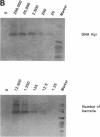
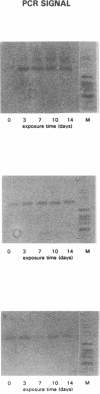
Abstract
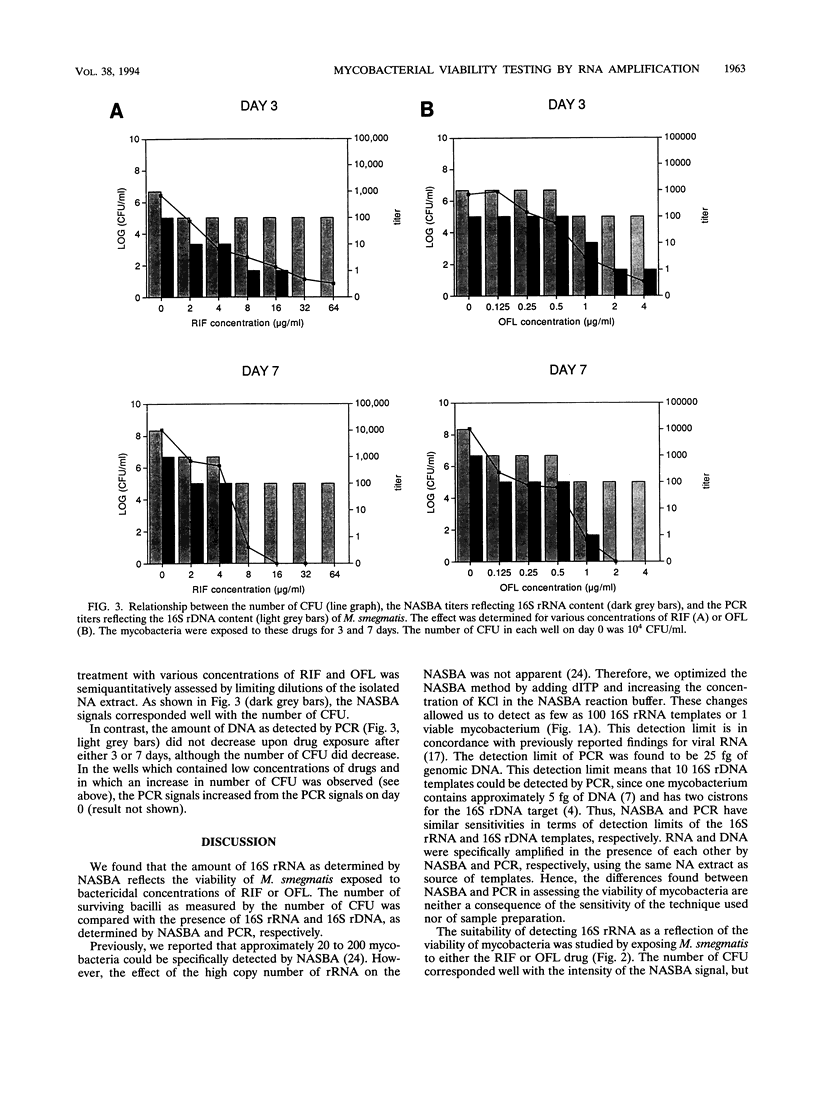
We investigated whether the presence of intact RNA is a valuable indicator of viability of mycobacteria with Mycobacterium smegmatis. M. smegmatis was exposed to various concentrations of rifampin and ofloxacin suspended in broth for different periods of time. The NASBA nucleic acid amplification system was used because of its rapid, sensitive, and specific detection of 16S rRNA. During drug exposure, the viability of the mycobacteria, expressed by the number of CFU, was compared with the presence of 16S rRNA as determined by NASBA and with the presence of DNA coding for 16S rRNA as determined by PCR. Both NASBA and PCR were shown to have a detection limit of approximately 5 x 10(2) CFU/ml. The intensity of the NASBA signal corresponded well with the number of CFU, and the lack of NASBA signal coincided with a loss of viability, which was reached after 3 days of exposure to bactericidal concentrations of both drugs. The presence of mycobacterial DNA, as determined by the intensity of the PCR signal, and the viability of M. smegmatis were not related, but an increase in the number of cells and intensity of PCR signal correlated well. Bacterial viability may thus be assessed by a rapid, sensitive, and specific, and semiquantitative technique by using NASBA. This system of viability testing provides the potential for rapid evaluation of drug susceptibility testing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrew P. W., Roberts I. S. Construction of a bioluminescent mycobacterium and its use for assay of antimycobacterial agents. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Sep;31(9):2251–2254. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.9.2251-2254.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrera L. F., Skamene E., Radzioch D. Assessment of mycobacterial infection and multiplication in macrophages by polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol Methods. 1993 Jan 4;157(1-2):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(93)90074-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bej A. K., Mahbubani M. H., Atlas R. M. Detection of viable Legionella pneumophila in water by polymerase chain reaction and gene probe methods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):597–600. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.597-600.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bercovier H., Kafri O., Kornitzer D., Sela S. Cloning and restriction analysis of ribosomal RNA genes from Mycobacterium smegmatis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;48(2):125–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böddinghaus B., Rogall T., Flohr T., Blöcker H., Böttger E. C. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of rRNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1751–1759. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1751-1759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Curtiss J. E., Jacobs W. R., Docherty M. A., Ritchie L. R., Curtiss R., 3rd Molecular analysis of DNA and construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.1093-1102.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooksey R. C., Crawford J. T., Jacobs W. R., Jr, Shinnick T. M. A rapid method for screening antimicrobial agents for activities against a strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis expressing firefly luciferase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1348–1352. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards U., Rogall T., Blöcker H., Emde M., Böttger E. C. Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7843–7853. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrada I. C., Lamb F. I., Colston M. J., Cox R. A. Partial nucleotide sequence of 16S ribosomal RNA isolated from armadillo-grown Mycobacterium leprae. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1449–1453. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartskeerl R. A., de Wit M. Y., Klatser P. R. Polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Mycobacterium leprae. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2357–2364. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huebner R. E., Good R. C., Tokars J. I. Current practices in mycobacteriology: results of a survey of state public health laboratories. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Apr;31(4):771–775. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.4.771-775.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iseman M. D. Treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 9;329(11):784–791. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309093291108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs W. R., Jr, Barletta R. G., Udani R., Chan J., Kalkut G., Sosne G., Kieser T., Sarkis G. J., Hatfull G. F., Bloom B. R. Rapid assessment of drug susceptibilities of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by means of luciferase reporter phages. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.8484123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson K. L., Gerba C. P., Pepper I. L. Polymerase chain reaction detection of nonviable bacterial pathogens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3513–3515. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3513-3515.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kievits T., van Gemen B., van Strijp D., Schukkink R., Dircks M., Adriaanse H., Malek L., Sooknanan R., Lens P. NASBA isothermal enzymatic in vitro nucleic acid amplification optimized for the diagnosis of HIV-1 infection. J Virol Methods. 1991 Dec;35(3):273–286. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(91)90069-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leysen D. C., Haemers A., Pattyn S. R. Mycobacteria and the new quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):1–5. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel B. K., Banerjee D. K., Butcher P. D. Determination of Mycobacterium leprae viability by polymerase chain reaction amplification of 71-kDa heat-shock protein mRNA. J Infect Dis. 1993 Sep;168(3):799–800. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.3.799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. H., Reeves D. S. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics. Microbiology, pharmacokinetics and clinical use. Drugs. 1988 Aug;36(2):193–228. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198836020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva M. T., Appelberg R., Silva M. N., Macedo P. M. In vivo killing and degradation of Mycobacterium aurum within mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2006–2016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2006-2016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. J., Jr, Nash D. R., Steele L. C., Steingrube V. Susceptibility testing of slowly growing mycobacteria by a microdilution MIC method with 7H9 broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):976–981. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.976-981.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W. Rifampin: mechanisms of action and resistance. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5 (Suppl 3):S407–S411. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_3.s407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet G. M., Schukkink R. A., van Gemen B., Schepers P., Klatser P. R. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) for the identification of mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Oct;139(10):2423–2429. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-10-2423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]