Abstract
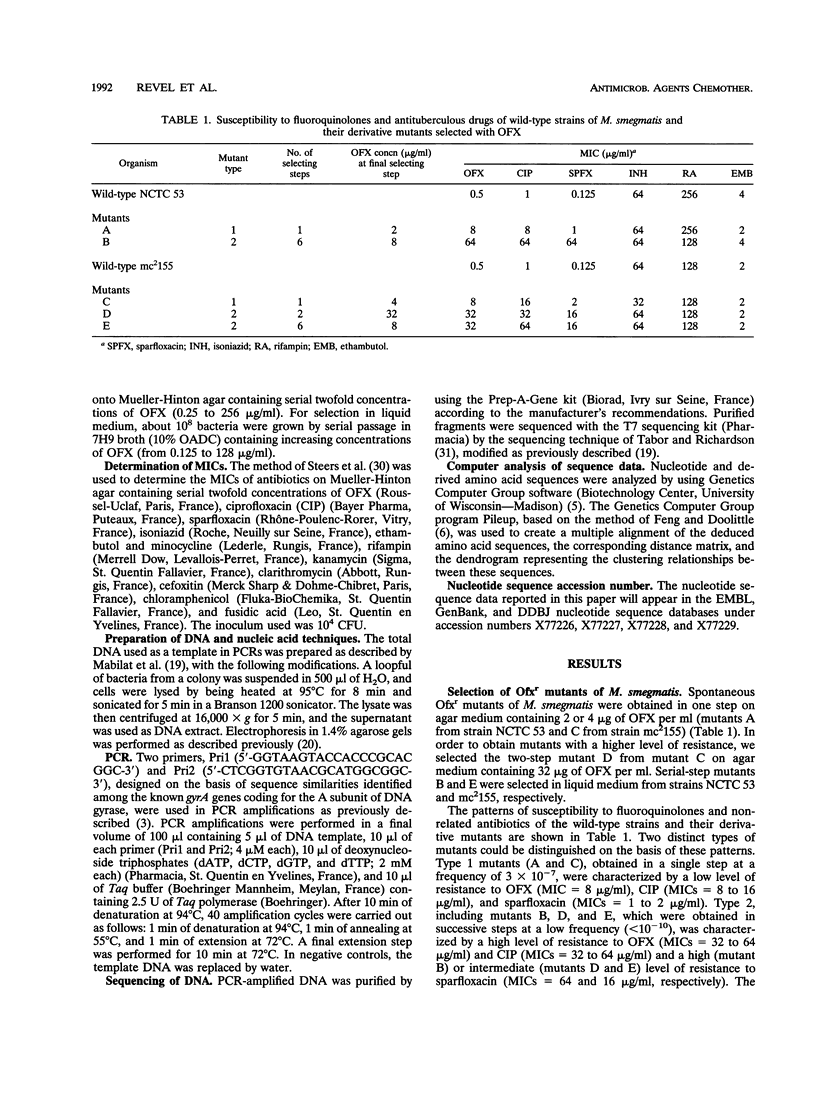
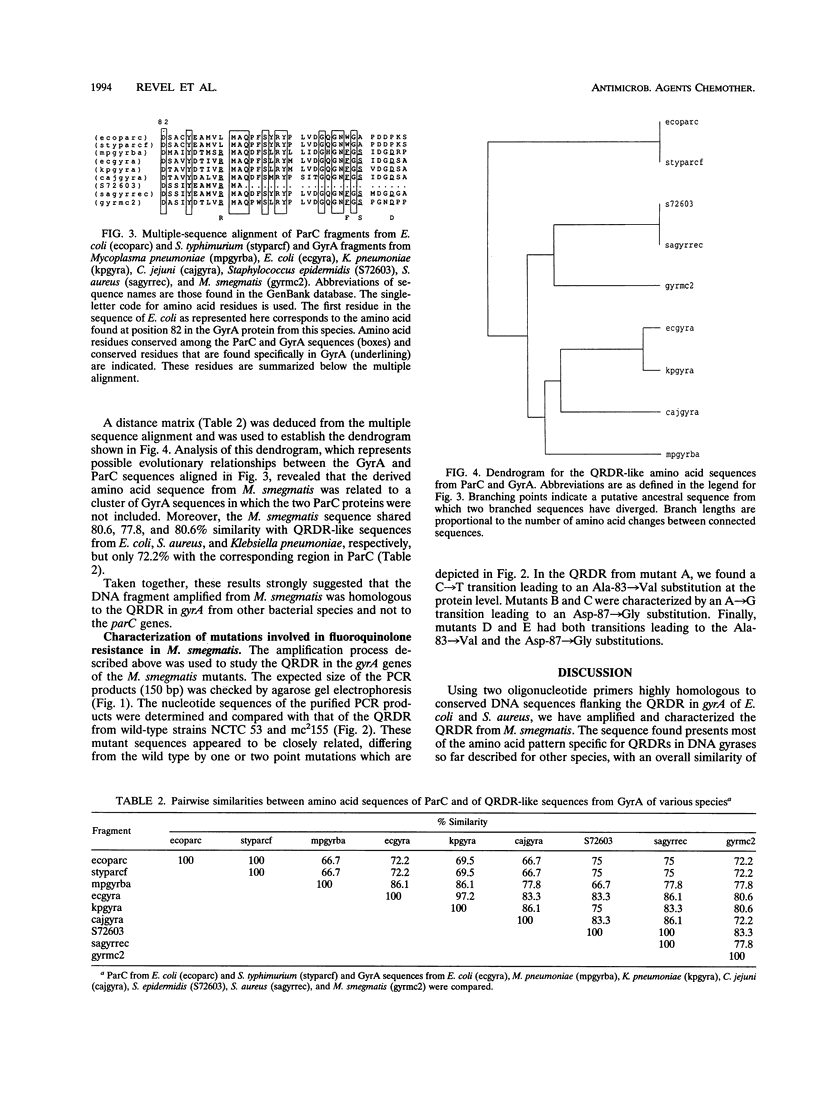
Fluoroquinolone-resistant mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis have been obtained in vitro by using ofloxacin as a selecting agent. Two types of mutants were identified according to their quinolone resistance patterns. Type 1 showed a low level of resistance to ofloxacin (MIC of 8 micrograms/ml), whereas a high level of resistance to this drug (MICs of 32 to 64 micrograms/ml) characterized type 2. By using two oligonucleotide primers homologous to DNA sequences flanking the quinolone resistance-determining region (QRDR) in the gyrA gene of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, a 150-bp DNA fragment was obtained by PCR amplification from total DNA of two wild-type and five mutant strains of M. smegmatis. The nucleotide sequences of the amplified fragments were determined. The deduced amino acid sequence from the wild-type strains showed ca. 79% similarity with the QRDR in the gyrase A subunit from other gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The DNA sequences obtained from the fluoroquinolone-resistant mutants of M. smegmatis exhibited nucleotide modifications compared with the wild-type QRDR. The QRDR from type 1 mutants had a C-T or an A-G transition leading to a change from Ala-83 to Val or Asp-87 to Gly, respectively. The QRDR from type 2 mutants had a Val-83 mutation or both Val-83 and Gly-87 mutations detected in the type 1 mutants. These results suggest that point mutations in the QRDR of the mycobacterial gyrA gene are responsible for acquired quinolone resistance in M. smegmatis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cambau E., Gutmann L. Mechanisms of resistance to quinolones. Drugs. 1993;45 (Suppl 3):15–23. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199300453-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambau E., Sougakoff W., Jarlier V. Amplification and nucleotide sequence of the quinolone resistance-determining region in the gyrA gene of mycobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Feb 1;116(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M. E., Wyke A. W., Kuroda R., Fisher L. M. Cloning and characterization of a DNA gyrase A gene from Escherichia coli that confers clinical resistance to 4-quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):886–894. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive sequence alignment as a prerequisite to correct phylogenetic trees. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(4):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF02603120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gootz T. D., Martin B. A. Characterization of high-level quinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):840–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswitz J. J., Willard K. E., Fasching C. E., Peterson L. R. Detection of gyrA gene mutations associated with ciprofloxacin resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: analysis by polymerase chain reaction and automated direct DNA sequencing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1166–1169. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosset J. H., Ji B. H., Guelpa-Lauras C. C., Perani E. G., N'Deli L. N. Clinical trial of pefloxacin and ofloxacin in the treatment of lepromatous leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1990 Jun;58(2):281–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett P., Maxwell A. Novel quinolone resistance mutations of the Escherichia coli DNA gyrase A protein: enzymatic analysis of the mutant proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):335–340. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisig P., Schedletzky H., Falkenstein-Paul H. Mutations in the gyrA gene of a highly fluoroquinolone-resistant clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Apr;37(4):696–701. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Wang J. C. Mapping the active site tyrosine of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5339–5344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
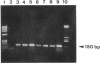
- Jarlier V., Nikaido H. Permeability barrier to hydrophilic solutes in Mycobacterium chelonei. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1418–1423. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1418-1423.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Nishimura Y., Imamura R., Niki H., Hiraga S., Suzuki H. New topoisomerase essential for chromosome segregation in E. coli. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90172-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalande V., Truffot-Pernot C., Paccaly-Moulin A., Grosset J., Ji B. Powerful bactericidal activity of sparfloxacin (AT-4140) against Mycobacterium tuberculosis in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):407–413. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttinger A. L., Springer A. L., Schmid M. B. A cluster of genes that affects nucleoid segregation in Salmonella typhimurium. New Biol. 1991 Jul;3(7):687–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabilat C., Goussard S., Sougakoff W., Spencer R. C., Courvalin P. Direct sequencing of the amplified structural gene and promoter for the extended-broad-spectrum beta-lactamase TEM-9 (RHH-1) of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Plasmid. 1990 Jan;23(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90041-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margerrison E. E., Hopewell R., Fisher L. M. Nucleotide sequence of the Staphylococcus aureus gyrB-gyrA locus encoding the DNA gyrase A and B proteins. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1596–1603. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1596-1603.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriya S., Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H. Structure and function of the region of the replication origin of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. III. Nucleotide sequence of some 10,000 base pairs in the origin region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2251–2265. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Jarlier V. Permeability of the mycobacterial cell wall. Res Microbiol. 1991 May;142(4):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90117-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram M., Fisher L. M. 4-Quinolone resistance mutations in the DNA gyrase of Escherichia coli clinical isolates identified by using the polymerase chain reaction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):387–389. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. B., Sawitzke J. A. Multiple bacterial topoisomerases: specialization or redundancy? Bioessays. 1993 Jul;15(7):445–449. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L. L., Mitscher L. A., Sharma P. N., O'Donnell T. J., Chu D. W., Cooper C. S., Rosen T., Pernet A. G. Mechanism of inhibition of DNA gyrase by quinolone antibacterials: a cooperative drug--DNA binding model. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):3886–3894. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper S. B., Melton R. E., Mustafa S., Kieser T., Jacobs W. R., Jr Isolation and characterization of efficient plasmid transformation mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1911–1919. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S., Oram M., Jensen B., Peterson L. R., Fisher L. M. DNA gyrase gyrA mutations in ciprofloxacin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus: close similarity with quinolone resistance mutations in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7260–7262. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7260-7262.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truffot-Pernot C., Ji B., Grosset J. Activities of pefloxacin and ofloxacin against mycobacteria: in vitro and mouse experiments. Tubercle. 1991 Mar;72(1):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(91)90025-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamura M., Nakamura E., Yoshii S., Amano H. Therapeutic effect of a new antibacterial substance ofloxacin (DL8280) on pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):352–356. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases: why so many? J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6659–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Huang W. M., Taylor D. E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the Campylobacter jejuni gyrA gene and characterization of quinolone resistance mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):457–463. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Oct;2(4):378–424. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.4.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura M., Nakamura S. Quinolone resistance-determining region in the DNA gyrase gyrA gene of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1271–1272. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.6.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]