoun M., Meunier F. Randomized study of vancomycin versus teicoplanin for the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections in immunocompromised hosts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Mar;35(3):451–457. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Meunier-Carpentier F., Klastersky J. Clinical study of combination therapy with oxacillin and rifampin for staphylococcal infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5 (Suppl 3):S515–S522. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_3.s515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer A. F., Frei R., Rajacic Z., Zimmerli W. Correlation between in vivo and in vitro efficacy of antimicrobial agents against foreign body infections. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):96–102. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. H., Grüneberg R. N. Teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Nov;14(5):441–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. P., Grüneberg R. N., Neu H. Dosage recommendations for teicoplanin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 Dec;32(6):792–796. doi: 10.1093/jac/32.6.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Waldvogel F. A., Vaudaux P., Nydegger U. E. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection: description and characteristics of an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):487–497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


