Abstract
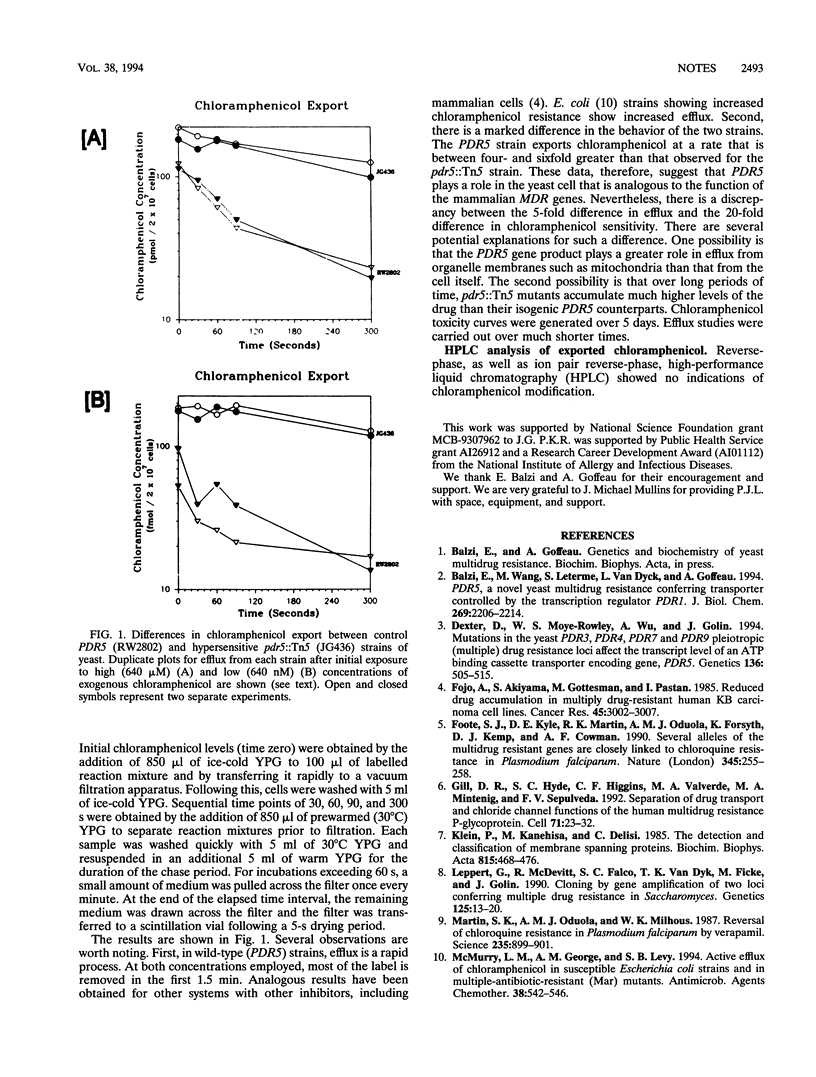
The yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) PDR5 gene product encodes a 160-kDa protein related to the large ABC family of transporters, including the human MDR1 multidrug resistance p-glycoprotein. Loss of function mutations in PDR5 result in chloramphenicol hypersensitivity. A pdr5::Tn5 loss of function mutant exhibits a markedly impaired efflux of chloramphenicol compared with that of an isogenic PDR5 (wild-type) control.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balzi E., Wang M., Leterme S., Van Dyck L., Goffeau A. PDR5, a novel yeast multidrug resistance conferring transporter controlled by the transcription regulator PDR1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2206–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter D., Moye-Rowley W. S., Wu A. L., Golin J. Mutations in the yeast PDR3, PDR4, PDR7 and PDR9 pleiotropic (multiple) drug resistance loci affect the transcript level of an ATP binding cassette transporter encoding gene, PDR5. Genetics. 1994 Feb;136(2):505–515. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo A., Akiyama S., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Reduced drug accumulation in multiply drug-resistant human KB carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1985 Jul;45(7):3002–3007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foote S. J., Kyle D. E., Martin R. K., Oduola A. M., Forsyth K., Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F. Several alleles of the multidrug-resistance gene are closely linked to chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):255–258. doi: 10.1038/345255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. R., Hyde S. C., Higgins C. F., Valverde M. A., Mintenig G. M., Sepúlveda F. V. Separation of drug transport and chloride channel functions of the human multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Cell. 1992 Oct 2;71(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90263-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert G., McDevitt R., Falco S. C., Van Dyk T. K., Ficke M. B., Golin J. Cloning by gene amplification of two loci conferring multiple drug resistance in Saccharomyces. Genetics. 1990 May;125(1):13–20. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. K., Oduola A. M., Milhous W. K. Reversal of chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum by verapamil. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):899–901. doi: 10.1126/science.3544220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L. M., George A. M., Levy S. B. Active efflux of chloramphenicol in susceptible Escherichia coli strains and in multiple-antibiotic-resistant (Mar) mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1994 Mar;38(3):542–546. doi: 10.1128/aac.38.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers S., Schauer W., Balzi E., Wagner M., Goffeau A., Golin J. Interaction of the yeast pleiotropic drug resistance genes PDR1 and PDR5. Curr Genet. 1992 May;21(6):431–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00351651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Panton L. J., Gluzman I. Y., do Rosario V. E., Gwadz R. W., Walker-Jonah A., Krogstad D. J. Chloroquine resistance not linked to mdr-like genes in a Plasmodium falciparum cross. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):253–255. doi: 10.1038/345253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Serrano A. E., Wasley A., Bogenschutz M. P., Shankar A. H., Wirth D. F. Amplification of a gene related to mammalian mdr genes in drug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1184–1186. doi: 10.1126/science.2658061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


