Abstract
Capsaicin, a natural product of the Capsicum species of red peppers, is known to induce apoptosis and suppress growth. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 (NAG-1) is a cytokine associated with pro-apoptotic and antitumorigenic property in colorectal and lung cancer. Our data demonstrate that capsaicin leads to induction of apoptosis and up-regulates NAG-1 gene expression at the transcriptional level. Overexpression of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β (C/EBPβ) caused a significant increase of basal and capsaicin-induced NAG-1 promoter activity. We subsequently identified C/EBPβ binding sites in the NAG-1 promoter responsible for capsaicin-induced NAG-1 transactivation. Electrophoretic mobility shift assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay confirmed binding of C/EBPβ to the NAG-1 promoter. Capsaicin treatment resulted in an increase of phosphorylated serine/threonine residues on C/EBPβ, and the immunoprecipitation study showed that capsaicin enhanced binding of C/EBPβ with glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) and activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3). The phosphorylation and interaction of C/EBPβ with GSK3β and ATF3 are decreased by the inhibition of the GSK3β and Protein Kinase C pathways. Knockdown of C/EBPβ, GSK3β or ATF3 ameliorates NAG-1 expression induced by capsaicin treatment. These data indicate that C/EBPβ phosphorylation through GSK3β may mediate capsaicin-induced expression of NAG-1 and apoptosis through cooperation with ATF3 in human colorectal cancer cells.
Introduction
Capsaicin is a homovanillic acid derivative (trans-8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) and a pungent ingredient found mostly in hot chili pepper. Recent reports have demonstrated that it has chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic activities in various cancer models (1–6). In an in vivo study, capsaicin treatment suppressed azoxymethane-induced aberrant cryptic foci formation in rats (7). Various mechanisms of capsaicin-induced apoptosis have also been proposed from different cancer cell models. Capsaicin induces apoptosis through activation of caspase-3 and the intracellular Ca2+ release pathway in esophagus carcinoma cells (3). In leukemia, capsaicin induces apoptosis through a p53-dependent mechanism (5), but in prostate cancer cells, capsaicin's effect is p53 independent (2). Capsaicin-induced apoptosis is elevated by co-treatment of the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activator in colorectal cancer cells (8). Thus, it is likely that various mechanisms are involved in capsaicin-induced apoptosis, and the efficacy of capsaicin is dependent on cell or tissue context.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-activated gene-1 (NAG-1) is a member of the transforming growth factor β superfamily and is cloned by our group from cyclooxygenase deficient human colorectal cancer cells (9). Expression of the full-length NAG-1 protein results in increased apoptosis and decreased tumor size in the xenograft mouse model (9). Results from our previous study indicated that transgenic mice overexpressing NAG-1 (NAG-Tg) were resistant to azoxymethane-induced aberrant cryptic foci, and NAG-Tg/APCMin+ mice showed less tumor load in the small intestine compared with littermate APCMin+ control mice (10). Recently, we have also shown that NAG-1 expression causes less tumor formation in urethane-induced lung tumor model (11). Thus, NAG-1 expression results in a suppression of tumor formation in colon and lung cancer animal models. Along with these findings, we have also reported that NAG-1 expression is induced not only by NSAIDs (9,12) but also by several antitumorigenic compounds, including PPARγ ligands (13), and dietary chemopreventive compounds, such as conjugated linoleic acid (14), indole-3-carbinol (15), 6-gingerol (16), resveratrol (17), catechins (18), and genistein (19). NAG-1 expression is mediated by a tumor suppressor protein such as p53 (17,19), early growth response gene-1 (12,20), glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) (21), and activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) (14). These results indicate that NAG-1 serves as a tumor suppressor gene and a target protein of several chemopreventive compounds (22).
The current study was performed to examine the role of NAG-1 in capsaicin-induced apoptosis and the molecular mechanisms by which capsaicin induces NAG-1 expression in human colorectal cancer cells. Here, we report for the first time that treating cells with capsaicin results in an increase of NAG-1 expression through GSK3β/C/EBPβ- and Protein Kinase C (PKC)δ/C/EBPβ-mediated pathways, and ATF3 is positively interacted with C/EBPβ activity.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Human colorectal cancer cells (HCT-116, SW480, HT-29, and LoVo) were purchased from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA), and culture media were purchase from Bio Whittaker (Rockland, ME). Capsaicin was purchased from Biomol (Plymouth Meeting, PA) and dissolved in ethanol. RO-31-8220, rottlerin, PD98059, SP600125, SB203585, AG490, MG132, wortmannin, AR-A014418, and rapamycin were purchased from Calbiochem (San Diego, CA). Antibody for Sp1 was purchased from Upstate (Lake Placid, NY) and antibodies for C/EBPα, C/EBPβ, cAMP response element binding (CREB), retinoic acid receptorα (RARα), ATF3, p53, actin and ATF3 small interfering RNA (siRNA) were purchased from Santa Cruz (Santa Cruz, CA). Antibody for phosphor-Ser/Thr was purchased from BD Bioscience (San Jose, CA) and antibody for GSK3β and GSK3β siRNA were purchased from Cell Signaling (Beverly, MA). The antibody for V5 was purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA) and NAG-1 antibody was described previously (9). Control and C/EBPβ short hairpin RNA (shRNA) was kindly provided by Dr Jessica Schwartz (University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI). All chemicals were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Pittsburgh, PA), unless otherwise specified.
Cell culture
HCT-116 and HT-29 cells were maintained in McCoy's 5A medium, and SW480 and LoVo cells were maintained in RPMI and Ham's F-12 medium, respectively. All media contained 10% fetal bovine serum. The cells were treated with capsaicin under serum-free media for 6–24 h as indicated in the figure 1–6 legends.
Human NAG-1 promoters
The NAG-1 promoters were described previously (23). Internal deletion clones were created using QuikChange II mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA) with the following primers: pNAG-1Δ-110/-103, forward 5′-cacccccagaccccgcccagcttggagtgttt-3′, and reverse 5′-gcctgcagagtaaacactccaagctgggcggggtc-3′; pNAG-1Δ-87/-80, forward 5′-tgtggtcattggagtg tttactcgggggaggaggg-3′, and reverse 5′-gctcagtccc gccctcctcccccgagtaaac-3′.
Expression vectors
Full-length C/EBPα, C/EBPδ, and CHOP (C/EBPζ) cDNAs were amplified from human lung cDNA (Clontech, Mountain View, CA) using ReadyMix Taq polymerase (Sigma, St Louis, MO) with the following primers: C/EBPα, forward 5′-tgccgggagaactctaactc-3′, and reverse 5′-caccggaatctcctagtcctg-3′; C/EBPδ, forward 5′-aggtgacagcctcgcttg-3′, and reverse 5′-gtatgggtcg ttgctgagtctct-3′; CHOP, forward 5′-agactgatccaac tgcagag-3′, and reverse 5′-tgcttggtgcagattcacc-3′. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed for 30 cycles at 94°C for 1 min, 55°C for 1 min, and 72°C for 2 min. PCR product of C/EBPα, C/EBPδ, and CHOP were subcloned into pcDNA3.1/V5/His TOPO vector (Invitrogen) to generate the V5-His-tagged clones, pcDNA3.1/C/EBPα/V5/His, pcDNA3.1/C/EBPδ/V5/His, and pcDNA3.1/CHOP/V5/His, respectively. For C/EBPβ expression vector, pOTB7 vector containing full length C/EBPβ cDNA (Open Biosystems, Huntsville, AL) were digested using EcoRI and XhoI and subcloned into pcDNA3.1 (Invitrogen) to generate pcDNA3.1/C/EBPβ. For cloning of N-terminally truncated C/EBPβ (C/EBPβ2) expression vector (24), PCR was performed using pcDNA3.1/C/EBPβ with forward primer (5′-ccccctgccgccgccgccgcctgc-3′) and reverse primer (5′-gcagtggccggaggaggcg-3′) and subcloned into pcDNA3.1/V5/His TOPO vector (Invitrogen) to generate pcDNA3.1/C/EBPβ2/V5/His. For GSK3β expression vector, full length of GSK3β cDNA were cloned into pcDNA3.1/V5/His TOPO vector to make pcDNA3.1/GSK3β/V5/His with forward primer (5′-gaaggaaaaggtgattcgcgaagag-3′) and reverse primer (5′-ggtggagttggaagctgatgcagaa-3′). CREB expression vector was kindly provided by Dr Joo-Heon Yoon (Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea), and Sp1 expression vector was previously described (23). The pCMX-hRARα expression vector was kindly provided by Dr Ronald M. Evans (The Salk Institute for Biological Studies).
Flow cytometric detection of apoptotic cells
The cells were plated in six-well tissue culture dishes and incubated with capsaicin. The attached and floating cells were collected, washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), resuspended in 80% ice-cold ethanol, and kept at −20°C overnight. The cells were rehydrated with PBS and stained with 70 μM propidium iodide solution including 1 mg/ml RNase A. Apoptosis and cell cycle distribution were analyzed using Beckman Coulter Epixs XL flow cytometer (Brea, CA) equipped with EXPO32 ADC and ModiFit LT software, respectively.
Transient transfections
Transient transfections were performed using Lipofectamine (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The cells were plated in 12-well plates at the concentration of 2 × 105 cells per well. The next day, plasmid mixtures containing 0.5 μg of NAG-1 promoter and 0.05 μg of pRL-null vector were co-transfected for 5 h in serum-free media. For the co-transfection experiment, 0.25 μg of NAG-1 promoter and 0.25 μg of expression vectors were co-transfected with 0.05 μg of pRL-null vector. After refreshment overnight, the transfected cells were exposed to ethanol or capsaicin for 24 h. The cells were harvested in 1× luciferase lysis buffer (Promega, Madison, WI), and luciferase activity was measured and presented as a ratio of firefly luciferase signal/renilla luciferase signal using a dual luciferase assay kit (Promega).
Reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction
Total RNA was prepared using RNA isolation kit (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) and reverse-transcribed with iScript cDNA kit (BioRad, Hercules, CA) according to the manufacturer's instruction. PCR was carried out for 25 cycles at 94°C for 30 s, 55°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 1 min using ReadyMix Taq polymerase (Sigma) with primers for human NAG-1 and GAPDH as follows: NAG-1: forward 5′-ctccag attccgagagttgc-3′, and reverse 5′-agagatacgcaggtg caggt-3′; GAPDH: forward 5′- gggctgcttttaactct ggt-3′, and reverse 5′- tggcaggtttttctagacgg-3′.
Western Blot Analysis
Western blot was performed as described previously (14). Briefly, the cell lysates were obtained using RIPA buffer containing protease inhibitors (1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 5 μg/ml aprotinin, and 5 μg/ml leupeptin) and phosphatase inhibitors (1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM NaF). Protein concentration was determined by bicinchoninic acid protein assay (Pierce, Rockford, IL) using bovine serum albumin as the standard. The proteins were separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (Osmonics, Minnetonka, MN). The membranes were incubated with a specific primary antiserum in Tris-buffered saline containing 0.05% Tween 20 and 5% non-fat dry milk at 4°C overnight. After three washes with Tris-buffered saline containing 0.05% Tween 20, the blots were incubated with peroxidase-conjugated immunoglobulin G for 1 h at room temperature and visualized using ECL (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ).
Immunoprecipitation
For detection of phosphor C/EBPβ, the cells were sonicated five times for 10 s and the cell lysates were precleared using Protein A/G-agarose beads (Santa Cruz) and then pulled down with C/EBPβ antibody for overnight. For immunoprecipitation of GSK3β and C/EBPβ, each expression vector was transfected into HCT-116 cells, and cell lysates were pulled down using Probond nickel resin (Invitrogen). Co-purified proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using specific antibodies for V5, GSK3β, C/EBPβ, and ATF3.
RNA interference
Interference for GSK3β was performed as described previously (14). Briefly, 100 nM of GSK-3 siRNA or control siRNA was transfected using TransIT-TKO transfection reagent (Mirus, Madison, WI) for 24 h. For interference of C/EBPβ, the 3 μg of control or C/EBPβ shRNA was transfected using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) for 48 h. For interference of ATF3, 200 nM of siATF3 or control siRNA was transfected using TransIT-TKO transfection reagent for 48 h.
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
HCT-116 cells were grown to reach 80% confluence in 100-mm plates. After serum starvation overnight, the cells were treated with ethanol or 50 μM of capsaicin for 6 h. After washing with PBS, nuclear extracts were prepared following the manufacturer's protocols (Active Motif, Carlsbad, CA). The electrophoretic mobility shift assay was performed as we described previously (12). Oligonucleotide probes contained the following sequences: NAG-1-110/-103: 5'-gctgtggtcattgctgtggtcattgctgtggtcatt -3' and NAG-1-87/-80: 5′- tctgcaggcaggtctgcaggca ggtctgcaggcagg-3′. Biotin-labeled oligonucleotide (100 nM) was incubated with nuclear protein (5 μg) and 1× binding buffer (Promega) at room temperature for 20 min. For C/EBPβ synthesis, in vitro translation was performed using TNT Quick Coupled Transcription/Translation Systems (Promega) per the manufacturer's protocol. For competition assay, nuclear proteins (5 μg) or in vitro synthesized C/EBPβ was preincubated with the unlabeled oligonucleotide (10- or 100-fold) for 10 min.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay
The chromatin immunoprecipitation assay was performed as we described previously (12). Briefly, the cells were fixed with 1% formaldehyde for 10 min at 37°C and sonicated four times for 10 s. The cell lysates (0.2 ml) were diluted with immunoprecipitation buffer (1.8 ml) and immunoprecipitated with 5 μg of specific antibodies for immunoglobulin G, C/EBPα, C/EBPβ, RARα, CREB, and ATF3 at 4°C for overnight. The chromatin-associated DNA was eluted, reverse cross-linked by heating at 65°C for 4 h and treated with proteinase K at 45°C for 2 h. DNA was purified by phenol/choloroform extraction, and precipitated DNA was amplified using the following primer pairs: forward, 5′-caccccc agaccccgcccagctgtggtcattg-3′ and reverse, 5′-cttgcgcggctcgcctcggccagagacagggcgccccc-3′. PCR products (268 bp) were separated using a 2% agarose gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with the Student's unpaired t-test.
Results
Capsaicin suppresses cell growth, increases apoptosis and NAG-1 expression in human colorectal cancer cells
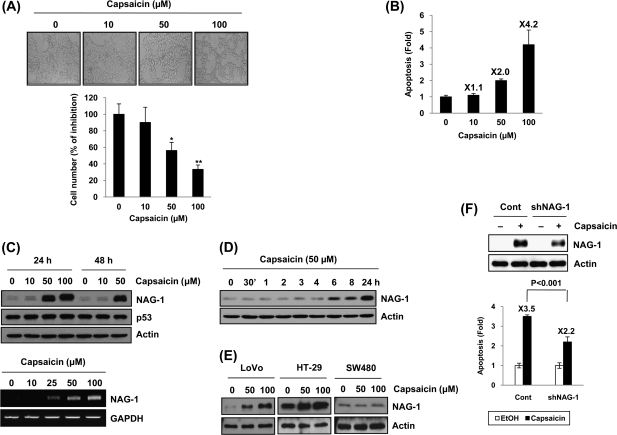
To observe whether capsaicin affects growth of human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells, we treated HCT-116 cells with different concentrations of capsaicin and measured cell growth. As shown in Fig. 1A, treatment of 50 and 100 μM capsaicin for 24 h showed changes of cell morphology as well as decreased cell number (upper panel) and led to a significant decrease of cell growth (lower panel). These results are from capsaicin-induced cell death because the number of apoptotic cells significantly increased in the groups treated with 50 and 100 μM of capsaicin for 24 h in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1B). To investigate whether capsaicin affects NAG-1 expression, HCT-116 cells were incubated with 0, 10, 50 and 100 μM of capsaicin for 24 and 48 h. As shown in Figure 1C (upper panel), NAG-1 protein levels increased in the cells treated with 50 μM of capsaicin at 24 and 48 h. It has been known that capsaicin increases p53 expression (25) and NAG-1 is a p53-target gene (17,19), but capsaicin treatment does not increase p53 expression in HCT-116 cells (p53 wild-type). The NAG-1 mRNA level also increased in capsaicin-treated cells in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 1C, lower panel), suggesting that capsaicin affects NAG-1 expression at the transcription level. In the presence of 50 μM of capsaicin, NAG-1 protein began to increase at 6 h and showed a time-dependent induction (Figure 1D). Capsaicin treatment increased NAG-1 in LoVo (p53 wild) and HT-29 (p53 mutant) cells, but not in SW480 (p53 mutant) cells (Figure 1E), indicating cell specificity of capsaicin effects on cell growth in a p53-independent manner. To examine the relevance of the NAG-1 expression to apoptosis by capsaicin, we knocked down the NAG-1 gene and then measured apoptosis. As shown in Figure 1F, knockdown of NAG-1 ameliorated induction of apoptosis by capsaicin treatment.
Fig. 1.
Capsaicin suppresses cell growth, increases apoptosis and NAG-1 expression in human colorectal cancer cells. (A) HCT-116 cells were treated with 0, 10, 50, and 100 μM of capsaicin for 24 h, and the shape and cell morphology was observed under an optical microscope (upper panel). At the same time, the cell number was counted and expressed as % of inhibition versus vehicle-treated cells (lower panel). Values are expressed as mean ± SD of three replicates. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus vehicle-treated cells. (B) HCT-116 cells were treated with 0, 10, 50, and 100 μM of capsaicin for 24 h and apoptosis measured as described in Materials and Methods. (C) HCT-116 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of capsaicin for 24 or 48 h and western blot was performed for NAG-1, p53 and actin as described in Materials and Methods (upper panel). HCT-116 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of capsaicin for 24 h, and Reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction was performed as described in Materials and Methods (lower panel) (D) HCT-116 cells were treated with 50 μM of capsaicin for indicated time points, and western blot was performed for NAG-1 and actin. (E) Three different human colorectal cancer cells (LoVo, HT-29, and SW480) were treated with 0, 50, or 100 μM of capsaicin for 24 h, and western blot was performed for NAG-1 and actin. (F) HCT-116 cells were transfected with control vector (pSuper-retro-puro) or NAG-1 shRNA (pSuper-retro-puro-shNAG-1) as described previously (14) and then treated with 100 μM capsaicin for 24 h. The validation of NAG-1 knockdown is indicated (upper panel). Apoptosis was analyzed using propidium iodide staining as described in Materials and Methods (lower panel).
C/EBPβ mediates capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression
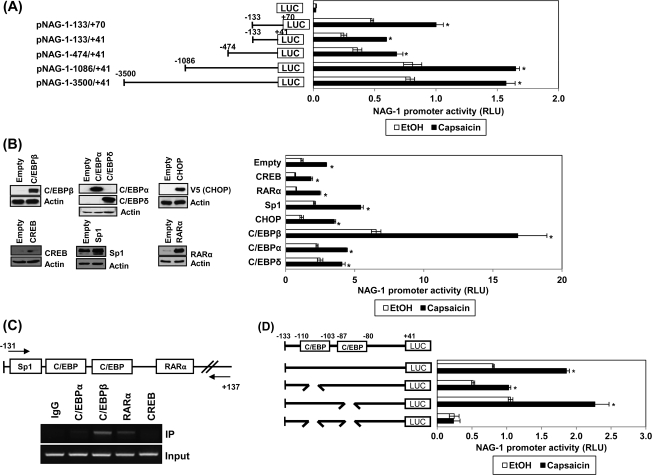
To investigate the molecular mechanism of capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression, a deletion assay using the human NAG-1 promoter was performed to observe whether capsaicin affects transcriptional regulation of the NAG-1 gene. As shown in Figure 2A, 50 μM of capsaicin treatment resulted in the stimulation of NAG-1 promoter activity in all the constructs tested, implying that the responsible cognate site by capsaicin is located between the −133 and +41 regions. The NAG-1 promoter containing the p53 binding site (pNAG-1-133/+70) showed similar activity with other promoters that do not contain p53 binding site, confirming that capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression is p53 independent. This is consistent with the data that p53 expression was not altered by capsaicin treatment (Figure 1C).
Fig. 2.
Identification of the responsible promoter region for capsaicin-induced NAG-1 transactivation. (A) HCT-116 cells were transfected with a reporter gene containing NAG-1 promoter and then treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 24 h. Luciferase activity was presented as relative luciferase unit. *P < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated cells. (B) The NAG-1 promoter (pNAG-1−133/+41) was co-transfected with indicated expression vector as described in Materials and Methods and then treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 24 h. The x-axis (right panel) shows relative luciferase unit. *P < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated cells. Left panel represents validation of expression vectors. Western blot analysis was performed after transfection with the indicated expressing vector. Empty indicates a pcDNA3.1 vector. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay was performed using a DNA–protein complex treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 24 h as described in Materials and Methods. The sequence of the NAG-1 promoter region (−131/+137) was amplified by PCR primer pairs as indicated by the arrows. The input represents PCR products obtained from 1% aliquots of chromatin pellets escaping immunoprecipitation. (D) HCT-116 cells were transfected with each internal deletion construct of the NAG-1 promoter and then treated with 50 μM of capsaicin for 24 h. The x-axis shows relative luciferase unit. *P < 0.001 versus vehicle-treated cells. RLU, relative luciferase unit.
The −133 and +41 region contains multiple putative transcription factor-binding sites including C/EBPs, Sp1, and RARα. To find the trans-acting elements responsible for NAG-1 transactivation, we cloned or obtained several expression vectors for C/EBPβ, C/EBPα, C/EBPδ, CREB, CHOP (C/EBPζ), and RARα (Figure 2B, left panel). CHOP and CREB could also bind to the C/EBP binding sites. Indicated expression vectors were cotransfected with the NAG-1 promoter constructs (pNAG-1−133/+41) and luciferase activity was determined. As a result, only C/EBPβ expression caused a dramatic increase of basal and capsaicin-induced luciferase activity (Figure 2B, right panel). In addition, the chromatin immunoprecipitation assay confirmed C/EBPβ as a binding protein to the −133/+41 region of the NAG-1 promoter (Figure 2C). Interestingly, RARα also binds to this region, but RARα expression itself does not increase basal and capsaicin-induced NAG-1 promoter activity (Figure 2B, right panel). To further identify potential regulatory cis-acting elements mediating capsaicin effects, we constructed internal deletion clones lacking potential binding sites for both C/EBPs. Since C/EBPβ binds to this region and its expression results in NAG-1 promoter activity (Figure 2B and C), the cells were transfected with wild-type or deletion constructs lacking C/EBPβ binding sites and treated with 50 μM of capsaicin for 24 h. As shown in Figure 2D, deletion of the distal C/EBP binding site (−110/−103) slightly decreased capsaicin's effect, whereas deletion of the proximal C/EBP binding site (−87/−80) did not affect luciferase activity. Unexpectedly, capsaicin's effect was completely abolished in cells transfected with a double deletion promoter construct lacking both distal and proximal C/EBP binding sites. These data suggest that these two binding sites are necessary for NAG-1 promoter activation by capsaicin treatment.
GSK3β- and PKC-mediated phosphorylation of C/EBPβ induces NAG-1 expression
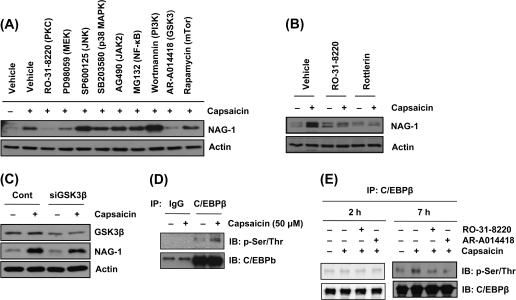
To gain further insight into signaling factors regulating NAG-1 expression by capsaicin, HCT-116 cells were pretreated with vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide) or different kinase inhibitors for 30 min and incubated with 50 μM capsaicin. Pretreatment of cells with RO-31-8220 (PKC inhibitor) and AR-A014418 (selective GSK3 inhibitor) abolished capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression, suggesting that these pathways mediate capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression (Figure 3A). Since NAG-1 expression is mediated by PKCδ in prostate cancer cells (26), we tested the effect of rottlerin (a PKCδ-selective inhibitor) on NAG-1 expression. Pretreatment of rottlerin abolished capsacin-induced NAG-1 activation (Figure 3B), indicating an involvement of PKCδ on capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression. Next, to confirm the possible regulatory effect of GSK3β on capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression, the cells were transfected with GSK3β siRNA, followed by capsaicin treatment. Knockdown of GSK3β attenuated NAG-1 induction by capsaicin (Figure 3C), indicating that GSK3β plays an important role in capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression.
Fig. 3.
GSK3β and PKCδ mediate C/EBPβ phosphorylation and capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression. (A) HCT-116 cells were pretreated with different tyrosine kinases (RO-31-8220, 2.5 μM; PD98059, 40 μM; SP600125, 30 μM; SB203580, 15 μM; AG490, 50 μM; MG132, 10 μM; wortmannin, 0.5 μM; AR-A014418, 30 μM; rapamycin, 0.1 μM) for 30 min and treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 7 h. Western blot was performed for NAG-1 and actin. (B) HCT-116 cells were pretreated with RO-31-8220 (2.5 μM) and rottlerin (10 μM) for 30 min and treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 7 h; then western blot was performed for NAG-1 and actin. (C) HCT-116 cells were transfected with control or siRNA of GSK3β for 24 h and then treated with 50 μM of capsaicin for 24 h; western blot was performed for GSK3β, NAG-1 and actin. (D) HCT-116 cells were treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 7 h, and the cell lysate was pulled down with C/EBPβ antibody. Western blot was performed for phosphor Ser/Thr and C/EBPβ as described in Materials and Methods. (E) HCT-116 cells were pretreated with RO-31-8220 (2.5 μM) or AR-A014418 (30 μM) for 30 min and then treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 2 h or 7 h. The cell lysate was immunoprecipiated using C/EBPβ antibody, and western blot was performed for phosphor Ser/Thr and C/EBPβ as described in Materials and Methods.
Furthermore, we measured the phosphorylated serine/threonine form of C/EBPβ using immunoprecipitation to see whether capsaicin affects phosphorylation of C/EBPβ protein. The cells were treated with capsaicin, and pulled down with C/EBPβ antibody, followed by immunoblot with antibody against phosphor serine/threonine or C/EBPβ. As shown in Figure 3D, capsaicin treatment induced phosphorylated serine/threonine residues on C/EBPβ, providing evidence that capsaicin enhances the phosphorylation of C/EBPβ. We further examined whether phosphorylation of C/EBPβ is mediated by PKC and GSK3β. As shown in Figure 3E, phosphorylation of C/EBPβ by capsaicin was inhibited in the presence of inhibitors of these pathways, supporting that C/EBPβ is a target transcription factor of PKC and GSK3β. We also tested whether capsaicin increases phosphorylation of C/EBPβ at early time point. The results show that capsaicin did not affect C/EBPβ phosphorylation after exposure to capsaicin for 2 h (Figure 3E).
Binding activity of C/EBPβ on the NAG-1 promoter
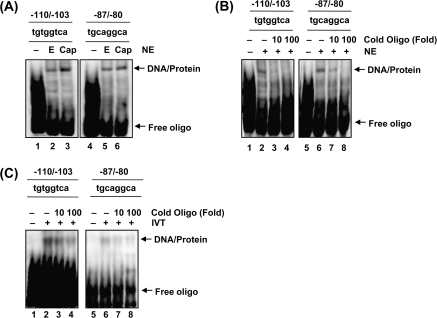
Results from promoter analyses indicated that two potential C/EBPβ binding sites are necessary to activate luciferase activity of the NAG-1 promoter (Figure 2D). To observe the association of C/EBPβ with the NAG-1 promoter, we carried out electrophoretic mobility shift assay using nuclear proteins with a biotin-labeled DNA probe corresponding to −110 to −103 (−110/−103) and −87 to −80 (−87/−80) of NAG-1 promoter. DNA–protein complex formation was enhanced by capsaicin treatment in oligonucleotides of −110/−103, whereas this increase was relatively smaller using an −87/−80 probe (Figure 4A). Preincubation of nuclear extracts with 10× and 100× cold oligonucleotide inhibited the binding activity in both oligonucleotides (Figure 4B, lanes 3–4, 7–8), suggesting that the binding protein is sequence specific. To test whether C/EBPβ binds to this oligonucleotide, in vitro translated C/EBPβ protein was incubated with the probe. As a result, C/EBPβ interacted with the NAG-1 promoter, and this interaction was inhibited by the addition of 10× or 100× cold oligonucleotides (Figure 4C), confirming the binding of C/EBPβ to these sequences.
Fig. 4.
DNA binding activity of C/EBPβ in the NAG-1 promoter. (A) HCT-116 cells were treated with ethanol (E) or 50 μM of capsaicin (Cap) for 6 h, and nuclear extracts were prepared. Biotin-labeled oligonucleotide (100 nM) was incubated with nuclear protein (5 μg) and 1× binding buffer (Promega) at room temperature for 20 min, as described in Materials and Methods. Oligonucleotide probes contained the following sequences: NAG-1-110/-103: 5′-gctgtggtcattgctgtggtcattgctgtggtcatt-3′ and NAG-1-87/-80: 5′- tctgcaggcaggtctgcaggcaggtctgcaggcagg-3′. The specific DNA–protein complexes are indicated by arrows. NE, nuclear extract. (B) The competition of the DNA binding was obtained using a 10 and 100-time excess of the unlabeled oligonucleotide (lane 3–4, 7–8). Nuclear protein (5 μg) was preincubated with the unlabeled oligonucleotide (10- or 100-fold) for 10 min and then incubated with biotin-labeled oligonucleotide and 1× binding buffer (Promega) at room temperature for 20 min. (C) The in vitro synthesized C/EBPβ protein was used for competition study as described in (B). For C/EBPβ synthesis, in vitro translation was performed with pcDNA3.1/C/EBPβ2/V5/His using TNT Quick Coupled Transcription/Translation Systems (Promega). IVT, in vitro translated protein.
Association of C/EBPβ with GSK3β and ATF3
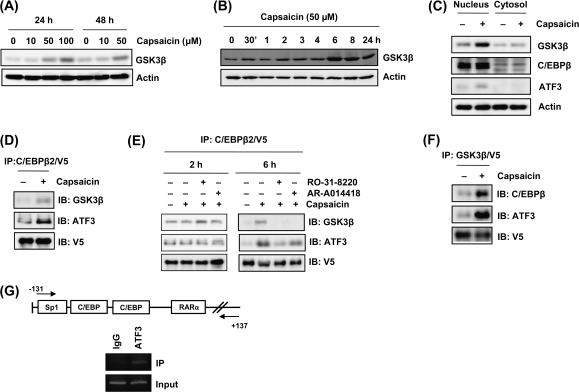
GSK3β activity is mainly regulated by phoshorylation, transcriptional level, or cellular localization (27). To gain further information of how capsaicin affects GSK3β activation, we compared expression of GSK3β proteins using immunoblot analysis. Interestingly, capsaicin treatment increased total protein levels of GSK3β (Figure 5A). The mRNA level of GSK3β was also increased (data not shown). It is notable that GSK3β expression begins to increase at 6 h time point (Figure 5B), when NAG-1 expression begins to increase (Figure 1D). Next, we examined GSK3β cellular localization because it has been known that apoptotic signals increase nuclear accumulation of GSK3β and their target genes are activated (28,29). As shown in Figure 5C, capsaicin treatment caused increased accumulation of GSK3β in the nucleus. These results suggest that capsaicin enhances the expression of GSK3β, thereby accumulating nuclear GSK3β protein and provide the hypothesis that GSK3β may directly associate and phosphorylate C/EBPβ in the nucleus in the presence of capsaicin. To investigate the possibility of direct physical interaction between C/EBPβ and GSK3β, we used histidine tag pull-down assays, followed by western blot after transient transfection of C/EBPβ expression vector (pcDNA3.1/C/EBPβ2/V5/His) in the presence of capsaicin. As shown in Figure 5D, capsaicin treatment increases protein–protein interaction between GSK3β and C/EBPβ. These interactions can be suppressed by the inhibition of PKC and GSK3β pathways (Figure 5E).
Fig. 5.
Capsaicin enhances GSK3β expression and protein interactions of GSK3β, C/EBPβ, and ATF3. (A) HCT-116 cells were treated with indicated concentrations of capsaicin for 24 or 48 h and western blot was performed for GSK3β and actin. (B) HCT-116 cells were treated with 50 μM of capsaicin for indicated time points, and western blot was performed for GSK3β and actin. (C) The cells were treated with 50 μM of capsaicin for 6 h and nuclear and cytosol fractions were isolated, and then western blot was performed for GSK3β, C/EBPβ, ATF3, and actin. (D) The cells were transfected with C/EBPβ expression vector-tagged V5 (pcDNA3.1/C/EBPβ2/V5/His) and treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 6 h. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with ProBond nickel-chelating resin (Invitrogen), separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel, transferred to membranes, and then immunoblotted with V5, GSK3β or ATF3 antibody. (E) HCT-116 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1/C/EBPβ2/V5/His, pretreated with RO-31-8220 (2.5 μM) or AR-A014418 (30 μM) for 30 min and then treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 2 or 6 h. Immunoprecipitation was performed as described in (D). (F) The cells were transfected with GSK3β expression vector (pcDNA3.1/GSK3β/V5/His) and treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 6 h. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with ProBond nickel-chelating resin (Invitrogen), separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel, transferred to membranes, and then immunoblotted with V5, C/EBPβ or ATF3 antibody. (G) Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay for ATF3 binding was performed using a DNA–protein complex treated with 50 μM capsaicin for 24 h as described in Materials and Methods. The sequence of the NAG-1 promoter region (−131/+137) was amplified by PCR primer pairs as indicated by the arrows. The input represents PCR products obtained from 1% aliquots of chromatin pellets escaping immunoprecipitation.
On the other hand, our previous studies showed that ATF3 plays an important role in the NAG-1 induction (14,18), and recent other studies demonstrated that ATF3 and C/EBPβ may act in concert to regulate their target gene (30,31). Interestingly, nuclear ATF3 level was increased after capsaicin treatment (Figure 5C). Thus, we examined ATF3 protein as an interacting protein with C/EBPβ in capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression. As shown in Figure 5D, C/EBPβ2 is able to associate with ATF3 at the basal level and capsaicin treatment increases interaction between C/EBPβ and ATF3. Interestingly, this interaction was also inhibited in the presence of GSK3β and PKC inhibitors (Figure 5E), indicating that interaction of C/EBPβ with ATF3 depends on its phosphorylation. However, incubation with capsaicin for 2 h did not affect formation of transcription factor complex (Figure 5E).
To confirm the interaction of GSK3β with C/EBPβ and ATF3, the reverse immunoprecipitation using V5 antibody for GSK3β pull down and C/EBPβ or ATF3 antibodies for immunoblotting was performed in the same way. The association of GSK3β with C/EBPβ and ATF3 could be detected in basal level and this association was induced by capsaicin treatment (Figure 5F).
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay was performed to see whether ATF3 is associated with formation of complex, which binds to the NAG-1 promoter. As shown in Figure 5G, ATF3 associated with NAG-1 promoter. Since electrophoretic mobility shift assay indicated that ATF3 did not bind directly to the NAG-1 promoter (data not shown), it is likely that ATF3 is involved in formation of complex with C/EBPβ, thereafter enhancing capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression.
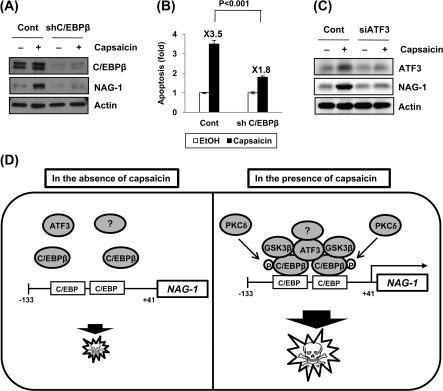
Knockdown of C/EBPβ blocks capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression and apoptosis
Finally, we tested whether C/EBPβ and ATF3 are required for the induction of NAG-1 in response to capsaicin. The cells were transfected with control or C/EBPβ shRNA and then treated with 50 μM capsaicin. Western blot confirmed complete knockdown of C/EBPβ expression (Figure 6A). NAG-1 expression was increased in capsaicin-treated cells; however, C/EBPβ shRNA-transfected cells completely abolished capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression (Figure 6A). To examine whether C/EBPβ has any relevance to the induction of apoptosis by capsaicin, we blocked C/EBPβ expression, and apoptosis analysis was performed by flow cytometry. As shown in Figure 6B, fold increase of apoptosis by capsaicin was lower in C/EBPβ shRNA-transfected cells compared with control vector-transfected cells (1.8-fold versus 3.5-fold; P < 0.001), suggesting a pivotal role of C/EBPβ expression in capsaicin-induced apoptosis in HCT-116 cells. We also examined the role of ATF3 in capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression using ATF3 siRNA. As shown in Figure 6C, knockdown of the ATF3 gene suppressed capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression, demonstrating a significant role of ATF3 in NAG-1 expression in response to capsaicin treatment.
Fig. 6.
Knockdown of C/EBPβ alters capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression and apoptosis. (A) HCT-116 cells were transfected with control or C/EBPβ shRNA using Lipofectamine 2000 for 48 h and then treated with vehicle or 50 μM capsaicin for 24 h. Western analysis was performed for C/EBPβ, NAG-1, and actin. (B) HCT-116 cells were transfected with control or C/EBPβ shRNA and treated with 100 μM of capsaicin for 24 h. Apoptosis was analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. Values are expressed as mean ± SD of three replicates. (C) HCT-116 cells were transfected with control or ATF3 siRNA (200 nM) using TransIT-TKO Mirus transfection reagent for 48 h and then treated with ethanol or 50 μM of capsaicin for 24 h. Western analysis was performed for ATF3, NAG-1, and actin. (D) Proposed mechanism by which capsaicin induces NAG-1 transcription in human colorectal cancer. Capsaicin activates C/EBPβ through GSK3β- and PKCδ-dependent phosphorylation. Capsaicin increase nuclear accumulation of GSK3β and phosphorylates C/EBPβ through direct interaction with C/EBPβ. Activation of C/EBPβ increases the binding affinity of C/EBPβ onto NAG-1 promoter and activates transcription of NAG-1 genes. ATF3 may play a role as a bridge protein or formation of supracomplex, including ATF3 and other transcription factors, thereby enhancing the recruitment of C/EBPβ to the NAG-1 promoter. Upregulation of the NAG-1 gene results in an increase of apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells.
Discussion
In this study, we report that capsaicin increases apoptosis and activates proapoptotic gene NAG-1 through C/EBPβ activation in human colorectal cancer cells. We also demonstrate a novel pathway that phosphorylation of C/EBPβ by GSK3β and PKC in the presence of capsaicin is associated with a bZIP protein, ATF3.
The relevance of the NAG-1 gene in apoptosis and cell proliferation by several phytochemicals and chemopreventive drugs has been reported in various cancer models (9,13,14,26). We also observed that NAG-1 induction is implicated in apoptotic activity by capsaicin in human colorectal cancer cells (Figure 1F). Capsaicin-induced cell growth arrest and induction of NAG-1 expression was observed at 50 μM in HCT-116 cells. A low dose (10 μM) of capsaicin is effective to inhibit cell proliferation in endothelial cancer cells (32), whereas a much higher concentration of capsaicin is required to induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells (8), prostate cancer cells (2), and gastric carcinoma cells (33).
In terms of physiological concentration of capsaicin, blood concentration of capsaicin was estimated to be 581 ng/ml (equivalent to 2 μM) after intravenous administration of 2 mg capsaicin per kg body wt to rats (34), and topical application of capsaicin resulted in blood capsaicin concentrations up to 10–20 μM (35). According to a recent human study, blood concentration of capsaicin is estimated at 2.47 ng/ml (equivalent to 8.1 nM) in male adults, after administrating 0.4 mg capsaicin per kg body wt (36). However, actual daily intake of capsaicin in the countries that use more chili peppers is much higher (estimated at 2.8 mg/kg body wt) (37,38). Although the concentration of capsaicin (50 μM) we used is higher than plasma levels, we believe that a much higher amount of capsaicin could reach the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. This can be observed in other phytochemicals such as epigallocatechin gallate, which has a concentration 28–165 times higher in the gastrointestinal tract than in plasma (39).
The transcriptional regulation of NAG-1 gene is mediated by several mechanisms, including p53 tumor suppressor gene (17,19), and early growth response gene-1 (12,20) pathways. It has been reported that capsaicin induces apoptosis through a p53-dependent pathway in stomach cancer and leukemia cells (5,25). However, in colorectal cancer cells, it is unlikely that capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression is p53 dependent, although NAG-1 is a target of p53 tumor suppressor gene.
Our data showed that knockdown of C/EBPβ suppressed capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression (Figure 6A). These results, together with the observations that overexpression of C/EBPβ is associated with the activation of the NAG-1 promoter (Figure 2B) implicate a crucial role of C/EBPβ in NAG-1 induction by capsaicin. Thus, NAG-1 appears to be one of the target genes for C/EBPβ transcription factor. C/EBPβ seems to play a role in promoting tumorigenesis in some cancer models, including breast (40) and prostate (41). For colorectal cancer, overexpression of C/EBPβ protein results in cellular growth arrest and apoptosis (42), although C/EBPβ expression is increased in human colorectal cancer (43). It remains unclear how C/EBPβ is involved in tumor suppression through its interaction with specific downstream genes in cancer cells. Our data demonstrate that C/EBPβ phosphorylation modulates recruitment of proapoptotic protein such as ATF3, enhancing its activity in NAG-1 expression.
The current data show that phosphorylation of C/EBPβ by capsaicin is positively regulated by GSK3β pathway. Although we did not examine the changes of all phosphor form of C/EBPβ in this study, it has been shown that GSK3β phosphorylates C/EBPβ on Ser177, Ser181, Ser185, and Thr189 residues (44). Although phosphorylation of C/EBPβ is regulated by GSK3β (44–46) in many types of cells, the detailed mechanisms are not fully elucidated. In this study, capsaicin treatment not only caused an increased expression of GSK3β but also increased accumulation of GSK3β in nuclear fraction (Figure 5A–C). In addition, the nuclear GSK3β directly associates with C/EBPβ (Figure 5D–F). Thus, our data suggest that capsaicin-induced overexpression of GSK3β results in the direct interaction with C/EBPβ and subsequent phosphorylation of C/EBPβ. Indeed, GSK3β increases rapidly early in the process of apoptosis and is able to modulate gene expression through its regulation of transcription factor (28). We observed that capsaicin induced GSK3β mRNA (data not shown), implying transcriptional regulation of GSK3β by capsaicin. Further study is required to obtain more detailed information on how capsaicin regulates GSK3β gene expression.
Like other C/EBP members, C/EBPβ phosphorylation at several serine and threonine residues allows recruitment of the transcriptional coactivator (47). C/EBPβ is able to form heterodimers, and such interactions alter DNA binding affinity and gene transcription. In fact, C/EBPβ has been shown to interact with non-bZIP proteins such as p50 subunit of nuclear factor-kappaB, glucocorticoid receptor, and retinoblastoma protein (48–51). Such heterodimerization indicates different transactivation potential and DNA binding affinity/specificity. Another interesting finding of this study is that ATF3 may cause NAG-1 expression, at least in part, through the recruitment of C/EBPβ. Although ATF3 does not bind to the NAG-1 promoter directly, the C/EBPβ-ATF3 complex would be an important factor for capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression. These observations interpret direct evidence to support the importance of ATF3 in increased DNA-binding potential of C/EBPβ, which consequently mediates enhancement of C/EBPβ-driven transactivation of the NAG-1 gene. One speculation would be that ATF3 may play a role as a bridge protein that facilitates recruitment of C/EBPβ to the NAG-1 promoter during its activation. Despite the predominant cooperative regulation of C/EBPβ, until now the question of whether ATF3 interacts with other transcription factors has not been addressed in the literature. Indeed, the fact that double deletion of C/EBP binding sites are required to abolish luciferase activity of capsaicin-induced NAG-1 expression supports this hypothesis. Secondly, capsaicin may lead to the formation of a supracomplex, including C/EBPβ, ATF3 and other transcription factors because C/EBP dimers are able to be cross-coupled to other transcription factors and show DNA-binding characteristics distinct from those of the individual transcription factor partners (52).
Our additional finding is that protein–protein interactions among GSK3β, C/EBPβ, and ATF3 were inhibited by pretreatment of GSK3β selective inhibitor (Figure 5E). These data suggest that phosphorylation of C/EBPβ by capsaicin increases recruitment of ATF3 for binding to C/EBPβ, which subsequently increases NAG-1 gene transcription. With respect to other kinase pathways, we observed that PKCδ is another mediator of C/EBPβ phosphorylation and NAG-1 induction by capsaicin (Figure 3). This is consistent with a previous study, showing that PKCδ targets NAG-1 gene transcription (26) and other proapoptotic signaling pathways in many cancer models (53,54).
We evaluated the effect of capsaicin on C/EBPβ phosphorylation and formation of transcription complex after shorter incubation (2 h) with capsaicin (Figures 3E and 5E). The results show that capsaicin did not affect C/EBPβ phosphorylation or complex formation at 2 h. It is notable that C/EBPβ phosphorylation usually occurs at a late time point (4–6 h) after stimulation (45,55). However, we do not exclude the possibility that C/EBPβ phophorylation occurs via different signaling (GSK3β, PKC, or other kinase). It is still unclear how complex alterations including C/EBPβ and ATF3 are able to participate in NAG-1 induction, but upon cellular activation by capsaicin, it is speculated that phosphorylation of C/EBPβ enhances the formation of the transcriptional complex with ATF3 and DNA binding affinity to the promoter regions because C/EBPβ at the resting state has weak DNA binding activity due to an intramolecular inhibitory element, whereas the phosphorylation of C/EBPβ releases the intramolecular inhibition and exposes the DNA binding site (56). In conclusion, capsaicin activates the transcription of the NAG-1 gene by activation of the C/EBPβ-dependent pathway. GSK3β modulates C/EBPβ phosphorylation by direct protein–protein interaction, and activation of C/EBPβ increases the binding affinity of C/EBPβ onto the NAG-1 promoter and increases transcription of NAG-1 genes. In this serial sequence, ATF3 may facilitate the recruitment of C/EBPβ to the NAG-1 promoter, and PKCδ also affects phosphorylation of C/EBPβ (Figure 6D).
Funding
American Cancer Society (CNE-111611), National Institutes of Health (R01CA108975), and the University of Tennessee, Center of Excellence in Livestock Diseases and Human Health to S.J.B. National Institutes of Health (R03CA137755) to S.-H.L. Royal Golden Jubilee PhD Program (PHD/0245/2545) and the Office of the Higher Education Commission, Thailand to C.K.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Jessica Schwartz (University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan) for kind provision of control and C/EBPβ shRNA, and Dr Ronald M. Evans (The Salk Institute for Biological Studies) for kind provision of the RARα expression vector. We also thank Misty Bailey for her critical reading of manuscript and Dr Kiyoshi Yamaguchi and Dianne Trent for their technical assistance.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- ATF3
activating transcription factor3
- C/EBPβ
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein
- CREB
cAMP response element binding
- GSK3 β
glycogen synthase kinase 3β
- NAG-1
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1
- RARα
retinoic acid receptorα
References
- 1.Sanchez AM, et al. Induction of apoptosis in prostate tumor PC-3 cells and inhibition of xenograft prostate tumor growth by the vanilloid capsaicin. Apoptosis. 2006;11:89–99. doi: 10.1007/s10495-005-3275-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mori A, et al. Capsaicin, a component of red peppers, inhibits the growth of androgen-independent, p53 mutant prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3222–3229. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wu CC, et al. Capsaicin induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human esophagus epidermoid carcinoma CE 81T/VGH cells through the elevation of intracellular reactive oxygen species and Ca2+ productions and caspase-3 activation. Mutat. Res. 2006;601:71–82. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hail N, Jr., et al. Examining the role of mitochondrial respiration in vanilloid-induced apoptosis. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:1281–1292. doi: 10.1093/jnci/94.17.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ito K, et al. Induction of apoptosis in leukemic cells by homovanillic acid derivative, capsaicin, through oxidative stress: implication of phosphorylation of p53 at Ser-15 residue by reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1071–1078. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-1670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Surh YJ. More than spice: capsaicin in hot chili peppers makes tumor cells commit suicide. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:1263–1265. doi: 10.1093/jnci/94.17.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yoshitani SI, et al. Chemoprevention of azoxymethane-induced rat colon carcinogenesis by dietary capsaicin and rotenone. Int. J. Oncol. 2001;19:929–939. doi: 10.3892/ijo.19.5.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kim YM, et al. Involvement of AMPK signaling cascade in capsaicin-induced apoptosis of HT-29 colon cancer cells. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2007;1095:496–503. doi: 10.1196/annals.1397.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baek SJ, et al. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors regulate the expression of a TGF-beta superfamily member that has proapoptotic and antitumorigenic activities. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001;59:901–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Baek SJ, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 over expression in transgenic mice suppresses intestinal neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:1553–1560. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cekanova M, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1 expression inhibits urethane-induced pulmonary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice. Cancer Prev. Res (Phila. Pa) 2009;2:450–458. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee SH, et al. ESE-1/EGR-1 pathway plays a role in tolfenamic acid-induced apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008;7:3739–3750. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-0548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yamaguchi K, et al. A novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma ligand, MCC-555, induces apoptosis via posttranscriptional regulation of NAG-1 in colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006;5:1352–1361. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lee S-H, et al. Conjugated linoleic acid stimulates an anti-tumorigenic protein NAG-1 in an isomer specific manner. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:972–981. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee S-H, et al. Indole-3-carbinol and 3,3′-diindolylmethane induce expression of NAG-1 in a p53-independent manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005;328:63–69. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.12.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee S-H, et al. Multiple mechanisms are involved in 6-gingerol-induced cell growth arrest and apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2008;47:197–208. doi: 10.1002/mc.20374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Baek SJ, et al. Resveratrol enhances the expression of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene (NAG-1) by increasing the expression of p53. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23:425–434. doi: 10.1093/carcin/23.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baek SJ, et al. Epicatechin gallate-induced expression of NAG-1 is associated with growth inhibition and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:2425–2432. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wilson LC, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene (NAG-1) is induced by genistein through the expression of p53 in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer. 2003;105:747–753. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Baek SJ, et al. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors induce the expression of the tumor suppressor gene EGR-1, which results in the up-regulation of NAG-1, an antitumorigenic protein. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005;67:356–364. doi: 10.1124/mol.104.005108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yamaguchi K, et al. Identification of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene (NAG-1) as a novel downstream target of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT/GSK-3beta pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:49617–49623. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408796200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Baek SJ, et al. Changes in gene expression contribute to cancer prevention by COX inhibitors. Prog Lipid Res. 2006;45:1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2005.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Baek SJ, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of human nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene promoter. Basal transcription is mediated by Sp1 and Sp3. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:33384–33392. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101814200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Calkhoven CF, et al. Translational control of C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta isoform expression. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1920–1932. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chow J, et al. TRPV6 mediates capsaicin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells—Mechanisms behind a possible new “hot” cancer treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2007;1773:565–576. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shim M, et al. Protein kinase C-dependent regulation of NAG-1/placental bone morphogenic protein/MIC-1 expression in LNCaP prostate carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:18636–18642. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M414613200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jope RS, et al. The glamour and gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004;29:95–102. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2003.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bijur GN, et al. Proapoptotic stimuli induce nuclear accumulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:37436–37442. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105725200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Watcharasit P, et al. Direct, activating interaction between glycogen synthase kinase-3beta and p53 after DNA damage. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:7951–7955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.122062299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Thiaville MM, et al. Deprivation of protein or amino acid induces C/EBPbeta synthesis and binding to amino acid response elements, but its action is not an absolute requirement for enhanced transcription. Biochem. J. 2008;410:473–484. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pan YX, et al. Activation of the ATF3 gene through a co-ordinated amino acid-sensing response programme that controls transcriptional regulation of responsive genes following amino acid limitation. Biochem. J. 2007;401:299–307. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Min JK, et al. Capsaicin inhibits in vitro and in vivo angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:644–651. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lo YC, et al. Capsaicin-induced cell death in a human gastric adenocarcinoma cell line. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005;11:6254–6257. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sariav A, et al. Distribution of capsaicin in rat tissues after systemic administration. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1982;34:273–275. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1982.tb04245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Richeux F, et al. Implications of oxidative stress and inflammatory process in the cytotoxicity of capsaicin in human endothelial cells: lack of DNA strand breakage. Toxicology. 2000;147:41–49. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(00)00184-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chaiyasit K, et al. Pharmacokinetic and the effect of capsaicin in Capsicum frutescens on decreasing plasma glucose level. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2009;92:108–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Scientific Committee on Food. Opinion of the scientific committee on food on capsaicin. 2002:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lopez-Carrillo L, et al. Chili pepper consumption and gastric cancer in Mexico: a case-control study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1994;139:263–271. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lambert JD, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate is absorbed but extensively glucuronidated following oral administration to mice. J. Nutr. 2003;133:4172–4177. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.12.4172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Raught B, et al. Expression of a translationally regulated, dominant-negative CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta isoform and up-regulation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha are correlated with neoplastic transformation of mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1996;56:4382–4386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kim MH, et al. Translationally regulated C/EBP beta isoform expression upregulates metastatic genes in hormone-independent prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 2008;68:1362–1371. doi: 10.1002/pros.20801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sun L, et al. Systemic delivery of full-length C/EBP beta/liposome complex suppresses growth of human colon cancer in nude mice. Cell Res. 2005;15:770–776. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rask K, et al. Increased expression of the transcription factors CCAAT-enhancer binding protein-beta (C/EBBeta) and C/EBzeta (CHOP) correlate with invasiveness of human colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer. 2000;86:337–343. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(20000501)86:3<337::aid-ijc6>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhao X, et al. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase regulates CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta functions through inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:32683–32692. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505486200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tang QQ, et al. Sequential phosphorylation of CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta by MAPK and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta is required for adipogenesis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:9766–9771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0503891102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Park BH, et al. Phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta at a consensus extracellular signal-regulated kinase/glycogen synthase kinase 3 site is required for the induction of adiponectin gene expression during the differentiation of mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004;24:8671–8680. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.19.8671-8680.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang H, et al. C/EBPbeta activates E2F-regulated genes in vivo via recruitment of the coactivator CREB-binding protein/P300. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:24679–24688. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705066200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lekstrom-Himes J, et al. Biological role of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family of transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:28545–28548. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.44.28545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.LeClair KP, et al. The p50 subunit of NF-kappa B associates with the NF-IL6 transcription factor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1992;89:8145–8149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Vallejo M, et al. C/ATF, a member of the activating transcription factor family of DNA-binding proteins, dimerizes with CAAT/enhancer-binding proteins and directs their binding to cAMP response elements. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1993;90:4679–4683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hsu W, et al. Fos and Jun repress transcription activation by NF-IL6 through association at the basic zipper region. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994;14:268–276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Stein B, et al. Functional and physical associations between NF-kappa B and C/EBP family members: a Rel domain-bZIP interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993;13:3964–3974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.DeVries-Seimon TA, et al. Induction of apoptosis is driven by nuclear retention of protein kinase C delta. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:22307–22314. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703661200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Reyland ME, et al. Protein kinase C delta is essential for etoposide-induced apoptosis in salivary gland acinar cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:19115–19123. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.27.19115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shuman JD, et al. Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta mediates oncogenic cooperativity between C/EBPbeta and H-RasV12. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004;24:7380–7391. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.17.7380-7391.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mo X, et al. Ras induces mediator complex exchange on C/EBP beta. Mol. Cell. 2004;13:241–250. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00521-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]