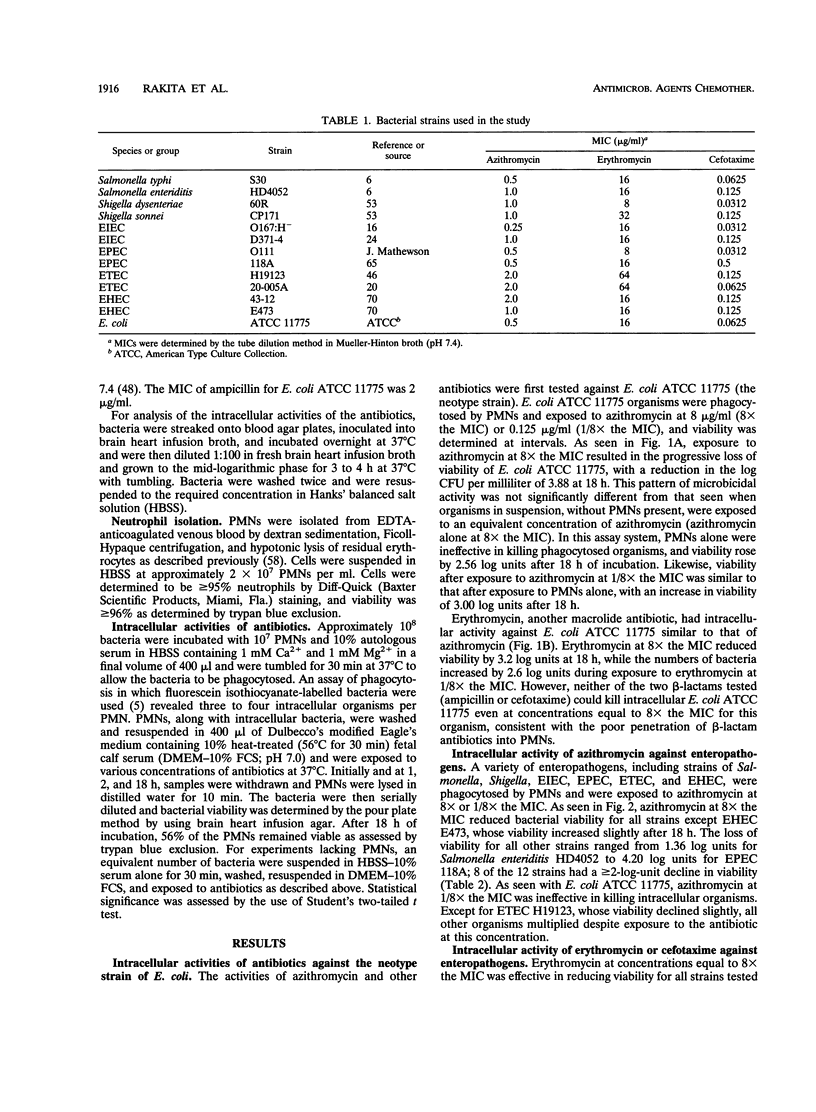
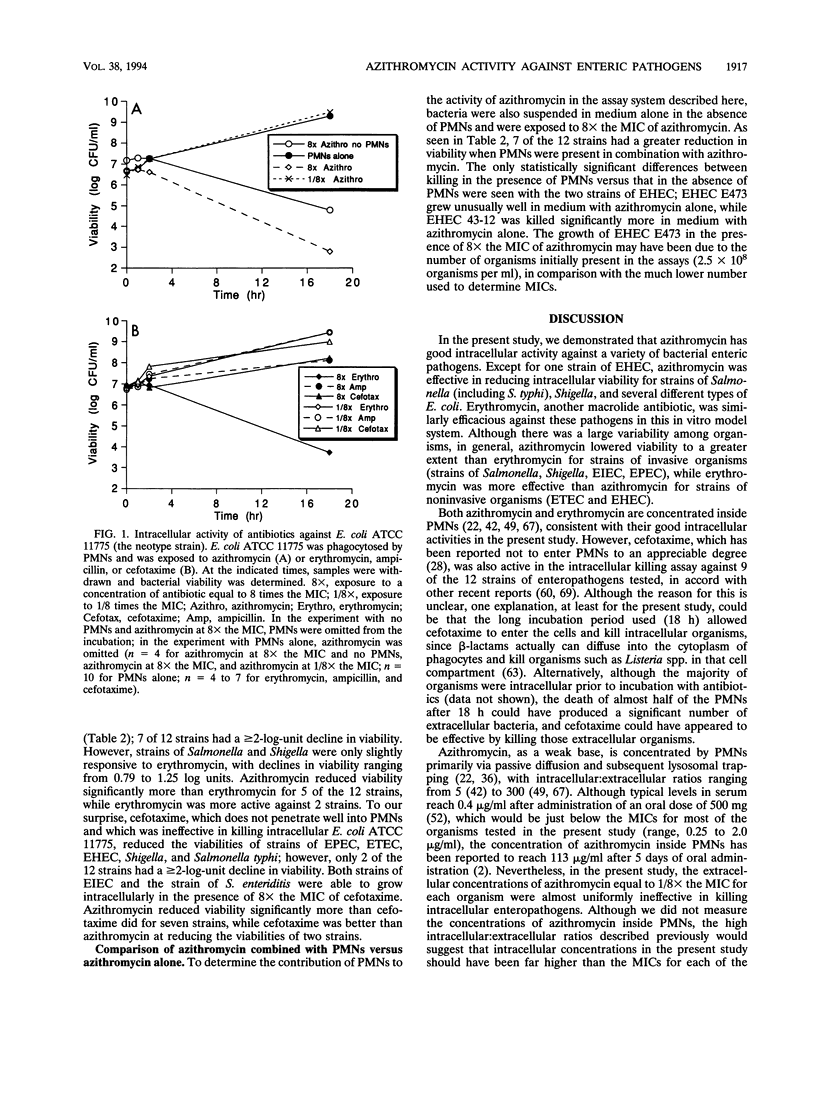
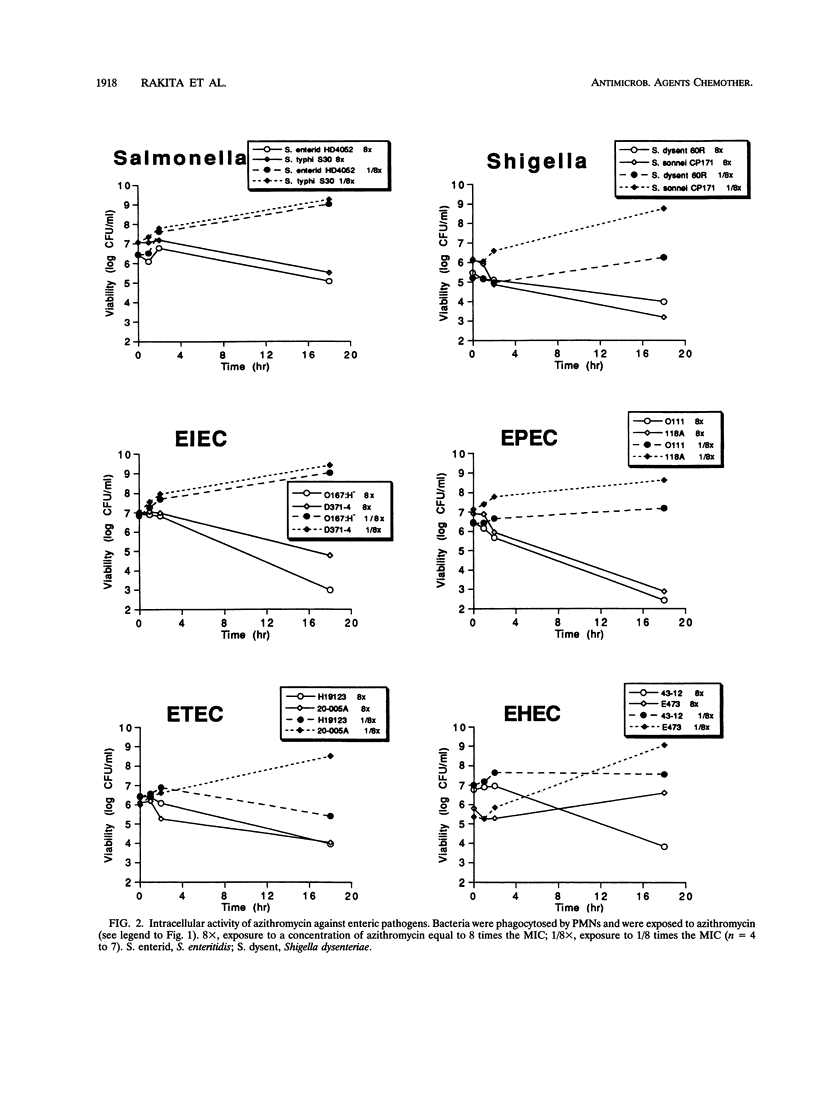
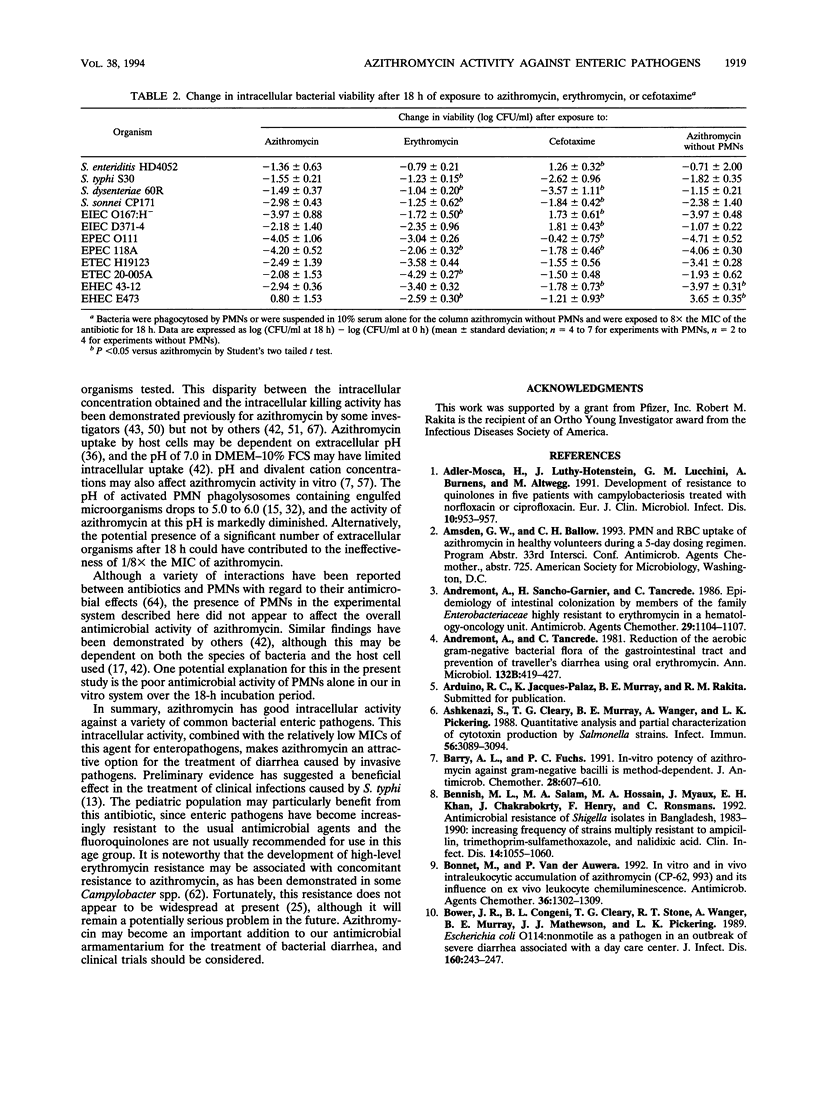
Abstract
Azithromycin, a new azalide antibiotic, is active in vitro against a variety of enteric bacterial pathogens. Since it is concentrated inside human neutrophils and other cells, it might be particularly useful in the treatment of infections caused by enteropathogens that invade host tissues. The intracellular activity of azithromycin against several enteric pathogens that had been phagocytosed by neutrophils was determined. Azithromycin was effective in reducing the intracellular viabilities of almost all strains tested, including representative strains of Salmonella, Shigella, and enteroinvasive, enteropathogenic, enterotoxigenic, and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Erythromycin was also effective in this model system, although azithromycin was generally more effective than erythromycin against strains of invasive enteric pathogens. Cefotaxime reduced intracellular bacterial viability to a lesser extent than either azithromycin or erythromycin. The presence of neutrophils did not significantly affect the activity of azithromycin in this system. Azithromycin may be a useful agent for the treatment of bacterial diarrhea, and clinical trials should be considered.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler-Mosca H., Lüthy-Hottenstein J., Martinetti Lucchini G., Burnens A., Altwegg M. Development of resistance to quinolones in five patients with campylobacteriosis treated with norfloxacin or ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Nov;10(11):953–957. doi: 10.1007/BF02005451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andremont A., Sancho-Garnier H., Tancrede C. Epidemiology of intestinal colonization by members of the family Enterobacteriaceae highly resistant to erythromycin in a hematology-oncology unit. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1104–1107. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andremont A., Tancrede C. Reduction of the aerobic Gram negative bacterial flora of the gastro-intestinal tract and prevention of traveller's diarrhea using oral erythromycin. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Nov-Dec;132 B(3):419–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi S., Cleary T. G., Murray B. E., Wanger A., Pickering L. K. Quantitative analysis and partial characterization of cytotoxin production by Salmonella strains. Infect Immun. 1988 Dec;56(12):3089–3094. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.12.3089-3094.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Fuchs P. C. In-vitro potency of azithromycin against gram-negative bacilli is method-dependent. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Oct;28(4):607–610. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.4.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennish M. L., Salam M. A., Hossain M. A., Myaux J., Khan E. H., Chakraborty J., Henry F., Ronsmans C. Antimicrobial resistance of Shigella isolates in Bangladesh, 1983-1990: increasing frequency of strains multiply resistant to ampicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and nalidixic acid. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 May;14(5):1055–1060. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.5.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnet M., Van der Auwera P. In vitro and in vivo intraleukocytic accumulation of azithromycin (CP-62, 993) and its influence on ex vivo leukocyte chemiluminescence. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1302–1309. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bower J. R., Congeni B. L., Cleary T. G., Stone R. T., Wanger A., Murray B. E., Mathewson J. J., Pickering L. K. Escherichia coli O114:nonmotile as a pathogen in an outbreak of severe diarrhea associated with a day care center. J Infect Dis. 1989 Aug;160(2):243–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bratoeva M. P., John J. F., Barg N. L. Molecular epidemiology of trimethoprim-resistant Shigella boydii serotype 2 strains from Bulgaria. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1428–1431. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1428-1431.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. P., Rocha H., Scheld W. M. Problems in salmonellosis: rationale for clinical trials with newer beta-lactam agents and quinolones. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Mar-Apr;8(2):189–207. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlier M. B., Zenebergh A., Tulkens P. M. Cellular uptake and subcellular distribution of roxithromycin and erythromycin in phagocytic cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20 (Suppl B):47–56. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.suppl_b.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech P., Lehrer R. I. Phagolysosomal pH of human neutrophils. Blood. 1984 Jan;63(1):88–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary T. G., Murray B. E. Lack of Shiga-like cytotoxin production by enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2177–2179. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2177-2179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di John D., Levine M. M. Treatment of diarrhea. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1988 Sep;2(3):719–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Kaper J. B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):3953–3961. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.3953-3961.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Ericsson C. D., Mathewson J. J., de la Cabada F. J., Conrad D. A. Oral aztreonam, a poorly absorbed yet effective therapy for bacterial diarrhea in US travelers to Mexico. JAMA. 1992 Apr 8;267(14):1932–1935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank M. O., Sullivan G. W., Carper H. T., Mandell G. L. In vitro demonstration of transport and delivery of antibiotics by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2584–2588. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladue R. P., Bright G. M., Isaacson R. E., Newborg M. F. In vitro and in vivo uptake of azithromycin (CP-62,993) by phagocytic cells: possible mechanism of delivery and release at sites of infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):277–282. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladue R. P., Snider M. E. Intracellular accumulation of azithromycin by cultured human fibroblasts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1056–1060. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordillo M. E., Reeve G. R., Pappas J., Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L., Murray B. E. Molecular characterization of strains of enteroinvasive Escherichia coli O143, including isolates from a large outbreak in Houston, Texas. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):889–893. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.889-893.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordillo M. E., Singh K. V., Murray B. E. In vitro activity of azithromycin against bacterial enteric pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 May;37(5):1203–1205. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.5.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Bobak D. A. Bacterial and protozoal gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 1;325(5):327–340. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108013250506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Hughes J. M., Lima N. L., Crane J. Diarrhea in developed and developing countries: magnitude, special settings, and etiologies. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12 (Suppl 1):S41–S50. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.Supplement_1.S41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N. L. Contrasts between phagocyte antibiotic uptake and subsequent intracellular bactericidal activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand W. L., King-Thompson N., Holman J. W. Entry of roxithromycin (RU 965), imipenem, cefotaxime, trimethoprim, and metronidazole into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1553–1557. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams K. C., Bourgeois A. L., Merrell B. R., Rozmajzl P., Escamilla J., Thornton S. A., Wasserman G. M., Burke A., Echeverria P., Green K. Y. Diarrheal disease during Operation Desert Shield. N Engl J Med. 1991 Nov 14;325(20):1423–1428. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199111143252006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro M., Koga H., Kohno S., Hayashi T., Yamaguchi K., Hirota M. Penetration of macrolides into human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Nov;24(5):719–729. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.5.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques Y. V., Bainton D. F. Changes in pH within the phagocytic vacuoles of human neutrophils and monocytes. Lab Invest. 1978 Sep;39(3):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K., Felmingham D., Ridgway G. In vitro activity of azithromycin (CP-62,993), a novel macrolide, against enteric pathogens. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1988;14(10):613–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitzis M. D., Goldstein F. W., Miégi M., Acar J. F. In-vitro activity of azithromycin against various Gram-negative bacilli and anaerobic bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jan;25 (Suppl A):15–18. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.suppl_a.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufen H., Wildfeuer A., Lach P. Mechanism of azithromycin uptake in human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Arzneimittelforschung. 1990 Jun;40(6):686–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepage P., Bogaerts J., Van Goethem C., Hitimana D. G., Nsengumuremyi F. Multiresistant Salmonella typhimurium systemic infection in Rwanda. Clinical features and treatment with cefotaxime. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Sep;26 (Suppl A):53–57. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.suppl_a.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H. The pharmacokinetics of azithromycin and their clinical significance. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;10(10):807–812. doi: 10.1007/BF01975832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez E. L., Diaz M., Devoto S., Grinstein S., Woloj M., Murray B. E., Rubeglio E., Mendilaharzu F., Turco M., Vasquez M. Evidence of infection with organisms producing Shiga-like toxins in household contacts of children with the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1991 Jan;10(1):20–24. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199101000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metchock B. In-vitro activity of azithromycin compared with other macrolides and oral antibiotics against Salmonella typhi. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jan;25 (Suppl A):29–31. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.suppl_a.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer A. P., Bril-Bazuin C., Mattie H., van den Broek P. J. Uptake of azithromycin by human monocytes and enhanced intracellular antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Nov;37(11):2318–2322. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.11.2318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milatovic D. Intraphagocytic activity of erythromycin, roxithromycin and azithromycin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;9(1):33–35. doi: 10.1007/BF01969530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Evans D. J., Jr, Penãranda M. E., Evans D. G. CFA/I-ST plasmids: comparison of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) of serogroups O25, O63, O78, and O128 and mobilization from an R factor-containing epidemic ETEC isolate. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):566–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.566-570.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L., Hill W. E. Utility of oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes for detecting enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1987 Apr;155(4):809–811. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.4.809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E. New aspects of antimicrobial resistance and the resulting therapeutic dilemmas. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1184–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E. Resistance of Shigella, Salmonella, and other selected enteric pathogens to antimicrobial agents. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 May-Jun;8 (Suppl 2):S172–S181. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_2.s172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panteix G., Guillaumond B., Harf R., Desbos A., Sapin V., Leclercq M., Perrin-Fayolle M. In-vitro concentration of azithromycin in human phagocytic cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 Jun;31 (Suppl E):1–4. doi: 10.1093/jac/31.suppl_e.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascual A., López-López G., Aragón J., Perea E. J. Effect of azithromycin, roxithromycin and erythromycin on human polymorphonuclear leukocyte function against Staphylococcus aureus. Chemotherapy. 1990;36(6):422–427. doi: 10.1159/000238799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen P., Simon C., Peters O., Hedderich J., Heim P. Influence of azithromycin and other macrolides on the intracellular killing of Staphylococcus aureus by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes of healthy donors and a patient with Chédiak-Higashi syndrome. Chemotherapy. 1992;38(3):185–190. doi: 10.1159/000238961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prado D., Cleary T. G., Pickering L. K., Ericsson C. D., Bartlett A. V., 3rd, DuPont H. L., Johnson P. C. The relation between production of cytotoxin and clinical features in shigellosis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):149–155. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retsema J. A., Bergeron J. M., Girard D., Milisen W. B., Girard A. E. Preferential concentration of azithromycin in an infected mouse thigh model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 Jun;31 (Suppl E):5–16. doi: 10.1093/jac/31.suppl_e.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retsema J. A., Brennan L. A., Girard A. E. Effects of environmental factors on the in vitro potency of azithromycin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;10(10):834–842. doi: 10.1007/BF01975836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retsema J., Girard A., Schelkly W., Manousos M., Anderson M., Bright G., Borovoy R., Brennan L., Mason R. Spectrum and mode of action of azithromycin (CP-62,993), a new 15-membered-ring macrolide with improved potency against gram-negative organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1939–1947. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen H., Michel B. R., Chait A. Phagocytosis of opsonized oil droplets by neutrophils. Adaptation to a microtiter plate format. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Nov 5;144(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90237-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salam M. A., Bennish M. L. Antimicrobial therapy for shigellosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Mar-Apr;13 (Suppl 4):S332–S341. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_4.s332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. E., Chang N. In vitro susceptibilities of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli to azithromycin and erythromycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1917–1918. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P. M. Intracellular distribution and activity of antibiotics. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;10(2):100–106. doi: 10.1007/BF01964420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vial P. A., Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L., Guers L., Levine M. M. Comparison of two assay methods for patterns of adherence to HEp-2 cells of Escherichia coli from patients with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):882–885. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.882-885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanger A. R., Murray B. E., Echeverria P., Mathewson J. J., DuPont H. L. Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli in travelers with diarrhea. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):640–642. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildfeuer A., Laufen H., Müller-Wening D., Haferkamp O. Interaction of azithromycin and human phagocytic cells. Uptake of the antibiotic and the effect on the survival of ingested bacteria in phagocytes. Arzneimittelforschung. 1989 Jul;39(7):755–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildfeuer A., Reisert I., Laufen H. Uptake and subcellular distribution of azithromycin in human phagocytic cells. Demonstration of the antibiotic in neutrophil polymorphonuclear leucocytes and monocytes by autoradiography and electron microscopy. Arzneimittelforschung. 1993 Apr;43(4):484–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsor D. K., Jr, Ashkenazi S., Chiovetti R., Cleary T. G. Adherence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains to a human colonic epithelial cell line (T84). Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1613–1617. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1613-1617.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek P. J. Antimicrobial drugs, microorganisms, and phagocytes. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11(2):213–245. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.2.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


