Abstract
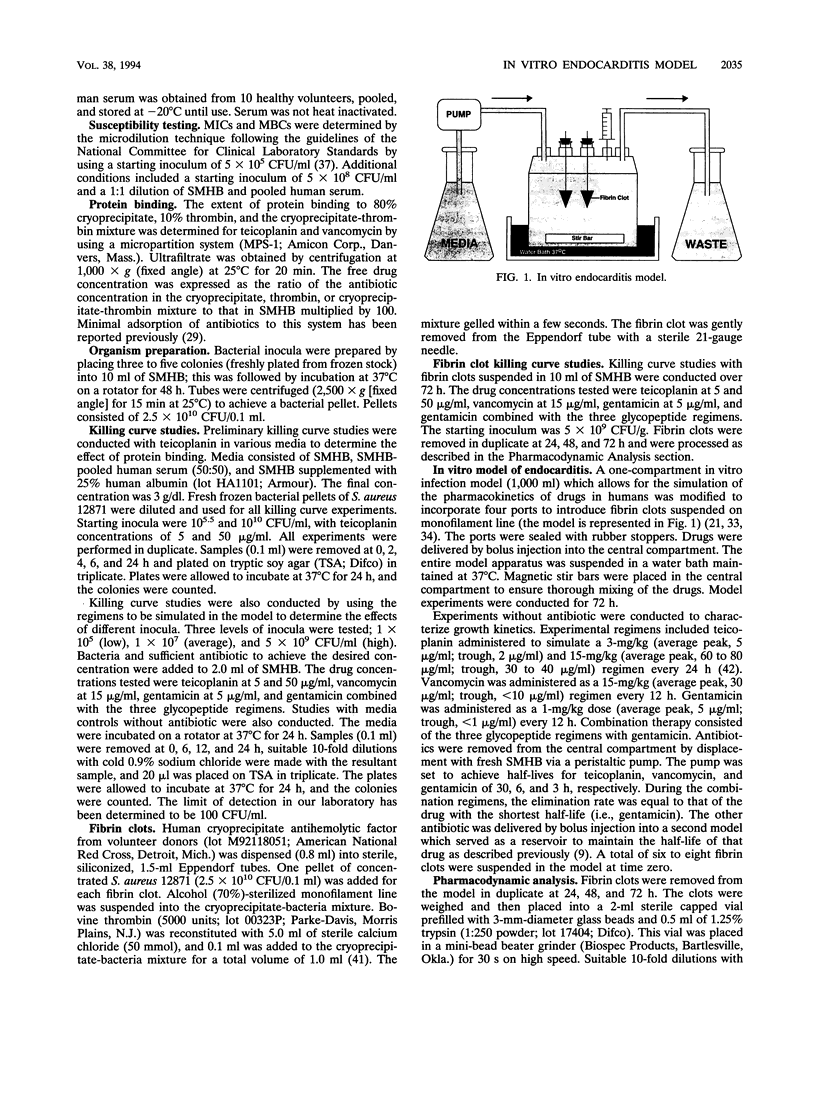
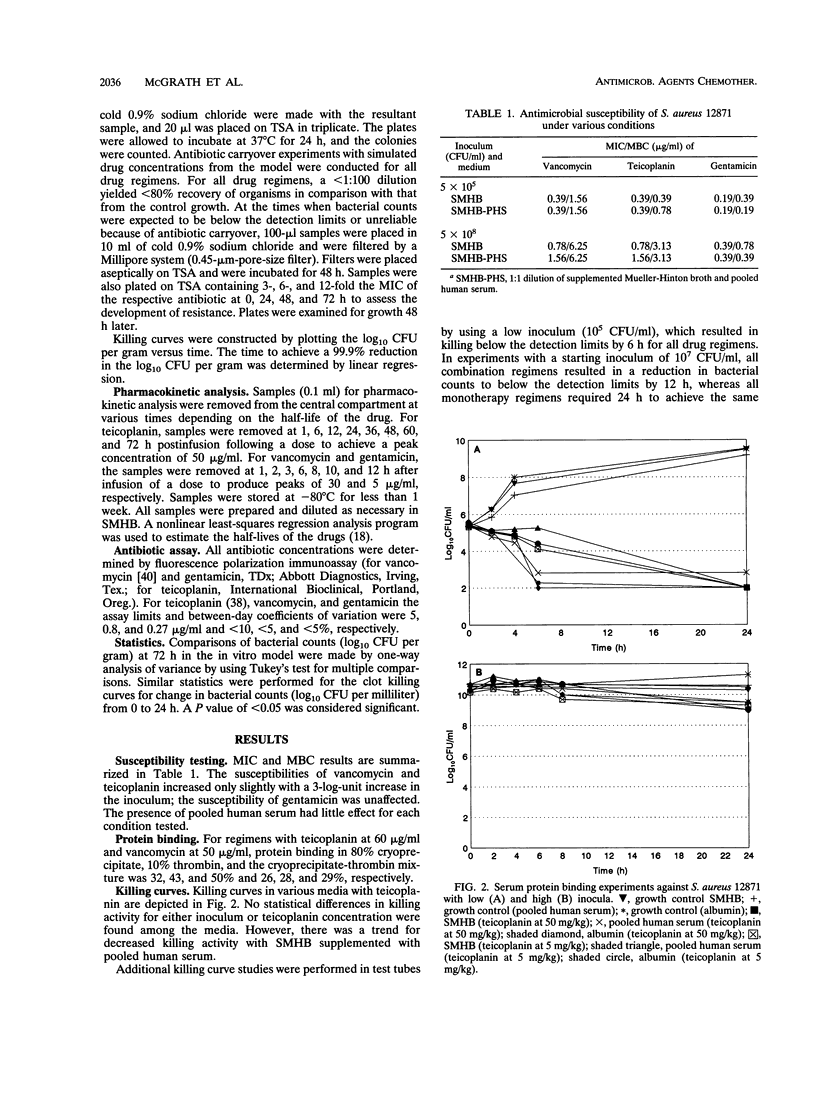
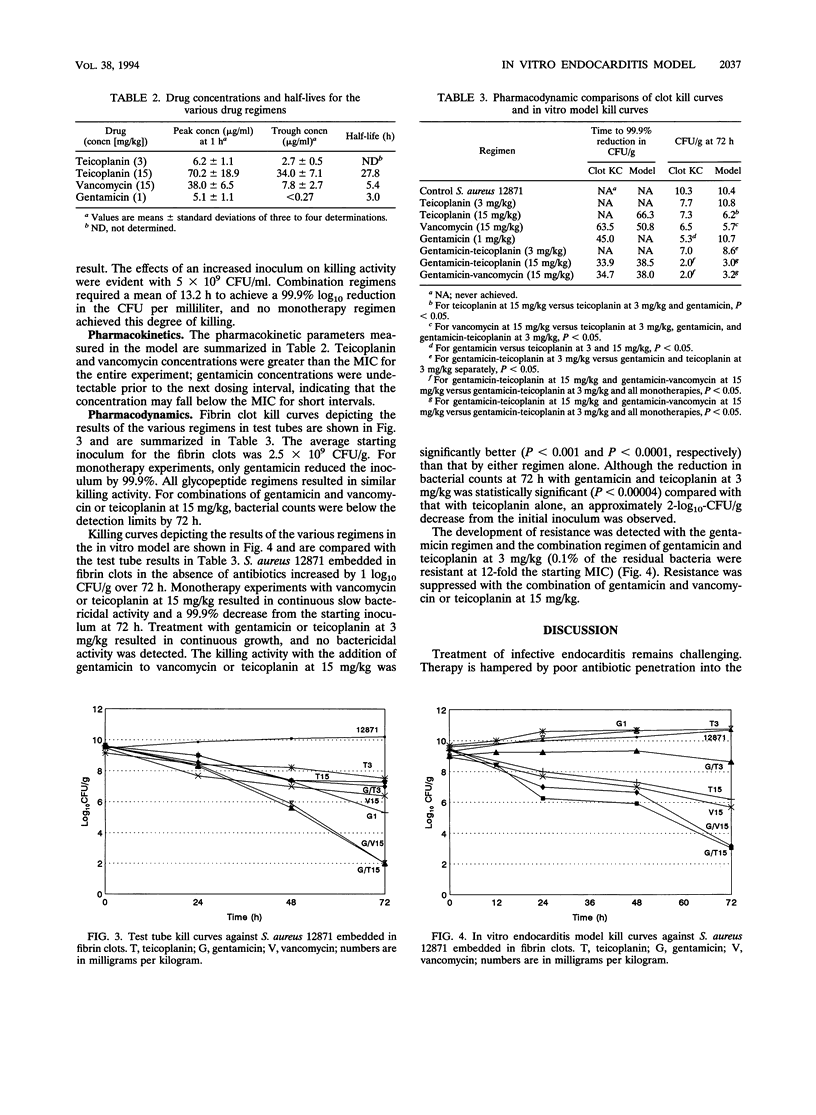
We adapted an in vitro pharmacodynamic model of infection to incorporate simulated endocardial vegetations. The bactericidal activities of teicoplanin, vancomycin, gentamicin, and various combinations of these drugs were studied against a strain of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus obtained from a patient being treated for endocarditis at Detroit Receiving Hospital. Bacteria were grown overnight, concentrated, and added to a mixture of cryoprecipitate (80%) and thrombin (10%) to achieve approximately 5 x 10(9) CFU/g. Fibrin clots (8 to 10) were suspended into the model, removed at 24, 48, and 72 h in duplicate, weighed, and homogenized in 1.25% trypsin. Control experiments were conducted to characterize the growth kinetics. The following antibiotics were administered to simulate the pharmacokinetics of the drugs in humans: teicoplanin at 3 and 15 mg/kg of body weight, vancomycin at 15 mg/kg, and gentamicin at 1 mg/kg. Fibrin clot samples used to detect resistance were plated on antibiotic-containing tryptic soy agar plates. For the teicoplanin and vancomycin regimens, protein binding to cryoprecipitate, thrombin, and fibrin clot was determined to be 32, 43, and 50% and 26, 28, and 29%, respectively. In comparison with no treatment, vancomycin or teicoplanin at 15 mg/kg or either of these regimens combined with gentamicin significantly reduced bacterial counts (P < 0.0001). Monotherapy with teicoplanin at 3 mg/kg or gentamicin resulted in no killing activity. Combination treatment with teicoplanin at 3 mg/kg and gentamicin resulted in the killing of approximately 2 log10 CFU/g by 72 h and the development of resistance to gentamicin. The results obtained with the in vitro model of endocarditis are similar to the results reported by several investigators with the rabbit model of infective endocarditis. This unique infection model is useful for designing initial drug dosage regimens and may be predictive of drug efficacy against infective endocarditis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J., Kaatz G. W. Comparative effect of protein binding on the killing activities of teicoplanin and vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jun;35(6):1089–1092. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.6.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Brusch J., Bergeron M. G., Weinstein L. Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. 3. Intermittent vs. continuous infusion and the effect of probenecid. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):73–78. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Weinstein L. Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. I. Comparison of penetration of ampicillin into fibrin clots, abscesses, and "interstitial fluid". J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):59–65. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S. Infective endocarditis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993 Sep;17(3):313–322. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellido F., Veuthey C., Blaser J., Bauernfeind A., Pechère J. C. Novel resistance to imipenem associated with an altered PBP-4 in a Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolate. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jan;25(1):57–68. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Nguyen B. M., Trottier S., Gauvreau L. Penetration of cefamandole, cephalothin, and desacetylcephalothin into fibrin clots. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Dec;12(6):682–687. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.6.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Robert J., Beauchamp D. Pharmacodynamics of antibiotics in fibrin clots. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 May;31 (Suppl 500):113–136. doi: 10.1093/jac/31.suppl_d.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron M. G., Simard P. Influence of three modes of administration on the penetration of latamoxef into interstitial fluid and fibrin clots and its in-vivo activity against Haemophilus influenzae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Jun;17(6):775–784. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.6.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibler M. R., Frame P. T., Hagler D. N., Bode R. B., Staneck J. L., Thamlikitkul V., Harris J. E., Haregewoin A., Bullock W. E., Jr Clinical evaluation of efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety of teicoplanin for serious gram-positive infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):207–212. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calain P., Krause K. H., Vaudaux P., Auckenthaler R., Lew D., Waldvogel F., Hirschel B. Early termination of a prospective, randomized trial comparing teicoplanin and flucloxacillin for treating severe staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1987 Feb;155(2):187–191. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.2.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon C. Impact of the antibiotic dosage schedule on efficacy in experimental endocarditis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;74:163–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Kennedy S. Effects of dosage, peak and trough concentrations in serum, protein binding, and bactericidal rate on efficacy of teicoplanin in a rabbit model of endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Apr;34(4):510–514. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.4.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Sande M. A. Teicoplanin versus nafcillin and vancomycin in the treatment of experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):61–64. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremieux A. C., Carbon C. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic requirements for antibiotic therapy of experimental endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Oct;36(10):2069–2074. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.10.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cremieux A. C., Maziere B., Vallois J. M., Ottaviani M., Azancot A., Raffoul H., Bouvet A., Pocidalo J. J., Carbon C. Evaluation of antibiotic diffusion into cardiac vegetations by quantitative autoradiography. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):938–944. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crémieux A. C., Mazière B., Vallois J. M., Ottaviani M., Bouvet A., Pocidalo J. J., Carbon C. Ceftriaxone diffusion into cardiac fibrin vegetation. Qualitative and quantitative evaluation by autoradiography. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1991;5(1):53–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1991.tb00701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham R., Cheesbrough J. Comparative activity of glycopeptide antibiotics against coagulase-negative staphylococci embedded in fibrin clots. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Sep;30(3):321–326. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galetto D. W., Boscia J. A., Kobasa W. D., Kaye D. Teicoplanin compared with vancomycin for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jul;154(1):69–75. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison M. W., Vance-Bryan K., Larson T. A., Toscano J. P., Rotschafer J. C. Assessment of effects of protein binding on daptomycin and vancomycin killing of Staphylococcus aureus by using an in vitro pharmacodynamic model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1925–1931. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison P. K., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis I. Staphylococcal endocarditis in rabbits resulting from placement of a polyethylene catheter in the right side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Jun;42(6):394–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. N., Wood C. A., Kimbrough R. C. Failure of treatment with teicoplanin at 6 milligrams/kilogram/day in patients with Staphylococcus aureus intravascular infection. The Infectious Diseases Consortium of Oregon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann M., Lai Q. J., Albrecht R. M., Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus to surface-bound platelets: role of fibrinogen/fibrin and platelet integrins. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):312–322. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Barriere S. L., Schaberg D. R., Fekety R. Ciprofloxacin versus vancomycin in the therapy of experimental methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):527–530. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Ciprofloxacin and rifampin, alone and in combination, for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1184–1187. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Development of resistance to fleroxacin during therapy of experimental methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Aug;35(8):1547–1550. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.8.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Barriere S. L., Albrecht L. M., Rybak M. J. Efficacy of ofloxacin in experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):257–260. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Dorman N. J., Lerner S. A. Emergence of teicoplanin resistance during therapy of Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):103–108. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Reddy V. N., Bailey E. M., Rybak M. J. Daptomycin compared with teicoplanin and vancomycin for therapy of experimental Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2081–2085. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kram H. B., Bansal M., Timberlake O., Shoemaker W. C. Antibacterial effects of fibrin glue-antibiotic mixtures. J Surg Res. 1991 Feb;50(2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90243-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamp K. C., Rybak M. J. Teicoplanin and daptomycin bactericidal activities in the presence of albumin or serum under controlled conditions of pH and ionized calcium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):605–609. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie G. Y., Bergeron M. G. Influence of four modes of administration on penetration of aztreonam, cefuroxime, and ampicillin into interstitial fluid and fibrin clots and on in vivo efficacy against Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):404–412. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine D. P., Fromm B. S., Reddy B. R. Slow response to vancomycin or vancomycin plus rifampin in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Nov 1;115(9):674–680. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-9-674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath B. J., Bailey E. M., Lamp K. C., Rybak M. J. Pharmacodynamics of once-daily amikacin in various combinations with cefepime, aztreonam, and ceftazidime against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an in vitro infection model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Dec;36(12):2741–2746. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.12.2741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath B. J., Lamp K. C., Rybak M. J. Pharmacodynamic effects of extended dosing intervals of imipenem alone and in combination with amikacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an in vitro model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Sep;37(9):1931–1937. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.9.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Wexler M. A., Steigbigel N. H. Single and combination antibiotic therapy of Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis: emergence of gentamicin-resistant mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):336–343. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak M. J., Bailey E. M., Reddy V. N. Clinical evaluation of teicoplanin fluorescence polarization immunoassay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Aug;35(8):1586–1590. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.8.1586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rybak M. J., Lerner S. A., Levine D. P., Albrecht L. M., McNeil P. L., Thompson G. A., Kenny M. T., Yuh L. Teicoplanin pharmacokinetics in intravenous drug abusers being treated for bacterial endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Apr;35(4):696–700. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwenzer K. S., Wang C. H., Anhalt J. P. Automated fluorescence polarization immunoassay for monitoring vancomycin. Ther Drug Monit. 1983;5(3):341–345. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198309000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. F., Letassy N. A., Thompson G. D. Fibrin glue: a review of its preparation, efficacy, and adverse effects as a topical hemostat. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1988 Dec;22(12):946–952. doi: 10.1177/106002808802201203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turcotte A., Bergeron M. G. Pharmacodynamic interaction between RP 59500 and gram-positive bacteria infecting fibrin clots. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Oct;36(10):2211–2215. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.10.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbist L., Tjandramaga B., Hendrickx B., Van Hecken A., Van Melle P., Verbesselt R., Verhaegen J., De Schepper P. J. In vitro activity and human pharmacokinetics of teicoplanin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):881–886. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINSTEIN L., DAIKOS G. K., PERRIN T. S. Studies on the relationship of tissue fluid and blood levels of penicillin. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Nov;38(5):712–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



