Abstract
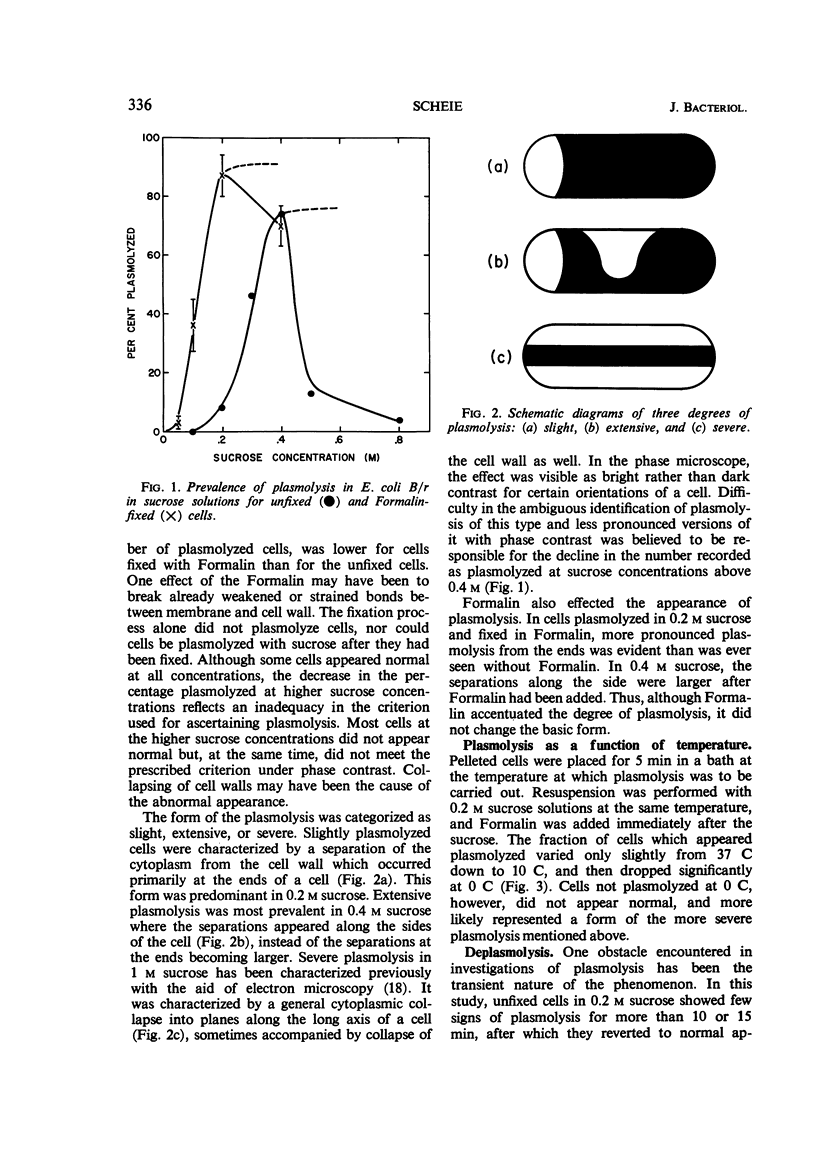
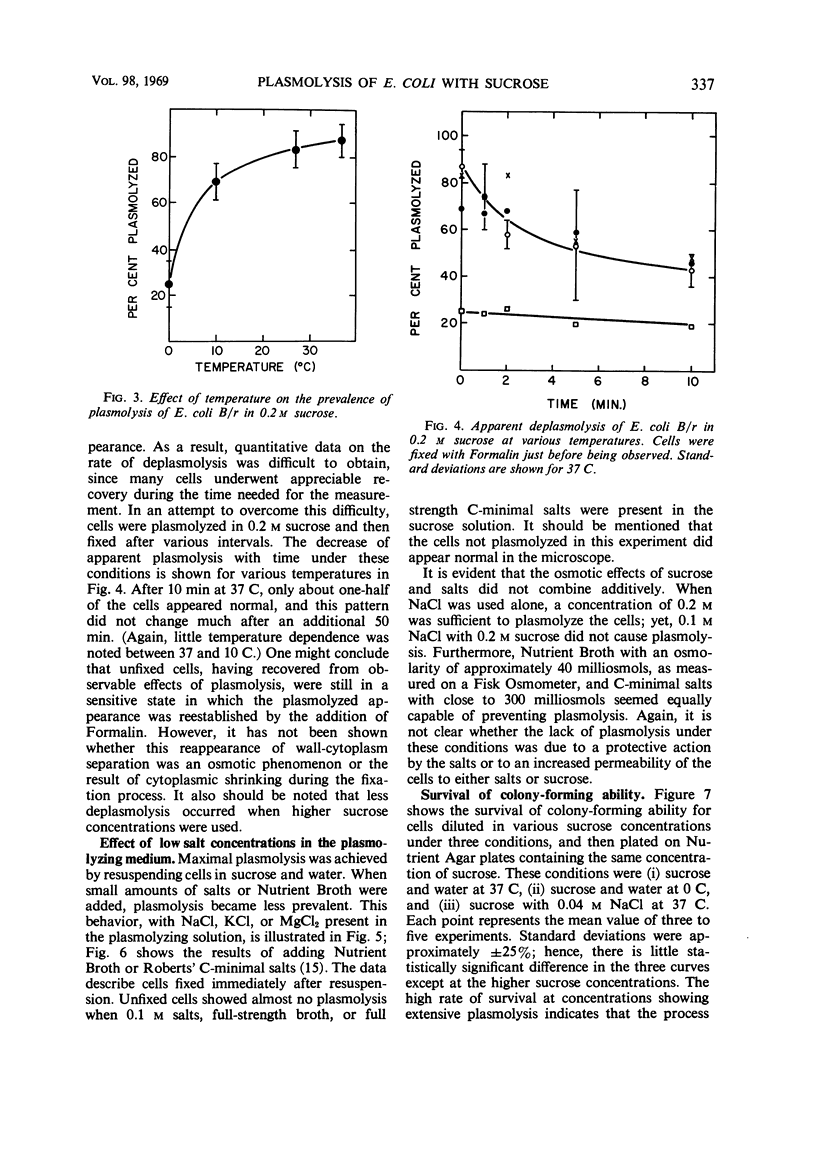
Escherichia coli B/r cells were plasmolyzed in sucrose solutions and observed under phase contrast. The prevalence of plasmolysis under various conditions was noted, and the degree of plasmolysis was categorized as slight, extensive, or severe. The presence of ions reduced the prevalence of plasmolysis. Survival curves showed that extensive plasmolysis was not lethal to colony-forming ability.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIM F. Factors which affect the size of the organisms and the optical density of suspensions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:53–58. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Oct;53(3):395–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-53-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E. Response of Cell Walls of Escherichia coli to a Sudden Reduction of the Environmental Osmotic Pressure. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1104–1112. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1104-1112.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Cota-Robles E. H. Production and ultrastructure of lysozyme and ethylenediaminetetraacetate-lysozyme spheroplasts of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):427–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.427-437.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTA-ROBLES E. H. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF PLASMOLYSIS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1963 Mar;85:499–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.3.499-503.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros F., Gallant J., Weisberg R., Cashel M. Decryptification of RNA polymerase in whole cells of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 14;25(3):555–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALE C. M. A note on the relationship between the Gram reaction and plasmolytic effects in bacteria. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Jun;12(3):657–659. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN D. H., UMBREIT W. W. FACTORS WHICH MODIFY THE EFFECT OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM ON BACTERIAL CELL MEMBRANES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1266–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1266-1273.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN D. H., UMBREIT W. W. INFLUENCE OF THE PHYSICAL STATE OF THE BACTERIAL CELL MEMBRANE UPON THE RATE OF RESPIRATION. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1274–1280. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1274-1280.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz C., Braun C. B., Peabody R. A. Washing bacteria by centrifugation through a water-immiscible layer of silicones. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1692–1695. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1692-1695.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGER J., KUCZYNSKI M., SCHATZBERG G., AVI-DOR Y. Turbidity changes in bacterial suspensions in relation to osmotic pressure. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):69–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A. Association of the nucleus and the membrane of bacteria: a morphological study. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):39–54. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.39-54.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheie P., Dalen H. Spatial anisotropy in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1413–1414. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1413-1414.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFIELD J. F., MURRAY R. G. The effects of the ionic environment on the chromatin structures of bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1956 May;2(3):245–260. doi: 10.1139/m56-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



