Abstract
The mechanism of the hypoglycemic activity of endotoxin in hyperreactive BCG mice was investigated. The mechanism was found to be an inhibition of the synthesis of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources. The possibilities of an induced hypermetabolic state and an induced release of insulin in response to endotoxin as causes for the hypoglycemic response were essentially ruled out. In addition, no clear-cut evidence of an insulin-like action by endotoxin was found in the in vivo setting.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEKIERKUNST A., ARTMAN M. Tissue metabolism in infection. DPNase activity, DPN levels, and DPN-linked dehydrogenases in tissues from normal and tuberculous mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1962 Dec;86:832–838. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1962.86.6.832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
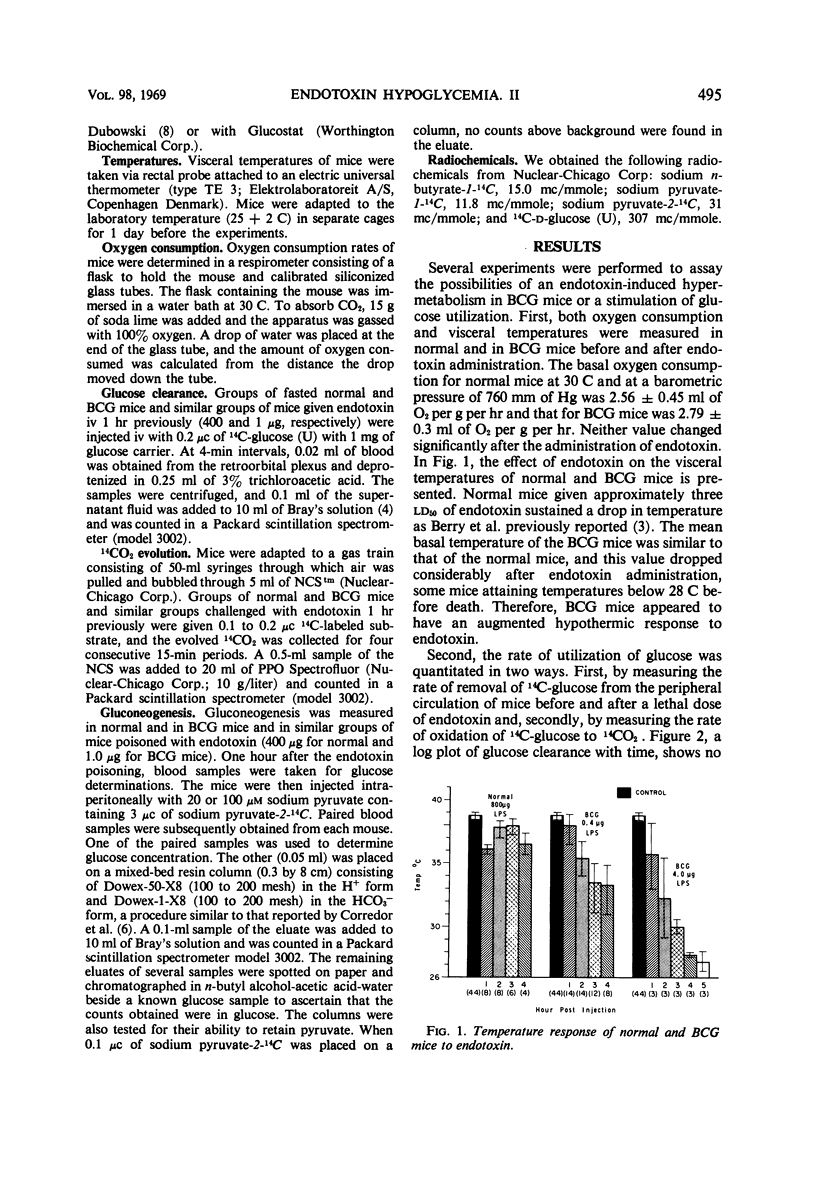
- BERRY L. J., SMYTHE D. S., YOUNG L. G. Effects of bacterial endotoxin on metabolism. I. Carbohydrate depletion and the protective role of cortisone. J Exp Med. 1959 Sep 1;110:389–405. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUDHURI S. N., SUTER E., SHAH N. S., MARTIN S. P. Metabolism in infection: study on the enzymatic damage in kidney of guinea pig infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Exp Med. 1963 Jan 1;117:71–79. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREMER N., WATSON D. W. Influence of stress on distribution of endotoxin in RES determined by fluorescein antibody technic. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jul;95(3):510–513. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
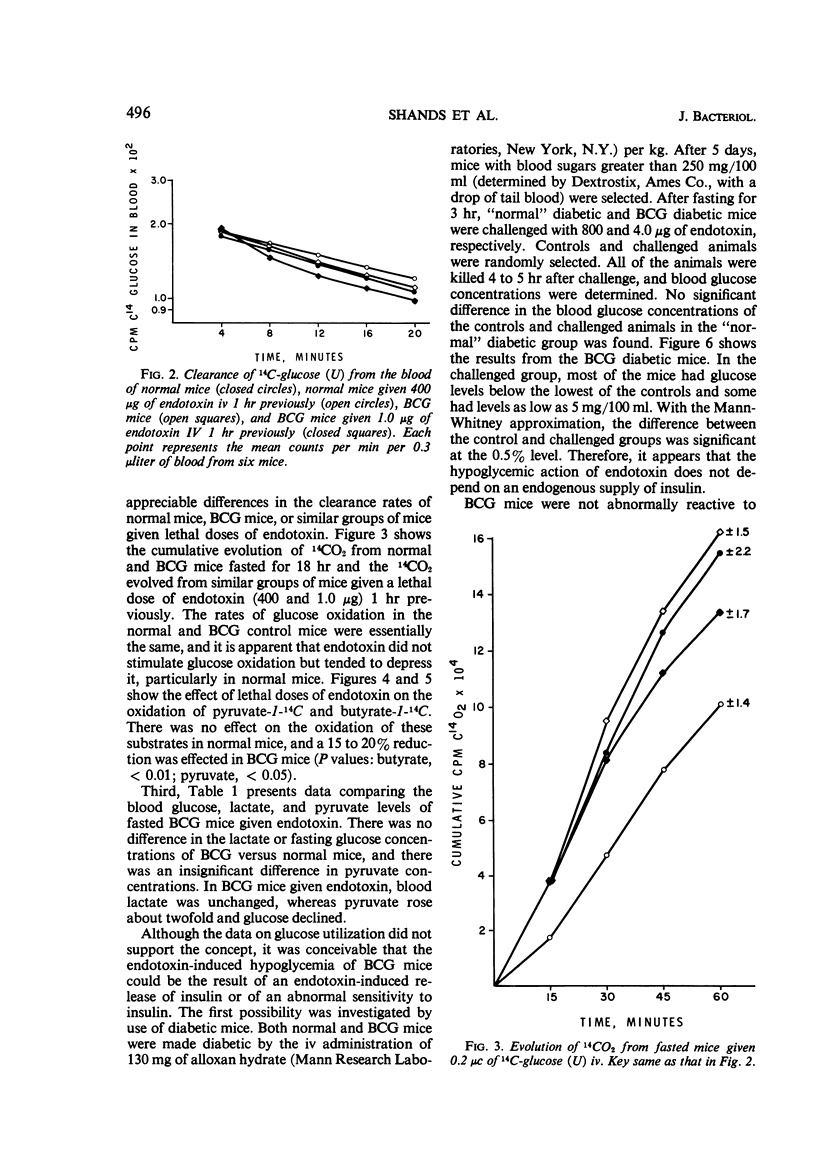
- Corredor C., Brendel K., Bressler R. Studies of the mechanism of the hypoglycemic action of 4-pentenoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2299–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOWSKI K. M. An o-toluidine method for body-fluid glucose determination. Clin Chem. 1962 May-Jun;8:215–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARRAR W. E., Jr, WATSON J. G. HYPOGLYCEMIA FOLLOWING ENDOTOXIN ADMINISTRATION IN ANIMALS WITH LIVER DAMAGE. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Mar;115:833–837. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. E., Jr, Corwin L. M. The essential role of the liver in detoxification of endotoxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):668–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
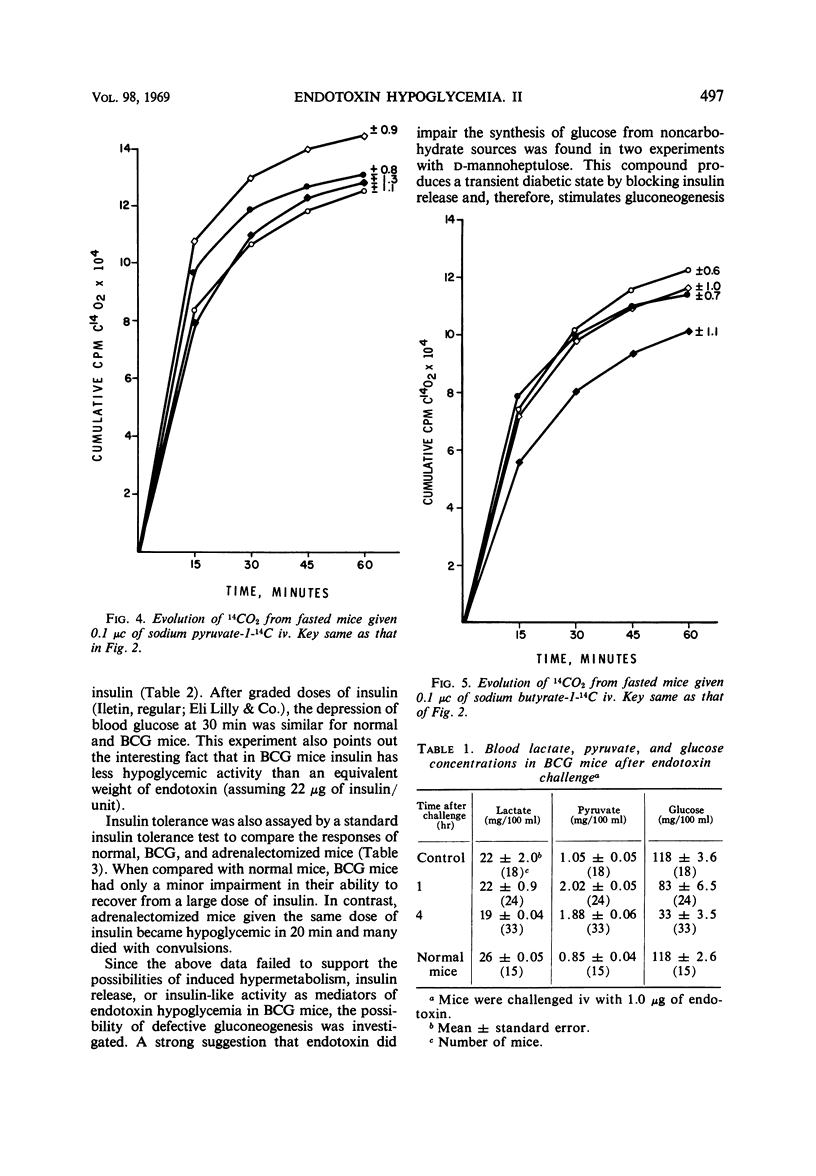
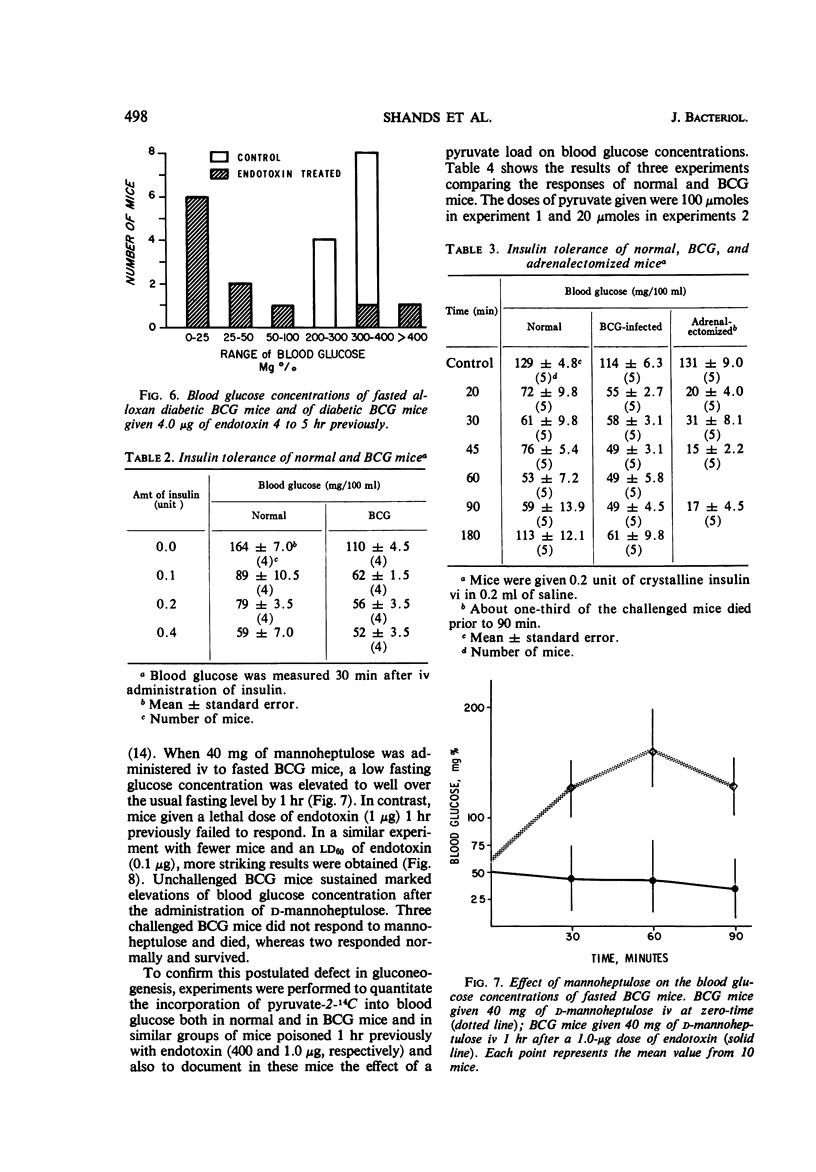
- LaNoue K. F., Mason A. D., Jr, Daniels J. P. The impairment of glucogenesis by gram negative infection. Metabolism. 1968 Jul;17(7):606–611. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGER J., THEODOR E. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiration and uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation by fractions of the Shigella paradysenteriae type III-somatic antigen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBENSTEIN H. S., FINE J., COONS A. H. Localization of endotoxin in the walls of the peripheral vascular system during lethal endotoxemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:458–467. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER E., KIRSANOW E. M. Hyperreactivity to endotoxin in mice infected with mycobacteria. Induction and elicitation of the reactions. Immunology. 1961 Oct;4:354–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E., Kraicer P. F. The blockade of insulin secretion by mannoheptulose. Isr J Med Sci. 1966 Nov-Dec;2(6):785–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



