Abstract
In Streptomyces ambofaciens NSA2002, pigmented wild-type colonies spontaneously give rise to pigment-negative (Pig-) mutants at a frequency of about 0.5%. This genetic instability is related to large deletions which can be associated with amplifications of DNA sequences. The influence of three fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, enoxacin, and norfloxacin) on this property was investigated. At a survival rate higher than 60%, most colonies showed a patchwork phenotype consisting of phenotypically heterogeneous colonies harboring numerous mutant sectors. Moreover, the frequency of Pig- mutants rose to more than 90% at survival rates equal to or higher than 10%. Induced Pig- mutants showed the same phenotypical features as did spontaneous mutants. Most of them also harbored deletions, associated in some cases with DNA amplifications, in two loci of the large unstable region, AUD6 and AUD90 (derived from amplifiable unit of DNA). The size of deletions in induced mutants could rise to 1.5 Mb. These results show that ciprofloxacin, enoxacin, and norfloxacin greatly stimulate genetic instability and the occurrence of DNA rearrangements in S. ambofaciens. Moreover, these three fluoroquinolones had the same rank order for both toxic (i.e., antibacterial) and genotoxic activities. If the antibacterial effect of fluoroquinolones in S. ambofaciens is due to their interference with DNA gyrase, as shown for some other organisms, the genotoxic effect observed could be due to their interaction with this type II topoisomerase. This suggests that DNA gyrase is involved in the process of genetic instability in S. ambofaciens.
Full text
PDF
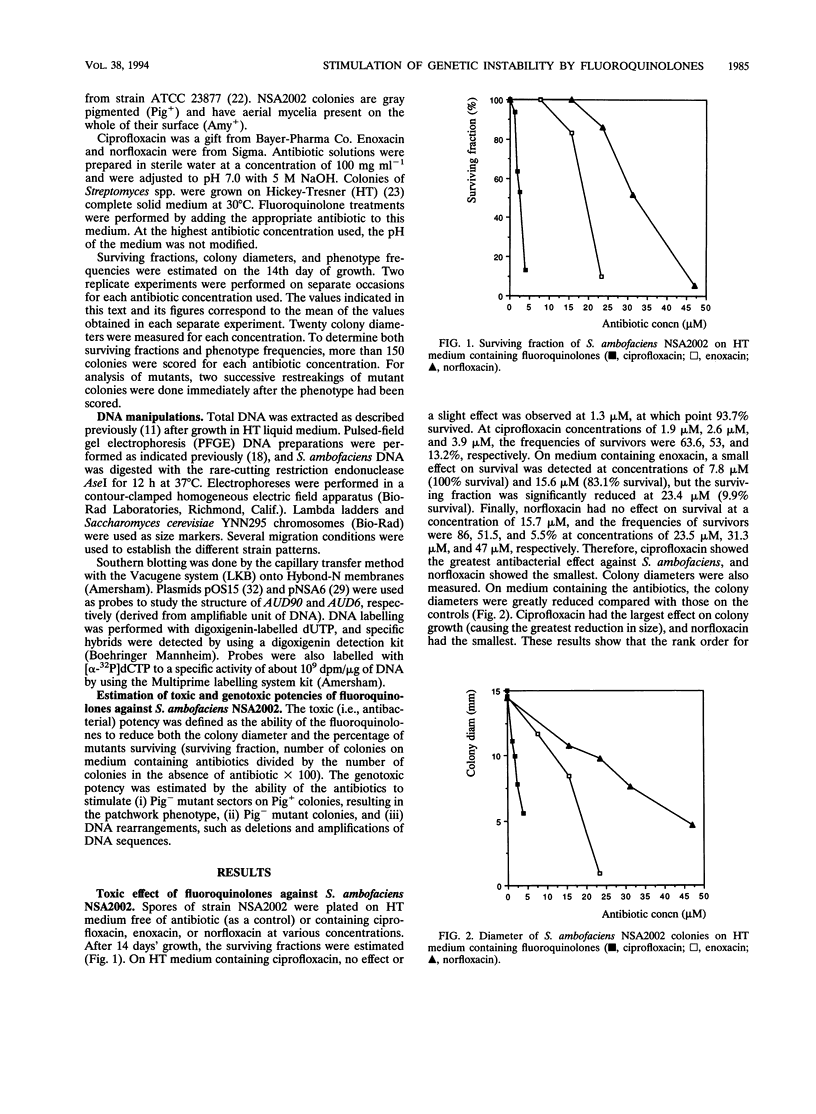
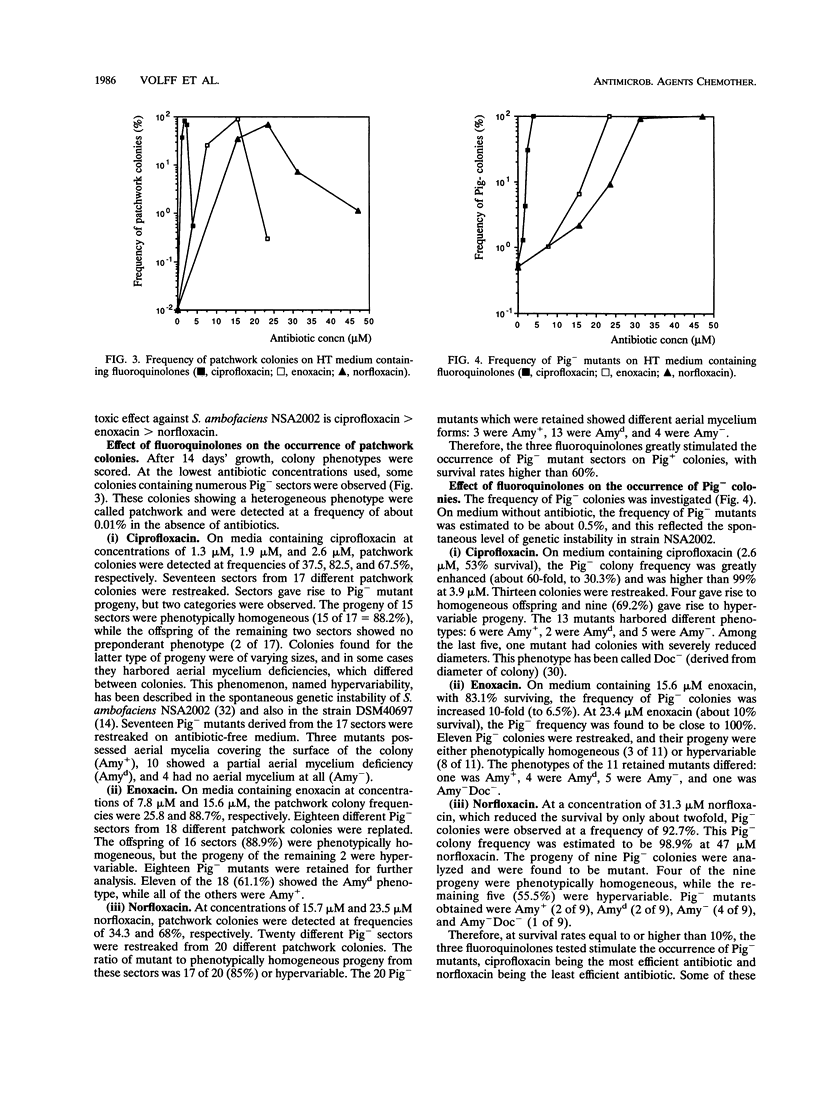

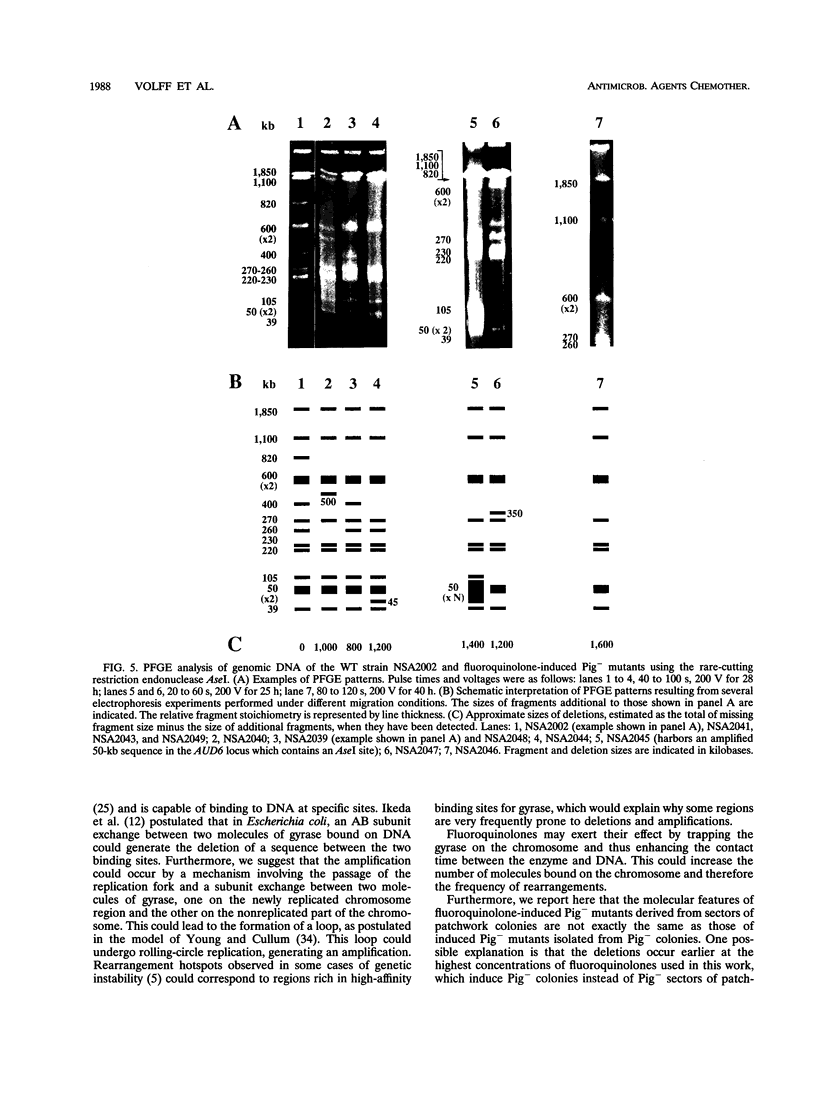


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bae Y. S., Chiba M., Ohira M., Ikeda H. A shuttle vector for analysis of illegitimate recombination in mammalian cells: effects of DNA topoisomerase inhibitors on deletion frequency. Gene. 1991 May 30;101(2):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90425-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae Y. S., Kawasaki I., Ikeda H., Liu L. F. Illegitimate recombination mediated by calf thymus DNA topoisomerase II in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2076–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch A., Häusler A., Hütter R. Genome rearrangement and genetic instability in Streptomyces spp. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4138–4142. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4138-4142.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dary A., Bourget N., Girard N., Simonet J. M., Decaris B. Amplification of a particular DNA sequence in Streptomyces ambofaciens RP181110 reversibly prevents spiramycin production. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jan;143(1):99–112. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90039-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Leonardo A., Cavolina P., Maddalena A. DNA topoisomerase II inhibition and gene amplification in V79/B7 cells. Mutat Res. 1993 Mar;301(3):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(93)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Leonardo A., Maddalena A., Cavolina P. Nalidixic acid-resistant V79 cells with reduced DNA topoisomerase II activity and amplification prone phenotype. Mutat Res. 1992 Oct;269(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(92)90214-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Schlossman S. F., Tedder T. F. 4-Quinolone drugs affect cell cycle progression and function of human lymphocytes in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):768–773. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gocke E. Mechanism of quinolone mutagenicity in bacteria. Mutat Res. 1991 May;248(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. E., Barett J. F., Huntington C. M., Muehlbauer P. A., Wahrenburg M. G. Genetic profile of a nalidixic acid analog: a model for the mechanism of sister chromatid exchange induction. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1989;13(3):238–252. doi: 10.1002/em.2850130308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda H., Moriya K., Matsumoto T. In vitro study of illegitimate recombination: involvement of DNA gyrase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 1):399–408. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajcovic J., Ebringer L., Polónyi J. Quinolones and coumarins eliminate chloroplasts from Euglena gracilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1883–1889. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P., Demuyter P., Moutier L., Laakel M., Decaris B., Simonet J. M. Hypervariability, a new phenomenon of genetic instability, related to DNA amplification in Streptomyces ambofaciens. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):419–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.419-423.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P., Demuyter P., Simonet J. M., Decaris B. Genetic instability and associated genome plasticity in Streptomyces ambofaciens: pulsed-field gel electrophoresis evidence for large DNA alterations in a limited genomic region. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4229–4233. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4229-4233.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P., Demuyter P., Simonet J. M., Decaris B. Genetic instability and hypervariability in Streptomyces ambofaciens: towards an understanding of a mechanism of genome plasticity. Mol Microbiol. 1990 May;4(5):707–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P., Francou F. X., Simonet J. M., Decaris B. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis of the genome of Streptomyces ambofaciens strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Oct;60(1-2):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90349-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P., Redenbach M., Cullum J. Physical map of the Streptomyces lividans 66 genome and comparison with that of the related strain Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3422–3429. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3422-3429.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Kieser H. M., Hopwood D. A., Chen C. W. The chromosomal DNA of Streptomyces lividans 66 is linear. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Dec;10(5):923–933. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura-Masuda A., Ikeda H. The DNA gyrase of Escherichia coli participates in the formation of a spontaneous deletion by recA-independent recombination in vivo. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Feb;220(3):345–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00391737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIDHAM T. G., ANDERSON P., FOLEY C., LINDENFELSER L. A., HESSELTINE C. W., BENEDICT R. G. A selection of media for maintenance and taxonomic study of Streptomyces. Antibiot Annu. 1956:947–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redenbach M., Flett F., Piendl W., Glocker I., Rauland U., Wafzig O., Kliem R., Leblond P., Cullum J. The Streptomyces lividans 66 chromosome contains a 1 MB deletogenic region flanked by two amplifiable regions. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Nov;241(3-4):255–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00284676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece R. J., Maxwell A. DNA gyrase: structure and function. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;26(3-4):335–375. doi: 10.3109/10409239109114072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saing K. M., Orii H., Tanaka Y., Yanagisawa K., Miura A., Ikeda H. Formation of deletion in Escherichia coli between direct repeats located in the long inverted repeats of a cellular slime mold plasmid: participation of DNA gyrase. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00340170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon E., Borrow J., Goddard A. D. Chromosome aberrations and cancer. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1153–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.1957167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volff J. N., Vandewiele D., Simonet J. M., Decaris B. Stimulation of genetic instability in Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877 by antibiotics that interact with DNA gyrase. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Nov;139(11):2551–2558. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-11-2551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volff J. N., Vandewiele D., Simonet J. M., Decaris B. Ultraviolet light, mitomycin C and nitrous acid induce genetic instability in Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC23877. Mutat Res. 1993 Jun;287(2):141–156. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(93)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Caron P. R., Kim R. A. The role of DNA topoisomerases in recombination and genome stability: a double-edged sword? Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90002-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Cullum J. A plausible mechanism for large-scale chromosomal DNA amplification in streptomycetes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 9;212(1):10–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]