Abstract
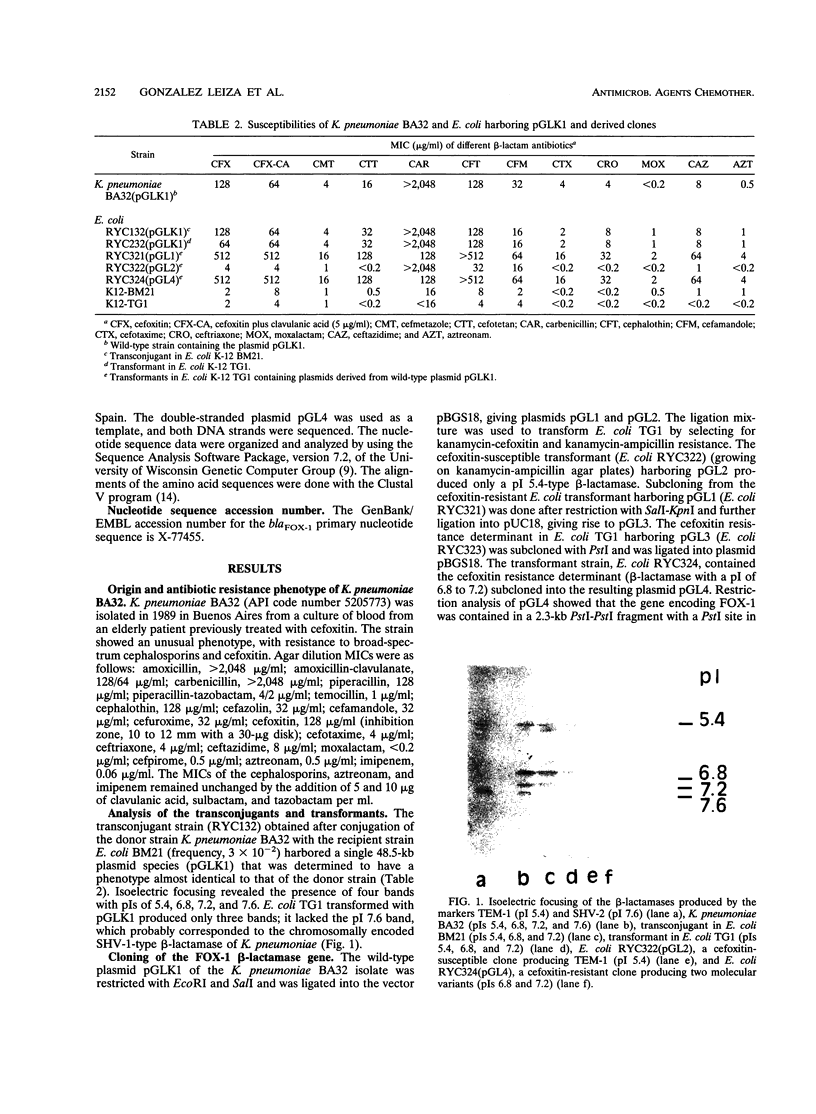
Klebsiella pneumoniae BA32, a clinical isolate from Buenos Aires, Argentina, was found to produce a plasmid-encoded beta-lactamase (FOX-1) which conferred resistance to broad-spectrum cephalosporins and cephamycins. Resistance could be transferred by conjugation or transformation into Escherichia coli K-12 via a 48.5-kb plasmid (pGLK1) that produced two FOX-1 molecular variants with isoelectric points of 6.8 and 7.2 and apparent molecular sizes of 37 and 35 kDa, respectively. The kinetic study revealed that the two variants had very similar substrate and inhibition profiles. These values resemble those of chromosomally mediated class C (group 1) cephalosporinases. The structural gene of FOX-1 (blaFOX-1) was cloned into a 2,270-bp PstI-PstI fragment and was expressed in E. coli TG1. The deduced 382-amino-acid sequence of FOX-1 exhibited a high degree of similarity with chromosomally encoded AmpC beta-lactamases of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Serratia marcescens, Enterobacter cloacae, E. coli, and Citrobacter freundii. These findings suggest that FOX-1 is a plasmid-mediated AmpC-type beta-lactamase that is encoded by a single gene and that has two molecular variants.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baquero F., Bouanchaud D., Martinez-Perez M. C., Fernandez C. Microcin plasmids: a group of extrachromosomal elements coding for low-molecular-weight antibiotics in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.342-347.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Chong Y., Schweighart S. Extended broad spectrum beta-lactamase in Klebsiella pneumoniae including resistance to cephamycins. Infection. 1989 Sep-Oct;17(5):316–321. doi: 10.1007/BF01650718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Normark S. Beta-lactam resistance in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli caused by elevated production of the ampC-mediated chromosomal beta-lactamase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Oct;16(4):427–433. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.4.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K. Classification of beta-lactamases: groups 1, 2a, 2b, and 2b'. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):264–270. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Sykes R. B. Methodology for the study of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jul;30(1):6–10. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlier P., Dideberg O., Frère J. M., Moews P. C., Knox J. R. Crystallographic data for the beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae P99. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 5;171(2):237–238. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenthal R., Cornish-Bowden A. The direct linear plot. A new graphical procedure for estimating enzyme kinetic parameters. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):715–720. doi: 10.1042/bj1390715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galleni M., Lindberg F., Normark S., Cole S., Honore N., Joris B., Frere J. M. Sequence and comparative analysis of three Enterobacter cloacae ampC beta-lactamase genes and their products. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):753–760. doi: 10.1042/bj2500753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghuysen J. M. Serine beta-lactamases and penicillin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:37–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honoré N., Nicolas M. H., Cole S. T. Inducible cephalosporinase production in clinical isolates of Enterobacter cloacae is controlled by a regulatory gene that has been deleted from Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3709–3714. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horii T., Arakawa Y., Ohta M., Ichiyama S., Wacharotayankun R., Kato N. Plasmid-mediated AmpC-type beta-lactamase isolated from Klebsiella pneumoniae confers resistance to broad-spectrum beta-lactams, including moxalactam. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 May;37(5):984–990. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.5.984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huovinen S. Rapid isoelectric focusing of plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases with Pharmacia PhastSystem. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Nov;32(11):1730–1732. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.11.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Carreras I. Activities of beta-lactam antibiotics against Escherichia coli strains producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 May;34(5):858–862. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.5.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T. ampC cephalosporinase of Escherichia coli K-12 has a different evolutionary origin from that of beta-lactamases of the penicillinase type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lindquist S., Normark S. Inactivation of the ampD gene causes semiconstitutive overproduction of the inducible Citrobacter freundii beta-lactamase. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):1923–1928. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.1923-1928.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Normark S. Sequence of the Citrobacter freundii OS60 chromosomal ampC beta-lactamase gene. Eur J Biochem. 1986 May 2;156(3):441–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge J. M., Minchin S. D., Piddock L. J., Busby S. J. Cloning, sequencing and analysis of the structural gene and regulatory region of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosomal ampC beta-lactamase. Biochem J. 1990 Dec 15;272(3):627–631. doi: 10.1042/bj2720627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura K., Yoshida T. Nucleotide sequence of the Serratia marcescens SR50 chromosomal ampC beta-lactamase gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Aug;58(3):295–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb13992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Edlund T., Grundström T., Bergström S., Wolf-Watz H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants hyperproducing chromosomal beta-lactamase by gene repetitions. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):912–922. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.912-922.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papanicolaou G. A., Medeiros A. A., Jacoby G. A. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (MIR-1) conferring resistance to oxyimino- and alpha-methoxy beta-lactams in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2200–2209. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. J., Woodford N., Amyes S. G. Characterization of the plasmid mediated beta-lactamase BIL-1. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Aug;30(2):119–127. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.2.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen B. A., Gluzman Y., Tally F. P. Cloning and sequencing of the class B beta-lactamase gene (ccrA) from Bacteroides fragilis TAL3636. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Aug;34(8):1590–1592. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.8.1590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saino Y., Kobayashi F., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of inducible penicillin beta-lactamase isolated from Pseudomonas maltophilia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):564–570. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuni A. A direct spectrophotometric assay and determination of Michaelis constants for the beta-lactamase reaction. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jan;63(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90185-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. beta-Lactamases of gram-negative bacteria: new challenges for new drugs. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 May;14(5):1089–1099. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.5.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. N., Plested S. J. The origin and properties of beta-lactamase satellite bands seen in isoelectric focusing. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Aug;12(2):127–131. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.2.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Hedge P. J., te Heesen S., Edelman A., Broome-Smith J. K. Kanamycin-resistant vectors that are analogues of plasmids pUC8, pUC9, pEMBL8 and pEMBL9. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzouvelekis L. S., Tzelepi E., Mentis A. F., Tsakris A. Identification of a novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase with chromosomal cephalosporinase characteristics from Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 May;31(5):645–654. doi: 10.1093/jac/31.5.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecoli C., Prevost F. E., Ververis J. J., Medeiros A. A., O'Leary G. P., Jr Comparison of polyacrylamide and agarose gel thin-layer isoelectric focusing for the characterization of beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):186–189. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. A spectrophotometric assay of beta-lactamase action on penicillins. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):789–790. doi: 10.1042/bj1390789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodford N., Payne D. J., Johnson A. P., Weinbren M. J., Perinpanayagam R. M., George R. C., Cookson B. D., Amyes S. G. Transferable cephalosporin resistance not inhibited by clavulanate in Escherichia coli. Lancet. 1990 Jul 28;336(8709):253–253. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91784-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




