Abstract
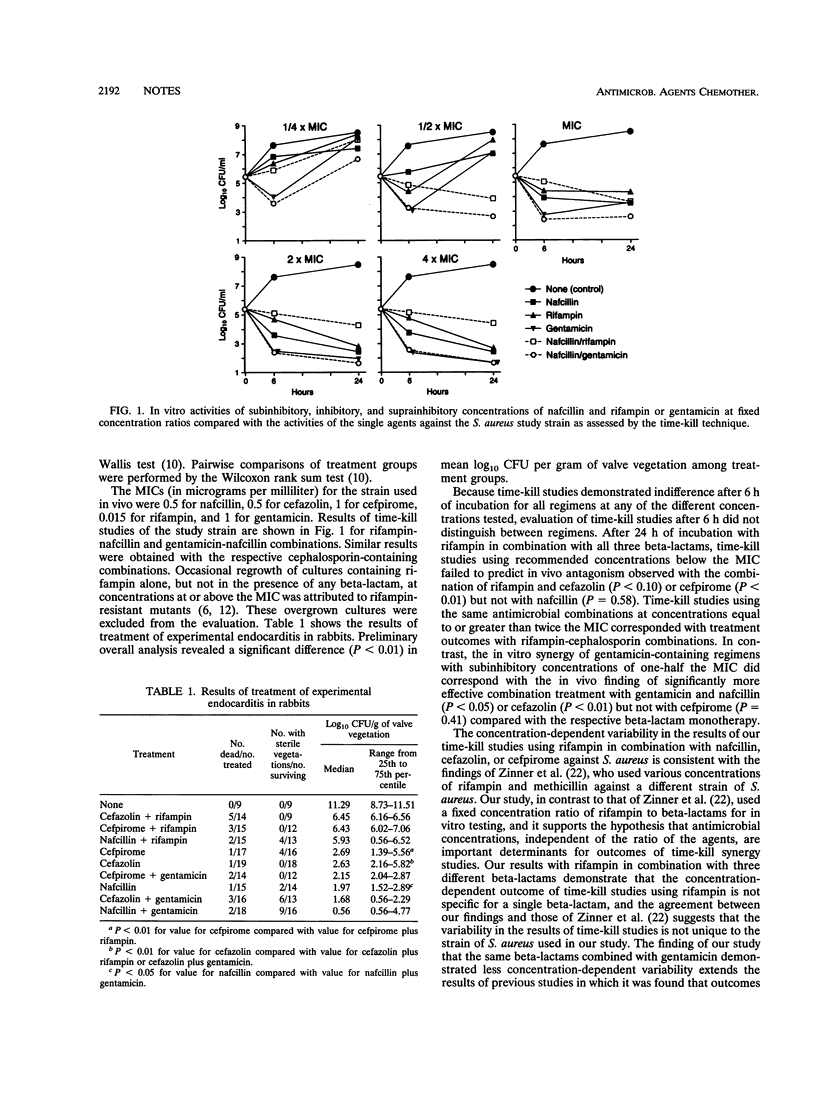
Results of in vitro time-kill synergy studies using subinhibitory, inhibitory, or suprainhibitory concentrations of bactericidal agents were compared with treatment outcomes of experimental infective endocarditis due to a methicillin-susceptible strain of Staphylococcus aureus. For rifampin-cephalosporin combinations, in vitro synergy testing using recommended fractions of the MIC failed to predict antagonism in vivo while concentrations above the MIC corresponded with antagonism in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartoloni A., Colao M. G., Orsi A., Dei R., Giganti E., Parenti F. In-vitro activity of vancomycin, teicoplanin, daptomycin, ramoplanin, MDL 62873 and other agents against staphylococci, enterococci and Clostridium difficile. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Nov;26(5):627–633. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.5.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer A. S., Lam K. Efficacy of vancomycin plus rifampin in experimental aortic-valve endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: in vitro-in vivo correlations. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jan;151(1):157–165. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison P. K., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis I. Staphylococcal endocarditis in rabbits resulting from placement of a polyethylene catheter in the right side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1970 Jun;42(6):394–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe W. R., Lorian V. Comparison of the antibacterial activity of rifampicin and other antibiotics. Am J Med Sci. 1968 Oct;256(4):255–265. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196810000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P. C., Shampo M. A. Statistical considerations for performing multiple tests in a single experiment. 2. Comparisons among several therapies. Mayo Clin Proc. 1988 Aug;63(8):816–820. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62363-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Cooper I., Willard K. E., Fasching C. E., Sinn L. M., Shanholtzer C. J., Gerding D. N. Activity of twenty-one antimicrobial agents including l-ofloxacin against quinolone-sensitive and -resistant, and methicillin-sensitive and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Chemotherapy. 1994 Jan-Feb;40(1):21–25. doi: 10.1159/000239165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Courtney K. B. Nafcillin-gentamicin synergism in experimental staphylococcal endocarditis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jul;88(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Johnson M. L. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Apr;131(4):367–375. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steckelberg J. M., Rouse M. S., Tallan B. M., Osmon D. R., Henry N. K., Wilson W. R. Relative efficacies of broad-spectrum cephalosporins for treatment of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus experimental infective endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Mar;37(3):554–558. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Auwera P., Joly P. Comparative in-vitro activities of teicoplanin, vancomycin, coumermycin and ciprofloxacin, alone and in combination with rifampicin or LM 427, against Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Mar;19(3):313–320. doi: 10.1093/jac/19.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., Lagast H., Klastersky J. Antistaphylococcal activity of rifampin with other antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1981 Oct;144(4):365–371. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.4.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


